* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download TRANSLATION
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
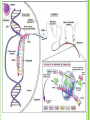
TRANSLATION Using RNA to make Protein WHAT DOES IT MEAN TO TRANSLATE? Definition in English: to turn from one language into another; to change form Definition in science: to read the coded message of an RNA molecule and synthesize a new polypeptide molecule (aka protein) at the ribosome in the cytoplasm Definition in our own words: use RNA to make protein KINDS OF RNA Before we talk about translation, let’s review: There are 3 types of RNA involved in the process of making protein mRNA: messenger RNA carries the message of how to make a protein (this is the one we talked about yesterday!) tRNA: transfer RNA transfers amino acids to the ribosome during translation rRNA: ribosomal RNA is one small piece making up the ribosome KINDS OF RNA mRNA KINDS OF RNA tRNA Amino Acid Folded RNA Strand Anticodon (complementary to the mRNA codon) KINDS OF RNA rRNA Ribosomal RNA Ribosome THE GENETIC CODE The mRNA molecule carries the message of how to make the specific protein That message is coded Let’s learn how to crack that code! THE GENETIC CODE On the mRNA molecule, bases are read 3 at a time A group of 3 bases in a row is called a codon There are 64 possible different codons that code for the 20 different amino acids codon for methionine (Met) codon for leucine (Leu) THE GENETIC CODE How do you know which codons code for which amino acids? Use this!!! THE GENETIC CODE AUG is the start codon This is where translation will begin UAA, UAG, UGA are stop codons This is where translation will end PRACTICE TRANSLATING CODONS: Codon=3 nucleotides that are read together If this is the strand of mRNA: UCGCACGGU The codons are: PRACTICE TRANSLATING CODONS: Codon=3 nucleotides that are read together If this is the strand of mRNA: UCGCACGGU The codons are: UCG-CAC-GGU PRACTICE TRANSLATING CODONS: Codon=3 nucleotides that are read together If this is the strand of mRNA: UCGCACGGU The codons are: UCG-CAC-GGU How many codons are there? PRACTICE TRANSLATING CODONS: Codon=3 nucleotides that are read together If this is the strand of mRNA: UCGCACGGU The codons are: UCG-CAC-GGU How many codons are there? 3 PRACTICE TRANSLATING CODONS: Codon=3 nucleotides that are read together If this is the strand of mRNA: UCGCACGGU The codons are: UCG-CAC-GGU How many codons are there? 3 What amino acids are coded for? PRACTICE TRANSLATING CODONS: Codon=3 nucleotides that are read together If this is the strand of mRNA: UCGCACGGU The codons are: UCG-CAC-GGU How many codons are there? 3 What amino acids are coded for? Serine, Histidine, Glycine THE GENETIC ANTI-CODE Anticodons are the compliments to codons Found on the tRNA As it matches to the codon, tRNA brings over the proper amino acid DO NOT USE THIS WITH THE CHART! Example: Codon (mRNA): AUG Anticodon (tRNA): UAC Amino Acid: Methionine THE PROCESS STEP 1: mRNA molecule leaves nucleus and binds with ribosome THE PROCESS PART 2 STEP 2: Beginning at the start codon (AUG), ribosome binds tRNA molecules with mRNA molecules according to correct codon—anticodon pairing EX: codon AUG is on the mRNA molecule, a tRNA molecule with the anticodon UAC will bind to it PROCESS CONTINUED STEP 3: The NEXT tRNA molecule brings its amino acid and the two amino acids are bonded together. PROCESS CONTINUED STEP 4: First tRNA is released and the mRNA is moved down so the next codon can be read. This continues until a stop codon is reached. Then the amino acid and mRNA is released.