* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Causes of Heart enlargement
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
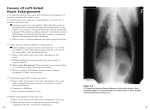
Causes of Cardiomegaly Causes of Cardiomegaly: Online Medical Books Cardiomegaly: Differential Diagnosis (In a Page: Signs and Symptoms) Congestive heart failure Ischemic heart disease Hypertension (with left ventricular hypertrophy) Valvular disease (primarily MR, AS, AR) Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Congenital heart disorders 1q deletion Heart cancer Ask the following questions: 1. Is there a murmur? Cardiomegaly with cardiac murmurs suggests valvular disease, but it also suggests congestive heart failure and advanced myocardiopathies. One should also be sure that the murmur is not a pericardial friction rub. 2. Is there fever? Fever with cardiomegaly should suggest rheumatic heart disease and bacterial endocarditis. However, it may also suggest an acute myocarditis or acute pericarditis. 3. Is there chest pain? Cardiomegaly with chest pain would certainly suggest a myocardial infarction, but it also may suggest an acute pericarditis. 4. Is there hepatomegaly? Cardiomegaly and hepatomegaly suggest congestive heart failure. Hepatomegaly also may suggest one of the systemic diseases that causes a myocardiopathy such as amyloidosis. 5. Is there edema? The presence of peripheral edema would suggest congestive heart failure, and if it is nonpitting, it would suggest myxedema. 6. Is there hypertension? Cardiomegaly with hypertension would suggest that the cardiomegaly is due to left ventricular enlargement from the chronic hypertension. 7. Is there cyanosis? Cardiomegaly with cyanosis, particularly if there is an associated murmur, suggests congenital heart disease of the cyanotic type. DIAGNOSTIC WORKUP A CBC, sedimentation rate, ANA, chemistry panel, VDRL test, thyroid profile, EKG, and chest x-ray should be done on all patients. An echocardiogram will be helpful in diagnosing valvular disease, myocardiopathies, congestive heart failure, and pericardial effusion. If congestive heart failure is suspected, venous pressure and circulation time can be measured, and one should do pulmonary function studies. If there is fever, then one would want to do a streptozyme test, ASO titer, and serial blood cultures. If there is hypertension, a hypertensive workup may be indicated. Patients with cyanosis need a workup for congenital heart disease, which will probably include cardiac catheterization and angiocardiography. Causes of Heart enlargement Causes of Heart enlargement: The following medical conditions are some of the possible causes of Heart enlargement. There are likely to be other possible causes, Heart Failure Hypertension Ischaemic Heart Disease Obesity Diabetes Smoking Increased alcohol consumption Homocystinemia Previous heart attacks High cholesterol High fat diet Low exercise Mitral valve disease Aortic valve disease Cardiomyopathies Viral infections Autoimmune Diseases Genetic causes Congenital heart block Acromegaly Ischemic heart disease Dilated cardiomyopathy Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Sarcoidosis Systemic lupus erythematosus Polyarteritis nodosa Rheumatoid arthritis Chagas disease Viral myocarditis (type of Myocarditis) Rickettsial myocarditis (type of Myocarditis) Duchenne's progressive muscular dystrophy Friedreich's ataxia Dystrophia myotonica X-linked humeroperoneal neuromuscular disease Leukemia Lymphoma Amyloidosis Hemochromatosis Cardiac glycogenosis Polysaccharide storage disease Tay-Sachs disease Fabry's disease Gout Oxalosis Mucopolysaccharidoses Hurler's syndrome Refsum's disease Phaeochromocytoma Thyrotoxicosis Myxoedema Cushing's syndrome Beri-Beri Kwashiorkhor Alcoholism Cobalt Systemic hypertension Aortic stenosis Coarctation of the aorta Cor pulmonale Reactive pulmonary hypertension Chronic thromboebolic pulmonary hypertension Pulmonary stenosis Eisenmenger's syndrome Carcinoid syndrome Appetite suppressant Mitral regurgitation Aortic regurgitation Systemic arteriovenous fistula Severe anaemia Congenital heart disease Persistent ductus arteriosus Ventricular septal defect Paget's disease of bone Erythroderma Tricuspid regurgitation List of 87 causes of Heart enlargement This section shows a full list of all the diseases and conditions listed as a possible cause of Heart enlargement in our database from various sources. 