* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Theory of Plate Tectonics
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geodesy wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
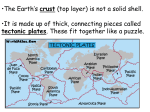
8.9AB: Plate Tectonic Theory Earth and Space Theory of Plate Tectonics (Lexile 970L) 1 As you may have discovered, Earth is not like the other planets in the solar system. Much like peeling an onion, Earth's layers answer questions that have baffled scientists for years. Earth's crust, the outermost layer, is not entirely one piece. It is broken into sections which resemble an oversized jigsaw puzzle. These giant sections, known as plates, are always on the move, creeping along at a snail's pace. The plates seem to float on top of the mantle, the layer of Earth composed of partially melted rock. 2 Have you ever put together a puzzle? The interlocking pieces must fit together perfectly in order to form a picture. Over 100 years ago, a German scientist named Alfred Wegener discovered something fascinating about a map of Earth. He realized that the continents seem to fit together like the pieces of a jigsaw puzzle. This giant piece of land, called Pangaea, existed over 250 million years ago. Over time, Pangaea's tectonic plates slowly drifted apart. These plates in their current positions make up the seven continents as we know them. 3 Earth's plates are continually being created or recycled. By studying the ocean floor, oceanographers have discovered mountainous ridges along the bottom of the ocean. These ridges form where two plates have started to move apart. Molten rock from the underlying mantle oozes out and fills the space that has been created by the plates' movement. Plate tectonic theory has also helped scientists explain another amazing Earth landform: the deep ocean trenches. These deep ocean trenches are areas where plates are being recycled. As plates come together, one plate may go on top of the other. The crust of the lower plate is slowly forced back down into Earth's mantle where it becomes molten rock again. This type of area is known as a subduction zone. It forms when continental land masses collide with ocean plates, or when two ocean plates collide with each other. 4 Movement of the plates does not just cause trenches and ridges on the ocean floor. It can also form mountains on land. When two continental plates push together, there is so much force that the plates buckle. Massive mountain ranges are formed. The friction during crustal movement can sometimes cause earthquakes and tsunamis. 5 The plates on Earth's crust change Earth's surface features in many ways. Having previously been pieced together in a giant landmass, they slowly moved apart to their current locations. The plates will continue to move, forming new rocks and recycling the old. Imagine how a map of Earth might look after another 250 million years of continental drift. 1 8.9AB: Plate Tectonic Theory Earth and Space 1 2 3 What analogy does the author use to describe how Earth's continents fit together? A The plates on Earth form a picture like a jigsaw puzzle does. B The mountains and volcanoes on Earth are pieced together. C The plates on Earth fit together like the pieces of a jigsaw puzzle. D The plates on Earth are slowly drifting apart. Which of the following best describes Pangaea? A the seven continents that we know now B an area on Earth that contains a ring of volcanoes C a giant landmass that existed over 250 million years ago D the process by which plates move How is Earth's crust recycled? A Earth's crust is not recycled, only created. B As molten rock seeps out of weak spots in the crust, volcanoes are formed. C When plates slide past each other, creating friction, an earthquake forms. D As new crust is created, old crust is forced down deep inside Earth's mantle, where it becomes molten rock again. 2 8.9AB: Plate Tectonic Theory Earth and Space 4 5 Scientists predict that in another 250 million years, the continents will be located in different positions. How is this possible? A The tectonic plates on Earth are continually moving at a slow rate. B The gravity on Earth causes the continents to move around. C Scientist think that the continents will move back into the shape of Pangaea again. D All of the above The diagram above illustrates a type of plate boundary. Which crustal feature is most likely to form at this type of boundary? A trench B ridges C tsunami D earthquake 3