* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Forces in Earth`s Crust Objectives After completing
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geodesy wikipedia , lookup
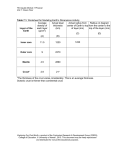
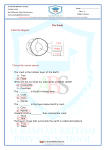
(#1) Forces in Earth’s Crust Objectives After completing the lesson, I will be able to: • 1) explain how stress in the crust changes Earth’s surface • 2) describe where faults are usually found and why they form • 3) identify the land features that result from plate movement (#2) Forces in Earth’s Crust Key Terms (A) 1) stress2) tension3) compression- (#3) Forces in Earth’s Crust Key Terms (B) 4) shearing5) normal fault6) hanging wall- (#4) Forces in Earth’s Crust Key Terms (C) 7) footwall8) reverse fault9) strike-slip fault 10) plateau- (#5) Forces in Earth’s Crust Checkpoint (175) How does shearing affect rock in Earth’s crust? (#6) Forces in Earth’s Crust Relating Cause and Effect Which type of stress tends to shorten part of the crust? (#7) Forces in Earth’s Crust Inferring Which half of a normal fault would you expect to form the floor of a valley? Why? (#8) Forces in Earth’s Crust Checkpoint (177) What is the difference between a hanging wall and a footwall? (#9) Forces in Earth’s Crust Predicting Using figure 4 on page 178 • If the folding in the diagram continued, what kind of fault might form? (#10) Forces in Earth’s Crust Checkpoint (178) What is an anticline? (#11) Forces in Earth’s Crust Reviewing What are the three main types of stress in rock? (#12) Forces in Earth’s Crust Relating Cause and Effect How does tension change the shape of Earth’s crust? (#13) Forces in Earth’s Crust Comparing and Contrasting Compare the way that compression affects the crust to the way that tension affects the crust? (#14) Forces in Earth’s Crust Describing What is a fault? (#15) Forces in Earth’s Crust Explaining Why do faults often occur along plate boundaries?