* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 45
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
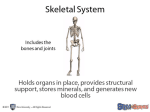
Chapter 45 Skeletal, Muscular and Integumentary Systems 45-1 * Human Body Plan Four types of Human Tissue 1. Muscle 2. Nervous 3. Epithelial 4. Connective Muscle Tissue *Can contract and relax. a) Skeletal muscle- voluntary, usually moves bones b) Smooth muscle- involuntary, breathing, digestion …. c) Cardiac muscle – involuntary, in the heart Nervous Tissue *Cells that receive and send messages by electrical impulse *Neurons- nerve cells *Neurons are in nervous tissue and sensory organs. They coordinate all activities. Epithelial Tissue *Layers of cells that cover or line internal and external surfaces. *Skin, but also in blood vessels, respiratory system, digestive system,…. *This forms a protective barrier Connective Tissue *Connects, supports, protects *Includes cartilage, bone, tendons, ligaments, fat, blood and lymph. Matrix- intercellular substance- can be solid (bone), semisolid (fat) or liquid (blood) Organ Systems- Page 907 1. Skeletal 7. Digestive 2. Muscular 8. Excretory 3. Integumentary 9. Nervous 4. Circulatory 10. Endocrine 5. Respiratory 11. Reproductive 6. Immune The systems work together, organs may overlap systems. Ex. Respiratory and Circulatory Systems 1 Body Cavities a) Cranial –brain b) Spinal c) Thoracic –above diaphragm d) Abdominal-below diaphragm 45-2 *Skeletal System 206 Bones *Axial- skull, ribs, spine, sternum *Appendicular- arms, legs, scapula, clavicle, pelvis Bones are used for *Support *Movement *Protection *Mineral Storage *Production of blood cells Bone Structure Bones contain living cells Periosteum *Thick membrane around the bone *contains blood vessels and nerves Compact Bone *Provides strength *has blood vessels running through Haversion Canals Osteocytes- the living bone cells embedded in the matrix. Spongy Bone *in the center of the bone and at the ends of the bone *it makes bones light and strong *acts as a “cushion” Bone Marrow Red- produces RBC and some WBC Yellow- contains fat, can convert to red bone marrow 2 Ossification *Cartilage becomes hard due to mineral deposits *starts at about the 3rd fetal month and continues to adulthood. *you must have proper minerals! Bone Growth *Elongation takes place at the Epiphyseal Plates (the ends of the bones)—older cells are in the middle of the bone, and newer cells are at the end. Joints *Places where bones meet a) fixed- skull b) semi-movable- vertebrae, ribs.. c) movable- know types and locations Ligaments *tough connective tissue *they hold bones together Joints contain Synovial Fluid and cartilage to reduce friction Skeletal Problems Rheumatoid arthritis-the immune system attacks the joint tissue Ostoearthritis-Cartilage wears away, bones rub Osteoporosis-loss of bone minerals- bones become brittle and weak. 45-3 *Muscular System Skeletal or Striated Muscles *Made of Muscle Fibers a) contain many nuclei b) have striations—light and dark stripes Muscle Structure— Made of 100’s to 1000’s of muscle fibers *covered by connective tissue *controlled by nerves Myofibrils (thread-like structure of a muscle fiber) Made of two types of protein filaments a) Myosin- thick fibers with “heads” b) Actin- thin fibers Z-Line- where actin fibers are attached Sarcomere- area from one Z-line to the next 3 Muscle Contractions *When a muscle contracts, the myosin “heads” pull the actin in * the muscle shortens *Muscle contractions require ATP—it is used to detach the myosin “heads” from the actin. All or None *the fiber is either contracted or relaxed *heavier objects require more muscle fibers Tendons—Page 917 *Attach muscle to bone Origin-stationary point where muscle attaches to bone Insertion- where muscle attaches to moving bone. Opposing Pairs Muscles work in pairs—one contracts and one relaxes Flexor-muscle that bends a joint ex. biceps Extensor- muscle that straightens a joint ex. Triceps Muscle Fatigue Muscle has used up ATP Continuous contractions—muscle cramps Oxygen Debt There is not enough oxygen to break down ATP Build up of lactic acid 45-4 Integumentary System Skin 1) Epidermis-outer layer 2) Dermis-inner layer Epidermis *Sheets of mostly dead cells *Cells contain Keratin-a protein, helps make skin almost waterproof *Constantly being replaced Melanin *Brown pigment in the skin. *Amount of melanin depends on 1) heredity 2) exposure to UV 4 Dermis *Living layer a) sensory neurons b) blood vessels c) muscles d) hair follicles e) exocrine glands Subcutaneous Fat *a layer of fat under the skin *energy store *insulation Nails and Hair Made of keratin—cells are dead The follicle—root of the hair, is alive. Sweat Glands *remove waste products *regulates body temperature Sebaceous Glands Produce Sebum (oil) Softens skin and hair Bacteria in glands cause acne. - 5