* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Describe an atom. What is it made up of?
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Video camera tube wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Cavity magnetron wikipedia , lookup
Giant magnetoresistance wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Nanogenerator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
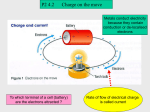
Describe an atom. What is it made up of? What is the difference between electrical insulators and electrical conductors? (Use the term “electron” in your answer) What is the difference between positively and negatively charged objects? (Use the term “electron” in your answer) What are “induced charges”? What is an electrical field? When two different materials are rubbed together do they acquire the same type of charge or different types of charge? What is voltage? What is current? How is the unit 1 A defined? In an insulator electrons are bound to their atoms. In a conductor they can move freely. If you approach a conductor with a charged rod, the electrons in the condoctor will be attracted and move towards the charged rod. After removing the rod the electrons will move back. The nucleus of an atom consists of protons (positively charged) and neutrons. - + - + - + + - - - + + - + - + - - Negatively charged (more electrons than protons) When two different materials are rubbed together they will acquire different charges. One material will lose electrons (becoming pos.) and the other will gain electrons (becoming neg.). + - + + - + - Positively charged (lack of electrons) If you bring a charge in an electric field it will be either attracted or repelled. The field lines have the same direction as the force acting upon a positive charge. A positive charge would move downwards. Thus the field lines point from top to bottom. Current tells you how much charge passes through a point in the conductor per second. Current = Charge / Time If 1 Coulomb passes per second the current equals 1 Ampere. Voltage propels the electrons. It does work on the electrons hence they gain energy. How can you compare voltage and pressure? How do you measure voltage? (How would you measure pressure in a tube?) How do you measure current? What is resistance? (How would you measure the flow rate of water in a tube?) What factors does the resistance of a wire depend on? Ohm’s Law Which charges repel / attract each other? What is an ohmic resistor? (Draw it’s circuit symbol, too) A battery is analogous to a pump in a water circuit. A pump takes in water at low pressure and does work on it, ejecting it at high pressure. A battery takes in charge at low voltage, does work on it and ejects it at high voltage. Current equals the amount of water passing through the tube. The resistance equals voltage divided by current. Hence: The smaller the current the greater the resistance. A material which decelerates the electrons more than another has a greater resistance. Voltage = Resistance x Current The greater the length, the greater the resistance. The greater the cross-sectional ares, the smaller the resistance. Material: The greater the resistivity, the greater the resistance. (E.g.: Copper has a small resitivity) The higher the temperature, the greater the resistance. If current and voltage are proportional, the resistor is ohmic. Circuit symbols Unlike chages attract: german: Like charges repel: english: