* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organic Molecules
Fluorescent glucose biosensor wikipedia , lookup
Chemical biology wikipedia , lookup
Puppy nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Biomolecular engineering wikipedia , lookup
Abiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
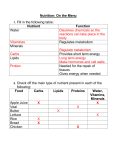
Organic Molecules SC Biology Standard- B3.4- 3.5Summarize how the structures of organic molecules are relative to their caloric value and the function of proteins, carbohydrates and fats in the human body. Organic Molecules: All organisms are made of organic molecules- which contain carbon Most organic molecules are made of smaller units(monomers) bonded together to form larger molecules(polymers) ENERGY is stored in the bonds that link these units together- varies with type of molecule formed This energy = the caloric value Continued: Proteins, Carbohydrates and fats/lipids are 3 organic molecules with different structures and different caloric values based upon those structures. Proteins: Composed of chains of amino acid monomers Amino acids are composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen—sometimes sulfur 20 different amino acids that chemically bond to make different proteins. 12 of these are made in the body, the rest must be consumed from foods such as nuts, beans or meat. Can be used for energy but only if no carbs or lipids are available Carbohydrates: Sugars and Starches Composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen Basic carbs are simple sugarsmonosaccharides such as glucose Main source of energy for the cell When carbs are consumed, process of digestion breaks the bonds between larger carbohydrate molecules so simple sugars can be absorbed Carbs continued: The bloodstream carries simple sugars throughout the body where they cross into the cell across the cell membrane Used as fuel for cellular respiration which releases energy as ATP The caloric value of carbs is dependent upon the number of carbon-hydrogen bonds. If an organism consumes more carbs than needed for energy requirements, then it is converted and stored as fat. Monosaccharides Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrate, made from only one sugar molecule. Glucose (Blood sugar) Galactose (Part of milk sugar) Fructose (Fruit sugar) Monosaccharides serve as a major fuel for cells and as raw material for building molecules Disaccharides/Polysaccharides Disaccharides are molecules made of two monosaccharides bonded together. Sucrose: glucose + fructose = table sugar Lactose: galactose + glucose = milk sugar Maltose: glucose + glucose = alcohol sugar Polysaccharides are polymers (made of more than two) of sugars. Polysaccharides have two main purposes in living things: Providing structure Energy storage Lipids/ Fats: Composed of carbon, hydrogen and small quantities of oxygen Made of two main molecules- glycerol and fatty acids so structurally different from carbohydrates Fats/lipids have more carbon-hydrogen bonds than carbs Do not form polymers Source of energy when carbs are scarce, but accumulates when plenty of carbs Fats/lipids continued: When fats are consumed- molecules are broken down and absorbed into the bloodstream Then blood carries fatty acids and glycerol molecules throughout the body where they enter into the cell through the cell membrane Stored in the cell for later use or as fuel for cellular respiration if no carbs are available Cellular respiration releases energy held in the chemical bonds of glycerol and fatty acids More: Due to the structure and number of C-H bonds, fats contain more energy (ATP) per gram which explains why fats have a higher caloric value Functions: Proteins are involved in almost every function of the human body More important as Building blocks than energy. Only energy if there is a shortage of carbs or lipids Used as support for connective tissue and keratin for hair and nails Transport proteins transport many substances throughout the body Function of Proteins continued: Hormone proteins coordinate activities such as insulin Contractile proteins control movements such as muscle movement Enzymes proteins accelerate the speed of chemical reactions such as digestive enzymes Function of Carbohydrates Important source of energy Primary source of energy for cellular respiration Some carbs are used for structural material in plants= cellulose Function of lipids: Used for energy when carbs are scarce Provide long term energy storage, cushion vital organs and insulation for the body Major component of cell membrane and one of the raw materials necessary for production of vitamins and hormones Identifying Organic compounds Must contain carbon Most inorganic compounds do NOT have carbon—Carbon dioxide (CO2) is NOT organic even though it has carbon Amino acids/ proteins contain an amino group (-NH2) and an organic acid group (-COOH) Lipids—the ratio of hydrogen to oxygen is greater than 2:1. Carbohydrates-the ratio of hydrogen to oxygen is exactly 2:1.