* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Meiosis Review
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
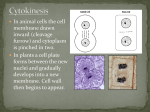
The Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Meiosis Review At the end of this unit, students should be able to answer the following questions: Describe binary fission. What is mitosis? Identify the phases of the eukaryotic cell cycle. What happens during interphase? Define cancer. How might the relationship between cancer and the cell cycle be used in the search for causes of cancer? Cells go through a series of events that include growth, DNA synthesis, and cell division. Why are these events best represented by a cycle diagram? Contrast cell division in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Why are the two types of cell division different? Explain how the cell cycle is regulated. Why is DNA replication essential to the cell cycle? What are chromosomes? When do they form? Identify the chromatids and the centromere of a chromosome. List the phases of mitosis. What happens during prophase of mitosis? During which phase of mitosis do sister chromatids separate? Describe what happens during cytokinesis in animal cells. If a cell skipped metaphase during mitosis, how might this affect the two daughter cells? Explain how chromosomes are related to chromatin. Why are chromosomes important for mitosis? Explain the significance of the spindle in mitosis. What are three types of asexual reproduction? Define gamete and zygote. What number of chromosomes does each have? What happens during fertilization? Outline the phases of meiosis. What is a life cycle? What is gametogenesis, and when does it occur? Create a diagram to show how crossing-over occurs and how it creates new gene combinations on each chromosome. An adult organism produces gametes that quickly go through fertilization and form diploid zygotes. The zygotes mature into adults, which live for many years. Eventually the adults produce gametes and the cycle repeats. What type of life cycle does this organism have? Explain your answer. Compare and contrast asexual and sexual reproduction. Explain why sexual reproduction results in genetically unique offspring. Explain how meiosis I differs from mitosis.