* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PT-Ch8 Using Energy and Heat
Efficient energy use wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
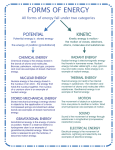
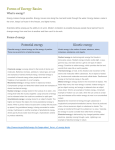
1. Using Energy and Heat (Ch8) 2. Forms of Energy (8.1) 3. Energy energy 5. Ability to cause change 5. Energy is used in everyday life 3. Potential Energy Potential Energy (PE) 5. Stored energy due to the interaction between objects or particles 5. Objects that fall due to gravity 5. Movement between particles due to magnetic/electrical forces 4. Gravitational Potential Energy Gravitational PE 5. Everything above the ground has gravitational PE 5. Depend on 2 factors: mass (grams) and distance (meters) 4. Chemical Energy Chemical Energy 5. Energy stored in and released between bonds of atoms 4. Nuclear Energy Ex: Sun Ex: Power Plant Electricity Nuclear Energy 5. Energy stored in and released from the nucleus of an atom 5. Nuclear fusion (nuclei come TOGETHER) 5. Nuclear fission (nuclei break APART) 3. Kinetic Energy KE 5. Energy due to motion 4. KE of Objects 5. Relate to mass (grams) and speed=distance/time (m/s) 5. Objects of larger mass and equal speed (will have greater KE) Electric Energy Ex: Light/muscle movement 4. Electric Energy 5. Energy in an electric current 5. Movement of electrons (e-) 3. Combined KE and PE A system is a collection of parts that are interact and act together as a whole 4. Mechanical Energy Mechanical Energy 5. KE+PE= mechanical energy (the sum in a given system) 5. Energy that can cause another object to move 4. Thermal Energy Thermal Energy Proportional/direct relationship 5. Sum of KE and PE of the particles that make up an object 5. When PE , KE , or both ; thermal energy also 3. wave Energy Carried By Waves 5. Disturbance that transfers energy from one place to another without transferring matter 5. In the example of a raindrop hitting the water, the wave caused, only allows energy to move outward (not matter) 4. Sound Energy Sound energy 5. Energy carried by sound waves (move through matter) 5. Sound travels through matter by vibrating particles. 5. Raindrops causes sound through particles in the air 4. Radiant Energy Radiant Energy Ex: Light energy 5. Energy carried by electromagnetic waves 5. Does not need to travel through particles (matter/vacuum) 5. Electric and magnetic waves move ┴ (perpendicular) to each other Wavelength Ex: Radio waves, infrared rays, visible light, UV rays, X-rays and Gamma rays Cause sunburn 5. Is the distance from one point on a wave to the nearest point just like it. 5. Wave length (shorter) ; Frequency Energy Wave length (longer) ; Frequency Energy 5. Gamma Rays and X-rays are often used in medical procedures 5. Ultraviolet (UV rays) rays have wavelengths that are a bit shorter than light 5. Infrared is felt as heat and is used to change channels (via remote control) 5. Radar, television, and radio waves have long wavelengths compared to visible light 2. Energy Transfers and Transformations (8.2) 3. Law of Conservation of Energy Law of Conservation of Energy Ex: Flashlight 5. Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed 5. Chemical (battery)electricalradiant (light) & heat 4. Energy transfer Energy Transfer 5. Energy moves from one object to another without changing form 4. Energy Transformations Energy Transformations 5. When form of energy is converted to another form of energy 4. Energy and Work work W=F x D 5. Transfer of energy that occurs when a force makes an object move in the direction of the force. 5. Work can be done when a force is acting on an object 5. Work is equal to the Force multiplied by the Distance 5. Unit for Work = J (joules); Force = N (Newtons); Distance = m (meters) 4. Inefficiency of Energy Transformations Ex: Chemical energy in a flashlight does not fully change to light energy since some converts to thermal (heat) 5. Some energy may appear to be lost. This is due to transfer not being only part of one thing. Do not always get what you put in 4. Open Systems Open System In a vacuum/space Closed System 5. System that exchanges matter or energy with the environment 4. Closed Systems 5. System that does not exchange matter or energy with the environment 3. Energy Transformations and Electrical Energy