* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
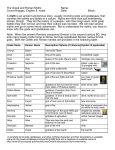
Classical Greek Culture Religion affected every aspect of Greek life. Homer described the gods worshiped in the Greek religion. Twelve chief gods and goddesses were thought to live on Olympus, the highest mountain in Greece. The twelve major gods were: He ruled the Olympians. He was the god of the sky, lightning and thunder carrying a thunderbolt as his symbol. He married Hera, his sister, which was a family habit. He fathered many children with various goddesses and mortals. Symbol: Lightning Bolt. She was the protector of marriage and the home. She was associated with the peacock, because of her great beauty. She and Zeus were always quarreling. She was called the queen of intriguers, a vindictive and jealous wife, who frequently outwitted her husband, Zeus. Symbol: Peacock or peacock feather. He built an underwater palace with a great pearl and coral throne. Although he chose Thetis, a beautiful water nymph, as his queen, he, like his brother Zeus, was a great wanderer fathering hundreds of children. He was a difficult god, changeful and quarrelsome, but created many curious forms for his sea creatures. He invented the horse for his sister Demeter, whom he loved. Symbol: the horse or the trident. He was the jealous brother to Zeus and Poseidon. He made Persephone his wife after stealing her from her mother, Demeter, who was his sister. Because he was a violent god, who was also very possessive of every new soul, he rarely left his underworld domain. Symbol: jewels or helmets. She was the goddess of growing things. She was the mother of Persephone, whose father was Zeus. Her daughter was kidnapped by Hades and taken to the Underworld for six months of the year causing the change of seasons. Symbol: Cornucopia She was the sister of Zeus and the daughter of Cronos and Rhea. She represented personal and communal security and happiness. She was thought of as the kindest and mildest of the goddesses. She was of little mythological importance, appearing in only a few stories. Symbol: Fire. She was born full grown out of the head of Zeus. She taught man to use tools and taught his wife to spin and weave. She was the best-loved goddess on Olympus. She hated Ares, god of war, often besting him in battle. The Greek city of Athens is named after her. She was said to have created the spider. Symbol: olive branch and owl. He was the twin brother of Artemis and the most handsome of the gods. He was also the god of the healing arts and of medicine. He drove his chariot across the sky to pull the sun each day. His son, Phaethon, drives Apollo’s sun chariot with disastrous results. Symbol: Lyre. She was the twin sister of Apollo, whose mother was Leto and father was Zeus. She was a chaste huntress, who always carried a silver bow and arrows. She ruled over the untamed places of the earth. Symbol: Moon. He is said to be the only god on Olympus with a mortal parent. His creation of wine brings ecstasy and drunkenness to his revelers. Much of the ancient world’s greatest poetry was created in his honor. Symbol: Grape Vine or Grapes. He was a ruthless and murderous god, who displayed the worst of humanity’s traits. He, along with grief, strife, panic, and terror, roams the earth. Ironically, he was a coward, who fled the field of battle. Symbol: Vulture He was the ugliest of the gods, who was rejected by his mother, Hera, when she hurled him off of Mount Olympus crippling him. He fashioned the armor and tools of the gods on a broken mountain near Mount Olympus. He made beautiful jewelry for the goddesses. Symbol: Blacksmith’s Hammer. She is the goddess of desire born from sea foam. Another myth credits her mother as Dione and her father as Zeus. After all the gods on Mount Olympus courted her, she married Hephaestus, the ugliest of the gods. Because she was judged the most beautiful of all the goddesses on Mount Olympus by Paris, the other goddesses envied her. Symbol: Swan. He was the precocious son of Zeus and Maia, a Titaness. God of thieves, travellers, roads, and money – a less important thing in the ancient Greek’s life. As a baby, he made a lyre and pipe for his halfbrother, Apollo. He carried Apollo’s golden staff and flew around the heavens and earth on winged sandals. Symbol: Winged Sandals. Festivals developed as a way to honor the gods and goddesses. Numerous events, including athletic games, took place in honor of the gods. The first such games were held at the Olympic festival in 776 B.C. The Greeks also had a great desire to learn the will of the gods. To do so, they made use of the oracle, a sacred shrine where a god or goddess was said to reveal the future through a priest or priestess. The most famous was the oracle of Apollo at Delphi. A priestess, thought to be inspired by Apollo, listened to the questions of mortals. Although the ancient Greek religion is no longer practiced, it was the source of most Greek drama and art. Not only did the Romans adopt the Greek gods, but many stories and references appear in European and American literature. The arts of the western world have been largely dominated by the standards set by the Greeks of the classical period. Classical Greek art was concerned with expressing eternal ideas. The subject matter of this art was the human being, presented as an object of great beauty. Some of the finest examples of Greek classical architecture were built in Athens. The most famous building on the Acropolis, the Parthenon is regarded as the greatest example of the classical Greek temple. Dedicated to Athena, the patron goddess of Athens, the Parthenon was an expression of the Athenians’ pride in their city-state. Classical Greek sculptors did not seek to achieve realism in their art, but rather a standard of ideal beauty. History, as we know it – a systematic analysis of past events – was created in the Western world by the Greeks. Herodotus wrote History of the Persian Wars, often seen as the first real account of history in the Western civilization. Its central theme is the conflict between the Greeks and the Persians, which Herodotus viewed as a struggle between freedom and Persian despotism. Many historians today consider Thucydides the greatest historian of the ancient world. Thucydides was an Athenian general who fought in wars and later wrote the history of wars. Unlike Herodotus, he saw war and politics as caused by the activities of man, not gods.