* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit: Interactions Among Organisms Sections: Energy in Ecosystems
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
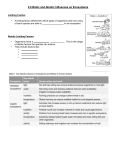
Unit: Interactions Among Organisms Sections: Energy in Ecosystems, Overpopulation Key Words: ecosystem, energy, food web, food chain, energy pyramid, carrying capacity, overpopulation, limiting factors Essential Questions: Energy in Ecosystems - How does energy flow through ecosystems? Why is food important to organisms? Why are all organisms connected to each other? Overpopulation - Why does overpopulation occur? What problems does overpopulation cause? How can overpopulation be reduced? Energy in Ecosystems Food Web - An interconnected network in an ecosystem Transfer of energy occurs Involves biotic and abiotic factors Affect one organism in the web, affect them all Food is necessary for survival o Growth and development (assimulation) o Energy for all cellular processes Law of Thermodynamics 0th Law (Zeroth) If 2 systems are in equilibrium with a 3rd system, then they are in equilibrium with each other Refers to temperature 1st Law 2nd Law 3rd Law Law of conservation of energy An isolated system, if not already in a state of equilibrium, will evolve towards it The entropy (disorder) of a system approaches a constant value as the temperature approaches zero energy cannot be created nor destroyed, only transferred Entropy - measure of how close a system is to equilibrium, or a measure of the disorder in the system Cannot ever reach absolute zero but can "arbitrarily" approach it heat and work are forms of energy transfer - - Thermodynamic system o Consists of a pure substance can be described as a collection of like molecules, each with its individual motion is describable in terms of velocity and momentum Calorie measurement o 1 calorie = the amount of heat energy required to raise 1 g of H2O up 1° Celsius (~4.19 J) Overpopulation Populations in an ecosystem - Quantity of the types of species in an ecosystem More diversity, more healthy and stable Delicate balance between cooperative and competitive relationships Depend upon resources to survive o Abiotic factors o Biotic factors o Can be limited Limiting Resources water - food shelter Any fluctuation of the limiting resources will affect the population o Increase Considered overpopulation Some environments can handle the increase Others cannot – considered overpopulation o Decrease Available resources shared Makes it more difficult for other species to survive o End result Drastic number loss of overpopulated species Dies out completely Due to famine (starvation) Due to disease o Carrying capacity The idea numbers of populations that an ecosystem can support based upon its resources available