1q deletion - cardiomegaly Acromegaly Alcoholism Amyloidosis Aortic regurgitation Aortic stenosis Aortic valve disease Appetite suppressant Autoimmune Diseases Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome - heart enlargement Beri-Beri Carcinoid syndrome Cardiac failure, low output Cardiac glycogenosis Cardiomyopathies Chagas disease Chronic thromboebolic pulmonary hypertension Coarctation of the aorta Cobalt Congenital heart block Congenital heart disease Cor pulmonale Cushing's syndrome Diabetes Dilated cardiomyopathy Duchenne's progressive muscular dystrophy Dystrophia myotonica Eisenmenger's syndrome Erythroderma Fabry's disease Friedreich's ataxia Fucosidosis type 1 - heart enlargement Fucosidosis type II - heart enlargement Gangliosidosis generalized GM1, type 1 - heart enlargement Genetic causes GM1 gangliosidosis - heart enlargement Gout Heart cancer - Cardiomegaly Heart Failure - heart enlargement Hemochromatosis High cholesterol High fat diet Homocystinemia Hurler's syndrome Hypertension Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Increased alcohol consumption Infantile sialic acid storage disorder - heart enlargement Ischaemic Heart Disease Ischemic heart disease - Cardiomegaly Kwashiorkhor Leukemia Low exercise Lyme disease - heart enlargement Lymphoma Mitral regurgitation Mitral valve disease Mucopolysaccharidoses Myxoedema Obesity Oxalosis Paget's disease of bone Persistent ductus arteriosus Phaeochromocytoma Polyarteritis nodosa Polysaccharide storage disease Previous heart attacks Pulmonary stenosis Reactive pulmonary hypertension Refsum's disease Rheumatoid arthritis Rickettsial myocarditis Sandhoff Disease - heart enlargement Sarcoidosis Severe anaemia Smoking Systemic arteriovenous fistula Systemic hypertension Systemic lupus erythematosus Tay-Sachs disease Thalassemia - heart enlargement Thyrotoxicosis Tricuspid regurgitation Ventricular septal defect Viral infections Viral myocarditis Drug side effect causes of Heart enlargement The following drugs , medications, substances or toxins may possibly cause Heart enlargement as a side effect. Emetine Chloroquine Daunorubicin Doxorubicin http://www.wrongdiagnosis.com/symptoms/heart_enlargement/causes.htm Common causes of Heart enlargement Introduction: This information shows the various causes of Heart enlargement, and how common these diseases or conditions are in the general population. This is not a direct indication as to how commonly these diseases are the actual cause of Heart enlargement, but gives a relative idea as to how frequent these diseases are seen overall. 9 diseases that are "very common". 8 diseases that are "common". 2 diseases that are "uncommon". 2 diseases that are "rare". 10 diseases that are "rare". 72 diseases without any prevalence information. Causes of Heart enlargement that are very common The following causes of Heart enlargement are diseases or medical conditions that affect more than 10 million people in the USA: Alcoholism Diabetes High cholesterol Hypertension Ischaemic Heart Disease Ischemic heart disease - Cardiomegaly Obesity Smoking Systemic hypertension Causes of Heart enlargement that are common The following causes of Heart enlargement are diseases or conditions that affect more than 1 million people in the USA: Autoimmune Diseases Congenital heart disease Heart Failure - heart enlargement Hemochromatosis Paget's disease of bone Rheumatoid arthritis Systemic lupus erythematosus Thyrotoxicosis Causes of Heart enlargement that are uncommon The following causes of Heart enlargement are diseases or conditions that affect more than 200,000 people, but less than 1 million people in the USA: Gout Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Causes of Heart enlargement that are rare The offical US government definition of a "rare" disease is one that affects 200,000 people or less. The following causes of Heart enlargement appear in the population at a rate of less than 200,000 people per year in the USA: Fabry's disease Sandhoff Disease - heart enlargement Causes of Heart enlargement that are very rare The following causes of Heart enlargement appear in the population at a rate of substantially less than 200,000 people per year in the USA: Acromegaly Amyloidosis Cardiomyopathies Coarctation of the aorta Cushing's syndrome Leukemia Lyme disease - heart enlargement Lymphoma Sarcoidosis Thalassemia - heart enlargement Causes of Heart enlargement without any prevalence information The following causes of Heart enlargement are ones for which we do not have any prevalence information. 