* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Consortium for Educational Communication
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
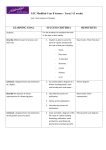
Consortium for Educational Communication GLOSSARY: Agriculture: Farming or husbandry; cultivation of animals, plants, fungi, and other life forms for food, fiber, biofuel and other products used to sustain life. Annual: A plant that germinates from seed grows to maturity and produces new seed all within one year or growing season; usually herbaceous; short life cycle duration. e.g. Capsella. Biennial: A plant that normally requires two seasons to complete its life cycle, growing usually as a rosette in the first season and producing flowers and fruits and then dying in the second season. Bolting: An unusual lengthening of plant stems, due to elongation of cells, which is induced by a group of plant hormones called gibberellins, producing a stem with long internodes. Carbohydrate: General term for sugars and related compounds containing carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, usually with the empirical formula (CH2O)n. Carpel: One of the individual female reproductive organs in a flower. A carpel is usually composed of an ovary, a style, and a stigma. In origin, carpels are leaves (megasporophylls) that have evolved to enclose the ovules. The term pistil is sometimes used to refer to a single carpel or to several carpels fused together. DNA: Short for deoxyribonucleic acid; a nucleic acid that carries the genetic information in the cell and is capable of self-replication and synthesis of RNA. DNA consists of two long chains of nucleotides twisted into a double helix and joined by hydrogen bonds between the complementary bases adenine and thymine or cytosine and guanine. The sequence of nucleotides determines individual hereditary characteristics. Ethylene: A gaseous plant hormone that inhibits elongation in most growing tissues and promotes leaf abscission and fruit ripening and other physiological responses in some plants. Plant cells produce ethylene from the amino acid methionine; also known as ethene. Florigen: A hypothetical flowering hormone, that may be induced in leaves and moves to the bud to stimulate flowering; florigen has never been identified or isolated. Flower: The reproductive structure of some seed bearing plants Consortium for Educational Communication (angiosperms), characteristically having either specialized male or female organs or both male and female organs, such as stamens and a pistil, enclosed in an outer envelope of petals and sepals; such a structure having showy or colorful parts; a blossom. Flowering: Processes leading to production a flower or flowers. Fruit: The ripened ovary or ovaries of a seed-bearing plant, together with accessory parts, containing the seeds and occurring in a wide variety of forms; an edible, usually sweet and fleshy form of such a structure. Gene: The basic unit of heredity; a sequence of DNA nucleotides on a chromosome that codes for a polypeptide or RNA molecule and thus determines of an individual’s inherited traits; the coding region of DNA that determines a protein product. Gibberellin: A type of plant hormone, produced in the apical regions of shoots and roots; controls stem elongation and seed germination. Growth: An increase in the size of an organism or part of an organism, usually as a result of an increase in the number of cells; the process of growing; full development; maturity; a stage of development. Homeotic genes: Genes that determine which parts of the body form what body parts; genes involved in developmental patterns; genes that are involved in embryologic development. e.g. homeotic genes that control floral organ identity in angiosperms. Hormone: A substance, usually a peptide or steroid, produced by one tissue and conveyed by the bloodstream to another to affect physiological activity, such as growth or metabolism; a synthetic compound that acts like a hormone in the body; any of various similar substances found in plants and insects that regulate development. Imbibition: The adsorption of water onto the internal surfaces of materials; one of the methods by which root hair and other plant parts obtain water. Meristem: A zone of unspecialized, dividing cells whose derivatives give rise to other tissues and organs of a flowering plant. Key examples are the root apical meristem and shoot apical meristem. Monocarpic: Plants flowering and bearing fruit only once. Consortium for Educational Communication Perennial: A plant continuing to live from year to year; one that lives more than two years. Petal: One of the often brightly colored parts of a flower immediately surrounding the reproductive organs; a division of the corolla. Photoreceptor: A nerve ending, cell, or group of cells specialized to sense or receive light. e.g. phytochrome, a red-light receptor, that controls photomorphogenesis in plants. Physiology: The study of the function of the cells, tissues and organs. Phytochrome: A group of blue-green, photoreceptive, proteinaceous pigments produced in plants and involved in phenomenon such as photoperiodism, the germination of seeds, and leaf formation. Pollinator: an insect that carries pollen from one flower to another during cross pollination. Reproduction: The act of reproducing or the condition or process of being reproduced; the sexual or asexual process by which organisms generate new individuals of the same kind; procreation. Scion: A detached shoot or twig containing buds from a woody plant, used in grafting. Seed: A structure that develops from the mature ovule of a seed plant; contains an embryo and stored food enclosed by protective seed coats(s); a reproduction and dispersal unit of plant. Sepal: One of the separate, usually green parts forming the calyx of a flower. Stamen: The pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower, usually consisting of a filament and an anther. Stimulus: Something causing or regarded as causing a response; agent, action, or condition that elicits or accelerates a physiological or psychological activity or response; something that incites or rouses to action; an incentive. Tissue: A group of cells organized into a structural and functional unit such as muscle and xylem; simple tissues are made up of similar cells, and complex tissues of different kinds of cells. Vegetative: Denoting the non-reproductive parts of a plant, i.e. Consortium for Educational Communication the stems, leaves, and roots, or growth that does not involve the reproductive parts; of, relating to, or capable of growth; of, relating to, or functioning in processes such as growth or nutrition rather than sexual reproduction; or relating to asexual reproduction, such as fission or budding. Vernalization: Subjection of seeds or seedlings to low temperature in order to hasten plant development and flowering; vernalization is commonly used for crop plants such as winter rye and is possible because the seeds and buds of many plants require cold in order to break dormancy.