* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download REVIEW Use the following terms to answer the
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
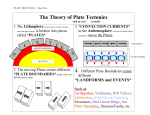
REVIEW Use the following terms to answer the questions 1-9 below. Collision plate boundary Transverse plate boundary Separation plate boundary Continental Drift Theory Pangea Plates Magma Trenches Lava 1. The plate boundary where two plates are moving apart creating new crust and making the oceans spread. 2. This is molten rock on the surface of the Earth. 3. This is the name of the supercontinent 250 million years ago. 4. These are pieces of the crust that "float" and move because of the mantle's convection currents. 5. Molten rock under the surface of the Earth is called. 6. A plate boundary in which the two plates crash into each other causing mountain building, earthquakes, and volcanic activity. 7. The idea that the Earth's plates are moving across the surface of the Earth. 8. A plate boundary in which the two plates are sliding in opposite directions. 9. The deepest area of the oceans. They are formed at a subduction zone. 10. What is the main material that the crust is made of? 11. What two metals make up the inner and outer core? 12. Name three pieces of evidence for the Continental Drift theory. 13. Label the four layers of the Earth and tell what main material makes up that layer. 14. The theory that Earth’s crust and upper mantle are broken into sections is called . a. seafloor spreading b. plate tectonics 15. Plates are composed of the . a. crust and part of the upper mantle b. lithosphere and asthenosphere 16. The lithosphere is composed of the . a. plates and seafloor b. crust and upper mantle 17. Plates float on the . a. asthenosphere b. lithosphere 18. Plates can . a. pull apart, collide, and move past one another b. erupt and form precipitation 19. The boundary between two plates that are moving apart is a boundary. a. convergent b. divergent 20. When ocean plates collide with continental plates, the denser ocean plate . a. sinks b. rises 21. The area where a plate descends is a . a. convergent boundary b. subduction zone 22. A is created where one plate moves under another. a. mantle b. trench 23. A subducted plate melts, forming . a. magma and volcanic mountains b. the lithosphere 24. Two continental plates may collide and cause . a. glaciers b. earthquakes 25. Scientists think plates are moved by . a. convection currents b. volcanoes 26. A place where plates slide past one another is a . a. divergent fault b. transform fault 27. The San Andreas Fault is a . a. volcano b. transform fault 28. The Himalayas were formed at a . a. convergent boundary b. transform fault PLATE TECTONICS Review Name: ______________ Matching a. b. c. d. e. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ Continent Continental Drift Seafloor Seafloor Spreading Converge f. g. h. i. j. Diverge Transform Plate Tectonics Plate Convection Current 1. current in Earth’s mantle that transfers heat in Earth’s interior and is the driving force for plate tectonics. 2. a large section of Earth’s oceanic or continental crust and rigid upper mantle that moves around on the asthenosphere 3. theory that Earth’s crust and upper mantle are broken into plates that float and move around on a plastic like layer of the mantle. 4. to convert or change 5. to move apart 6. to come together 7. Hess’s theory that new seafloor is formed when magma is forced upward toward the surface at a mid-ocean ridge 8. portion of Earth’s crust that lies beneath ocean waters 9. Wegener’s hypothesis that all continents were once connected in a single large landmass that broke apart about 200 million years ago and drifted slowly to their current positions. 10. one of the six or seven great divisions of land on the globe a. b. c. d. e. Volcano Lava Magma Tectonics Fault f. g. h. i. j. Stress Earthquake Crust Mantle Core ____ 11. the centermost layer of the Earth, a solid sphere of metal, mostly iron & nickel. ____ 12. the layer of rock between the Earth’s outer core & crust in which rock is hot enough to flow in convection currents ____ 13. a thin outer layer of rock above a planet’s mantle, including all dry land & ocean basins ____ 14. the shaking of the ground caused by the sudden movement of large blocks of rocks along a fault ____ 15. the force applied by an object pressing on, pulling on, or pushing against another object ____ 16. fracture in the Earth’s lithosphere along which blocks of rocks move past each other ____ 17. the process in which the motion of hot material under a crust changes the crust of a planet ____ 18. molten rock below the Earth’s surface ____ 19. molten rock that reaches the Earth’s surface through a volcano ____ 20. an opening in the Earth’s crust through which molten rock, rock fragments, and hot gases erupt a. Earthquake f. Liquefaction b. c. d. e. Seismograph Aftershock Focus Tsunami g. h. i. j. Epicenter Seismic Waves Fault Magnitude ____ 21. the vibrations caused by an earthquake ____ 22. the shaking of the ground caused by the sudden movement of large blocks of rocks along a fault ____ 23. the point on the Earth’s surface directly above the focus of an earthquake ____ 24. in an earthquake, the point underground where the rocks first begin to move. ____ 25. an instrument that constantly records ground movement ____ 26. measure of earthquake size: a measure of the energy of an earthquake, specified on the Richter scale ____ 27. a smaller earthquake that follows a more powerful earthquake in the same area ____ 28. a water wave caused by an earthquake, volcanic eruption, or landslide ____ 29. a process in which the shaking of the ground causes loose, wet soil to act like a liquid. ____ 30. a fracture in the Earth’s lithosphere along which blocks of rocks move past each other