1q deletion - cardiomegaly Acromegaly Alcoholism Aortic regurgitation Aortic stenosis Aortic valve disease Appetite suppressant Autoimmune Diseases Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome - heart enlargement Beri-Beri Carcinoid syndrome Cardiac failure, low output Cardiac glycogenosis Chagas disease Chronic thromboebolic pulmonary hypertension Coarctation of the aorta Cobalt Congenital heart block Congenital heart disease Cor pulmonale Cushing's syndrome Diabetes Dilated cardiomyopathy Duchenne's progressive muscular dystrophy Dystrophia myotonica Eisenmenger's syndrome Erythroderma Friedreich's ataxia Fucosidosis type 1 - heart enlargement Fucosidosis type II - heart enlargement Gangliosidosis generalized GM1, type 1 - heart enlargement Genetic causes GM1 gangliosidosis - heart enlargement Heart cancer - Cardiomegaly Heart Failure - heart enlargement High cholesterol High fat diet Homocystinemia Hurler's syndrome Hypertension Increased alcohol consumption Infantile sialic acid storage disorder - heart enlargement Kwashiorkhor Low exercise Lymphoma Mitral regurgitation Mitral valve disease Mucopolysaccharidoses Myxoedema Obesity Oxalosis Persistent ductus arteriosus Phaeochromocytoma Polyarteritis nodosa Polysaccharide storage disease Previous heart attacks Pulmonary stenosis Reactive pulmonary hypertension Refsum's disease Rheumatoid arthritis Rickettsial myocarditis Severe anaemia Systemic arteriovenous fistula Systemic hypertension Systemic lupus erythematosus Tay-Sachs disease Thyrotoxicosis Tricuspid regurgitation Ventricular septal defect Viral infections Viral myocarditis X-linked humeroperoneal neuromuscular disease Approach to the Diagnosis The diagnosis of cardiomegaly can be further developed be a good history and the association of other symptoms and signs. Is there a history of hypertension, alcoholism, rheumatic fever or other systemic disease? Has the patient experienced shortness of breath, angina, fever, joint pains, and so forth? Are there findings of pedal edema, hepatomegaly, or jugular venous distention (CHF)? Are there hypertension and proteinuria (renal disease or essential hypertension)? Is there a significant heart murmur (congenital heart disease, rheumatic heart disease)? The diagnostic workup will include a CBC, urinalysis, chemistry panel, sedimentation rate, a chest x-ray, and ECG. At this point, it is wise to consult a cardiologist. Echocardiography will be helpful in diagnosing valvular heart disease, myocardiopathy, and pericardial effusion. If CHF is suspected, a venous pressure and circulation time as will as spirometry will support the diagnosis. Echocardiography can diagnose congestive heart failure by determining the left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF). If there is unexplained fever, an ASO titer or streptozyme test should be ordered to rule out rheumatic fever and perhaps serial blood cultures need to be done to exclude subacute bacterial endocarditis. If there is hypertension the patient may need a hypertensive workup TopOther Useful Tests 1. Exercise tolerance test (coronary insufficiency) 2. Thallium scan (coronary insufficiency) 3. Phonocardiogram (valvular heart disease) 4. ANA analysis (collagen disease) 5. Cardiac catheterization studies (congenital heart disease, rheumatic heart disease) 6. Angiocardiogram (valvular heart disease) 7. Coronary arteriogram (coronary insufficiency) 8. Thyroid profile (myxedema) 9. 24-hour urine catecholamine (pheochromocytoma) 10. Urine thiamine afterload (beriberi) 11. Muscle biopsy (collagen disease, trichinosis) 12. CT scan (mediastinal mass) 13. MRI (dissecting aneurysm)