* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name: Date: Science 6 Study Guide Vocabulary to know: Climate
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
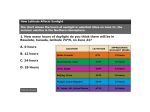
Name: Date: Science 6 Study Guide Vocabulary to know: Climate: Climate is the pattern of weather that occurs in an area over many years Latitude: Measure of how far north and south of the equator a place is Climatologists: people who study climates Global warming: gradual increase in the overall temperature of the Earth’s atmosphere due to the greenhouse effect. Greenhouse effect: the trapping of the sun’s warmth in a planet’s lower atmosphere by various atmospheric gases How do large bodies of water affect climate? -They absorb and give off heat. Normally areas near a large body of water are warmer in winter and cooler in summer. How do ocean currents affect climate? -Warm ocean currents begin near the equator. They flow toward the north and south poles and warm the areas as they pass. As they near the poles the currents cool off. Cool currents flow back to the equator cooling the air and climates of nearby lands. How do ocean currents affect climate? -Winds blowing from the sea are often moister than those blowing from land. The moist sea air passes over the land bringing rain. The sea air gives coastal areas a wetter climate than inland areas far from the sea. How do mountains affect climate? -at the same latitude, the climate is colder in the mountains than at sea level. Thin mountain air has fewer molecules to absorb heat than air near sea level. Therefore mountain air tends to be cooler. How do large cities affect climate? -streets, parking lots, and buildings in large cities absorb the sun’s rays and heat up. Heat is transferred to the air where air pollution traps it. This trapped heat creates what is known as heat-island effect. Temperatures can be 5 degrees Celsius higher in cities. What are the six main climate zones? -tropical, mild/moderate, dry, continental, polar, high elevation They are further broken down, example Dry (arid/semiarid) Why does the Earth have seasons? -As Earth revolves around the sun different parts of the planet are tilted toward the sun. Areas tilted toward the sun get more solar radiation than other areas tilted away from the sun. What is an ice age? A time when large sheets of ice covered Earth’s surface. This happened about 2 million years ago. Ice ages are followed by warm periods called interglacial periods. What is an interglacial period? Period following an ice age where there is a warm tropical climate. Lasted between 10-15 thousand years. We are in one today that began around 11,500 years ago. What causes climatic change? -Short term: (months to years) meteorite collisions, large volcanic eruptions -Long term: (thousands to millions of years) change in Earth’s orbit or axis, movement of Earth’s plates What is the difference between weather and climate? -Weather can change in just a few hours, climate takes hundreds, even thousands of years to change What are the five main causes of climate on Earth? Latitude, elevation, ocean/wind currents, closeness to bodies of water, terrain (refer to worksheet) What are examples of greenhouse gases and where do they come from? ● CO2 and CO- Burning fossil Fuels (oil, gas, coal) ● Methane- from Agriculture ● N2O- Fertilizer, burning fossil fuels How can we stop global warming? ● Not use a car- bike/walk instead ● Plant a tree! Plants and trees absorb CO2 from the air naturally ● Don’t eat meat! No seriously- large scale farming contributes to global warming ● Buy locally produced food and items