* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Allies Turn the Tide
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Mediterranean and Middle East theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Invasion of Normandy wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
United States Navy in World War II wikipedia , lookup
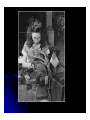
The Allies Turn the Tide World History The Allies Commit to Total War The United States had just been attacked at Pearl Harbor and is now at war with Germany, Italy, and Japan. Total war means all of a nation’s resources are used to fight a war. Factories were ordered to convert to war materials and rationing programs were started. Women help to lead war production at home. People are encouraged to consume less, donate what they can, and grow their own food. Japanese Internment in the United States In the United States, many Americans with Japanese Heritage were sent to internment camps within the country. They lost their jobs, property, and civil rights. The United States believed that these people were security threats. The War Turns in Favor of the Allies 1942 - 1943 marked the turning point of the war. The Japanese Navy was defeated at the Battle of Coral Sea and the Battle of Midway. Both were conducted mainly by planes from carriers. At the Battle of Midway, the Japanese lost four aircraft carriers. They would not be able to go on the offensive again in the war. These two battles were the beginning of the end for the Japanese Navy, although they would continue to fight for over three more years. The Allies win in North Africa The German Army in North Africa surrenders in 1943. This allowed the Allies to move into Italy. The Italian people overthrow Mussolini but Hitler sends troops to fight for Italy. The Battle of Stalingrad, 1942 The German Army had stalled in Russia. It was unable to take Leningrad so Hitler changed direction and tried to attack Stalingrad. He failed after almost a year. From then on, the Red Army was chasing the Germans out of Russia. Stalingrad was one of the bloodiest battles of the war. Everyone suffered, fighting was fierce. The Battle of Stalingrad "My hands are done for, and have been ever since the beginning of December. The little finger of my left hand is missing and - what's even worse - the three middle fingers of my right one are frozen. I can only hold my mug with my thumb and little finger. I'm pretty helpless; only when a man has lost any fingers does he see how much he needs then for the smallest jobs. The best thing I can do with the little finger is to shoot with it. My hands are finished." Anonymous German soldier "I was horrified when I saw the map. We're quite alone, without any help from outside. Hitler has left us in the lurch. Whether this letter gets away depends on whether we still hold the airfield. We are lying in the north of the city. The men in my unit already suspect the truth, but they aren't so exactly informed as I am. No, we are not going to be captured. When Stalingrad falls you will hear and read about it. Then you will know that I shall not return." Anonymous German soldier The Allied Air Offensive Throughout 1944, the Allies conducted huge bombing raids over Germany and occupied Europe. They targeted factories and infrastructure as well as Axis troops. Allied Bombing Allied Bombing would have a tremendous effect. In 1944, 10 days of bombing killed at least 40,000 civilians and left a million homeless. In 1945, Dresden was firebombed and over 100,000 people were killed. D-Day: June 6, 1944 The Allies Open a New Front Under Dwight Eisenhower, the Allies attack Southern France on D-Day. The Allies open a new front and continue to move closer and closer to Germany. The Big Three Meet at Yalta Stalin, Churchill, and Roosevelt meet in 1945 to decide what will happen after the war. They agree that Germany will temporarily be divided into four zones, controlled by the US, the USSR, England, and France.