* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 13.4-Food Chains and Food Webs
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
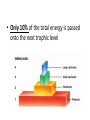
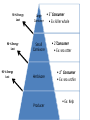
Notes: Food Chains and Food Webs FOOD CHAIN • • • Single sequence that links species by their feeding relationships. Traces the transfer of energy Simplest way to look at energy flow in an ecosystem Trophic Levels level in a food chain 1. Producers always first level 2. Primary consumers next level (herbivore) 3. Secondary consumer- eat herbivores (small carnivore or omnivore) 4. Tertiary consumer-carnivores that eat secondary consumers. Large Carnivore • 3˚ Consumer (tertiary) • Killer Whale Small Carnivore • 2˚Consumer (secondary) • Ex: Sea Otter Herbivore • 1˚ Consumer (primary) • Ex: Sea Urchin Producer • Ex: Kelp FOOD WEB • Interconnected food chains • Organisms usually have multiple feeding relationships FOOD WEB • More realistic display of feeding relationships • Arrows show transfer of ENERGY ENERGY TRANSFER • trophic level: position in a series of energy transfers • Only 10% of the total energy is passed onto the next trophic level • Only 10% of the total energy is passed onto the next trophic level 1. lost to biological processes (digestion, growth and repair, running, walking etc.) 2. lost as heat 90 % Energy Lost 90 % Energy Lost 90 % Energy Lost Large Carnivore Small Carnivore Herbivore Producer • 3˚ Consumer • Ex: killer whale • 2˚Consumer • Ex: sea otter • 1˚ Consumer • Ex: sea urchin • Ex: Kelp • Why is a Pyramid used to display Energy transfer between trophic levels? Hint: Why not a square? KEYSTONE SPECIES • Has a disproportionately large effect on the ecosystem KEYSTONE SPECIES • Has a disproportionately large effect on the ecosystem • Dictates community structure KEYSTONE SPECIES • Has a disproportionately large effect on the ecosystem • Dictates community structure • Demonstrated by removal of keystone species from community EX. sea stars in tidepools Sea star feeds on all bivalves. When the sea star is removed from the tide pools one bivalve (mussel) out competes the rest for resources and becomes the dominant species. Sea star feeds on all bivalves. When the sea star is removed from the tide pools one bivalve (mussel) out competes the rest for resources and becomes the dominant species.