* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biome
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biosphere 2 wikipedia , lookup
Pleistocene Park wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Arctic ecology wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
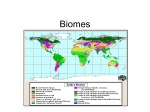
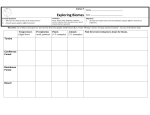
Bell-Ringer – AP Practice 1) The part of the earth that is occupied by living things is... a) Lithosphere b) Atmosphere c) Hydrosphere d) Transophere e) Biosphere 2) A relationship in which one species benefits and the other remains unchanged is called... a) Predation b) Symbiosis c) Mutualism d) Commensalism e) Parasitism 3) The most common population distribution found in nature is... a) Random distribution b) Uniform distribution c) Clumped distribution d) Symbiotic distribution e) Non-random distribution 4) Which answer below gives an example of mutualism? a) Leeches live inside a host, feeding on their blood until the host dies. b) A bird lives on the back of a wildebeest, eating the insects the wildebeest attracts. c) A bear hunts and eats salmon that swim upstream to spawn. d) Two elk fight over potential mates. e) Bees get food from a flower and move its pollen to every surrounding flower they visit. Biomes pgs 163-168 Earth’s Biomes • Biome – a large ecological unit defined by its dominant life forms (plant and animal) and vegetation. Earth’s Biomes • Biome – a large ecological unit defined by its dominant life forms (plant and animal) and vegetation. • Temperature and precipitation are the most important factors in determining biome types and location. Biome Placement • Biomes tend to occur at similar latitudes. • This is due to similar temperatures and atmospheric circulation leading to similar precipitation (due to Hadley cells) along the lines of latitude. The Edge Effect • Ecotone – a transition area between two adjacent but different communities (such as biomes). • This transition area may be a blending of the two biomes or a sharp boundary. The Edge Effect The Edge Effect • Ecotones present interesting ecosystems, as species from each separate community can be found together. • Animals are able to exploit both habitats, while plants colonize as deeply within the adjacent biome as possible. The Edge Effect • Because the habitat of an ecotone is blended, a higher degree of life is able to thrive there. • Due to this fact, ecotones tend to have a higher degree of biodiversity than surrounding habitats – this is known as the “edge effect.” Earth’s Biomes • The earth is roughly divided into ten biomes. Biomes Reading Guide • Read through pages 163-168. For each biome, record the appropriate information in a table designed like the one below. There are ten biomes listed in the book. Biome Where Is Summary of Characteristic Other Plant and It Temperature Relevant Animal Life Located? and Info Precipitation Bell Ringer 1) What is the edge effect? a) Finding less biodiversity in the interior of a biome b) Finding less biodiversity in each biome as one moves north from the equator c) Finding ecotones between biomes d) Finding more biodiversity in the transition areas between biomes e) Finding species evenness values vary from the interior to the edge of a biome 2) Similar biomes tend to be grouped… a) Around lines of latitude b) Around lines of longitude c) By continent d) Around the equator e) By both lines of latitude and longitude 3) The two most important factors in determining biome type are: a) precipitation and soil type b) humidity and altitude c) altitude and precipitation d) precipitation and temperature e) temperature and altitude 4) The graph below represents what biome? a) Tropical dry forest c) Desert d) Tundra b) Savanna e) Boreal Forest • As we watch Planet Earth, note each biome as we pass through it. Beside the name of each biome, note the type of vegetation and wildlife mentioned.