* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Psychoactive Drugs
Specialty drugs in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Psychedelic therapy wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Orphan drug wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
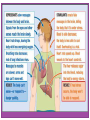
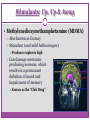
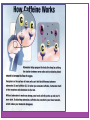
Consciousness OBJECTIVE: PROVIDED NOTES & AN ACTIVITY, SWBAT CHART NAMES & EFFECTS OF DEPRESSANTS, STIMULANTS, & HALLUCINOGENIC DRUGS AGENDA: -DO NOW -NOTES -ACTIVITY Topic: Psychoactive Drugs Consciousness: Psychoactive Drugs PART ONE Consciousness: Psychoactive Drugs Psychoactive Drugs Chemical substances that modify mental, emotional or behavioral functioning Continued use of a psychoactive drug produces tolerance; thus creating a situation in which greater quantities are needed to produce the desired effect Leads to…? Consciousness: Psychoactive Drugs Physical Dependence Condition occurring when a person’s body becomes unable to function normally without a particular substance Psychological Dependence The feeling that a drug is needed to continue a feeling of emotional or psychological well-being Withdrawal Physical symptoms that can include nausea, pain, tremors, crankiness & high blood pressure, resulting from the lack of an addictive substance Depressants: Down in the Valley Depressants: Down in the Valley Depressants A class of drugs that decrease the functioning of the central nervous system Depressants: Down in the Valley Alcohol The most commonly used & abused depressant 10 t0 20 million American suffer from alcoholism Impact of Alcoholism Health risks (liver, heart, brain, etc.) Loss of work time, loss of job, loss of economic stability MANY, MANY, MANY RISKS… Depressants: Down in the Valley Signs of Alcohol Abuse Range from… Binge drinking + drunkenness Guilt associated with drinking Drinking in the morning and/or drinking alone Drinking to recover from drinking Drinking enough to have blackouts or memory loss Lying about drinking Sensitivity to comments What constitutes “a drink?” (see handout) Depressants: Down in the Valley Barbiturates/Major Tranquilizers Drugs that depress the activity of the central nervous system, reducing anxiety but impairing memory and judgment Sedative effects Range from mild sedation or sleepiness to unconsciousness or coma Highly addictive; users rapidly develop a tolerance Examples Nembutal Seconal Depressants: Down in the Valley Benzodiazepines/Minor Tranquilizers Drugs that lower anxiety and reduce stress Considered safer than Barbiturates; prescribed much more often Examples Valium Xanax Librium Minor tranquilizers can STILL be very addictive & dangerous Depressants: Down in the Valley Opiates (Narcotics) Opium and its derivatives (morphine and heroin); depress neural activity, temporarily lessening pain and anxiety Bind to & stimulate receptor sites for endorphins; when brain is repeatedly flooded with an artificial opiate, it eventually stops producing its own Highly addictive & associated with severe withdrawal Treatment options? • Methadone… Stimulants: Up, Up & Away Stimulants: Up, Up & Away Stimulants A class of drugs that cause either the sympathetic division or the central nervous system (or both) to increase levels of functioning, at least temporarily Excite neural activity & speed body functions “Uppers” Stimulants: Up, Up & Away Amphetamines Stimulates neural activity, causing accelerated body functions, as well as energy & mood changes Synthesized in laboratories DO NOT provide extra energy; simply cause people to burn energy reserves; leads to an inevitable crash Methamphetamine Related compound; sometimes prescribed to treat ADHD, obesity and narcolepsy DANGER: “Crystal Meth” Stimulants: Up, Up & Away Cocaine A natural drug that induces euphoria, energy, power & pleasure followed by a crash Leads to agitated depression; the “high” depletes the brain’s supply of dopamine, serotonin & norepinephrine Highly addictive Three basic signs of physical dependency • Compulsive use • Loss of control • Disregard for consequences Stimulants: Up, Up & Away Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) Also known as Ecstasy Stimulant (and mild hallucinogen) Produces euphoric high Can damage serotoninproducing neurons, which results in a permanent deflation of mood and impairment of memory Known as the “Club Drug” Stimulants: Up, Up & Away Caffeine Naturally occurring in coffee beans, tea leaves, cocoa nuts & at least 60 other types of plants Mild stimulant; increases heart and breathing rates Found in coffee, tea, most sodas, chocolate & many over-the-counter drugs Stimulants: Up, Up & Away Nicotine Relatively mild, though toxic stimulant; produces a slight “rush” or sense of arousal; raises blood pressure & accelerates heart rate; also stimulates the release of adrenalin Nearly 438,000 Americans die from nicotine-related illnesses each year According to the CDC (2002), that’s more people than those who die from accidents, alcohol, cocaine, heroin and other drug abuse, AIDS, suicide and homicide COMBINED Rates of usage? Addictive power? Hallucinogens: Higher & Higher Hallucinogens: Higher & Higher Hallucinogens A class of drugs that cause false sensory messages (hallucinations), altering the perception of reality Example In some cases sensations can cross over each other (e.g. colors have sound, sounds have smells, etc.) Hallucinogens: Higher & Higher Lysergic Acid Diethylamide (LSD) A synthetic hallucinogen; extremely potent Synthesized from a grain (rye) fungus called ergot Takes people out of the real world & puts them into a world of the brain’s creation; NOT ALWAYS A PLEASANT PLACE! Phencyclidine (PCP) A synthetic drug so dangerous that it became useful only as an animal tranquilizer ***Depending on its dosage, can be a hallucinogen, stimulant, depressant or analgesic drug Hallucinogens: Higher & Higher Marijuana (Cannibas Sativa) Mild hallucinogen derived from the leaves and flowers of a particular type of hemp plant Best known and most commonly abused hallucinogen Effects relatively mild compared to others • Mild euphoria and relaxation • Altered time sense • Mild visual distortions Associated with high levels of psychological dependency & low (no) levels of physical dependency Mouse Party http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/ad diction/mouse/