* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MODE OF TRANSMISSION/ PATTERNS OF INHERITENCE
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
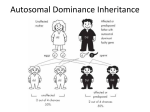
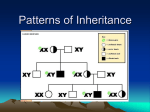
MODE OF TRANSMISSION/ PATTERNS OF INHERITENCE Learning Objectives • • • Enlist different mode of inheritance Describe each type Give examples of each type Pattern of Inheritance • • Mendelian Autosomal dominant Autosomal recessive X linked Non Mendelian Mitochondrial Inheritance Monogenic Inheritance Autosoamal Dominant Sex Linked Recessive Dominant X linked Y linked Recessive Autosomal Dominant • • • • • Males and females affected in equal proportions Autosomal chromosomes All generations are affected Both parents transfer alleles to their offspring Risk if both parents are affected? Autosomal dominant Autosomal Recessive • • • • • Males and females affected in equal proportions Skip Generation Both parents can transmit alleles to the offspring Consanguinity Genetic risks – – – – Both parents affected One parent affected Both parents carriers One diseased other is a carrier (pseudodominance) Autosomal Recessive X linked Recessive Diseases • • • • • • • • Affect males Hemizygous for the allele Mothers → affected sons Father → carrier daughters → male grand children No male – male transmission Every generation is affected Genetic Risks Females can be affected – – Homozygosity for the allele Skewed X inactivation X linked Dominant Diseases • • • • • Affected males→ all daughters Affected female → 50% of her sons Vitamin D resistant rickets Males and females are affected but with an excess of females Females are less severely affected than males X Linked Inheritance X Linked dominant Inheritance Y linked Inheritance • • • • Affected males only Affected males transmit to their sons Hairy ears Spermatogenesis genes → azoospermia Y linked Inheritance Non Mendelian Inheritance • • • • • Mitochondrial Inheritance Phenotypic variability Own DNA 16,569 bp, no intron Cytoplasmic location it is exclusively inherited through maternal line • No repair of DNA 10 time high mutation rate • Reference Kaplan Biochemistry & Medical Genetics