* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Key List for Foundation GCSE Maths Cal
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
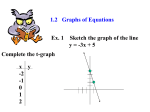
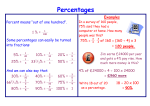
Foundation Calculator Key Topic List and Clues This is only a prediction and should not be used as an exhaustive list * Are the key topics to look at REVISION OVER HALF TERM 1st June at 12:30pm – 3:30pm 2nd June at 12:30pm – 3:30pm HANDLING DATA * Mean/Median/Mode/Range * Scatter Graphs – draw line of best fit. Remember relationship means a sentence Stem and Leaf – watch the key 2 Way Tables – try and spot these questions Frequency Polygon – draw bar chart then join crosses up in the middle Taking a sample – remember need a good number of responses/different venues/different times etc Pictogram NUMBER * Percentages with a calculator * Exchange Rates Prime Numbers – only factor itself and 1 e.g. 2,3,5,7,11,13,17 Cube Numbers – 1,8,27,64,125 Square Numbers – 1,4,9,16,25,36,49,64,81,100 Output and Input Machines Fractions of an amount – divide by the bottom and times by the top * Ratio inc recipe questions Estimation – watch out for this key word Estimation of heights – e.g. a man is 6ft, a bus is 3 x bigger so 18ft * Best Buys – scale up so that they are both the same amount * Electric Bills – difference is the key here ALGEBRA * Trial and Improvement Substitution – plug the values in. Know the difference between (4x)2 and 4x2 Simplifying – e.g. 3 x c x d= 3cd or 5d + 3e – 2d + 4e = 3d + 7e Coordinates – no silly mistakes Solving equations – look for word solve – remember whatever you do to one side you must do to the other * Inequalities – drawing inequalities/ listing integer solutions /writing inequalities/ solving (use same rules as solving equations) Expanding brackets – 4x(x + 7) / 3(x +4) - 4(x – 2) (watch double negative) * Drawing graphs – You must know the graphs x = 2, y = -1 and y=x * Nth Term – e.g 5, 8, 11, 14 = 3n +2 Also if sequence is 5n + 1. The first term n=1 so 5x1+1=6 The second term n=2 so 5x2 +1 = 11 The third term n= 3 so 5x3 + 1 = 16 SHAPE, SPACE AND MEASURE * Angles – always give reasons clearly – remember isosceles triangles base angles equal Perimeter – around the outside Area – rectangle = base x height triangle = base x height divide by 2 Volume of a cube = base x height x length Names of 2D shapes and 3D shapes up to 10 sided Speed – Speed = Distance/Time Time/Distance Graphs – understand how these work Parallel Lines – lines equal distance apart – think train tracks Perpendicular Lines – meet at 90 degrees Symmetry – understand lines of symmetry (i.e. cut exactly in half) and rotational symmetry. (How many times it looks the same whilst rotated 360 degrees?) Tessellations – same shape over and over no gaps Bearings – remember to read where it is from. Bearings always measure from north, measure clockwise and give answers as 3 digits Little box into Big Box - practice How many tiles on a wall – practice * Drawing a triangle – use compass or protractor Construction/Loci – use a compass – single point is a circle/straight line is a line Elevations – remember elevations and plan (means birdseye view) Planes of symmetry – cut a 3D shape in half Transformations – learn the four plus associated information. Translation - vector (watch scale, 2 years ago the graph went in 2s) Enlargement - Scale Factor, Centre of Enlargement Metric Units – mm, cm, metres, km, litres, ml, grams, kg Imperial Units – inches, feet, yards, miles, gallons, pints, oz, pounds, stone Parts of a circle * Area and Circumference of a Circle * Pythagoras