* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Guide Exam 3
Survey
Document related concepts
History of anatomy wikipedia , lookup
Remember versus know judgements wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Living things in culture wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
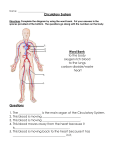
Biology 3A Professor Garrison STUDY GUIDE FOR EXAM 3 Be able to explain the key concepts at the end of the chapters, as well as answer the test our knowledge questions. Know the information described below, and the terminology associated with each of these learning objectives. Use of the term “understand” means to understand, be able to define and be able to explain the structure, process, etc. 1. Understand open and closed circulatory systems. Know which phyla have each type, as well as which phyla have no circulatory system and why they don’t need a circulatory system. Know what hemolymph is in those phyla with open circulatory systems. 2. Understand the vertebrate circulatory system with emphasis on the mammalian (human) system, including purpose and function of the various organs and structures. Understand and be able to explain the various components of the blood, and the function of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. Know the structure and function of arteries, capillaries and veins. Know the structure and function of the heart. Be able to name the various chambers, valves, vessels, etc. Be able to explain what makes the heart contract, and the role played by the heart valves in the process. Know the position and function of the SA and AV nodes. 3. Be able to explain the pathway of blood as it flows into the mammalian heart, goes to the lungs, returns to the heart and then goes out to the tissues of the body. Be able to name the structures/organs through which the blood flows, including heart chambers, valves and vessels. Be sure you can explain if these structures are on the right or left side of the heart. 4. Understand and be able to explain the mammalian lymphatic system, including purpose, function and all the organs involved in the system. Know what lymphatic vessels (lymphatic capillaries) and nodes are. Understand and be able to explain with what other organ systems the lymphatic system is closely involved. 5. Understand the diversity and polyphyletic grouping of the “kingdom” Protista. Know the general traits found in the different groups of this kingdom. Know the names of the five supergroups in the kingdom. Know the phyla of the protists studied in lab, and the characteristics of each phylum. Be able to identify members of each phylum, and typical structures found in each, along with the function of those structures. Know the habitats/life styles of various protists, and which are toxic, show bioluminescence, etc. 6. Know the various methods of feeding found within each group of protists. Understand what flagella, cilia and pseudopods are, how they function, and which groups of protists use them. Know which protists have contractile vacuoles, chloroplasts, etc. Know the location, structure and function of organelles or structures we studied in each group of protists. 7. Know the reproductive methods of the groups in which we studied those details. 8. Know the scientific names and any unique structures found in the protists which cause amoebic dysentery, sleeping sickness and malaria. Know the life cycle of Plasmodium sp. 9. Know the specific names of the protist examples studied in lab, which phylum each belongs to, and the characteristics of each. 10. Understand and be able to explain primary and secondary endosymbiosis. 11. Know the traits of organisms belonging to the kingdom Plantae. Know the evolutionary history of this kingdom, including ancestry, and evidence for it. Know the hurdles for aquatic protists moving onto land. Know and understand the adaptations that allowed plants to succeed on land, and why these adaptations were successful. Know the classification and the traits of the various phyla and classes of non-vascular, vascular seedless and vascular seed plants. Understand the advancement of adaptations as you move through these phyla. Know what type of environment each lives in. 12. Understand the difference between homospory and heterospory, and which plants show each of these. Understand the development and function of the following in heterosporous plants: microspores, male gametophyte, pollen, sperm, megaspores, female gameteophyte, ovule, egg 13. Understand and be able to explain the generalized life cycle of plants, as well as the specific life cycle of each plant group. Know the names of each mature reproducing generation, as well as the intermediate stages, and how they reproduce. Know which stages are haploid and which are diploid. Know which stages undergo mitosis and which undergo meiosis. 14. Understand where in the plant life cycle spores develop, what structures spores develop in, and how they develop. Understand the same info for gametes. Be able to identify this information for each group of plants. 15. Understand the significance of seeds, seed anatomy, seed dispersal and the variety of methods used to accomplish dispersal. 16. Understand the significance of pollination and the variety of methods used to accomplish this. Understand the coevolution of flowering plants and their pollinators. 17. Know the anatomy and all the plant terminology used in your lab manual and lab atlas. 18. Know the basic structure and function of plant tissue types. Be sure to know the names, characteristics and functions of the two types of vascular tissues. Know what type of cells is in each tissue type. Know where they are located in the plant. Know what transpiration is. Understand and be able to explain the processes involved in movement of water up from the roots of a plant. Understand and be able to explain the processes involved in movement of photosynthetic products down from the leaves to non-photosynthetic parts of a plant (translocation). 19. Know the various reproductive structure of plants, the anatomy of these structures, which are male and female, what develops inside of them. 20. Understand how plants grow. What tissues are involved in primary and secondary plant growth, where in the plant these tissues occur, and how the growth occurs. Know how tree rings form, and what info this can give biologists. 21. Know what a horomone is. Understand and be able to explain the functions of plant hormones: auxins, gibberellins, ethylene, phytochrome. 22. Understand and be able to explain the processes involved in phototropism, gravitropism and photoperiodism. 23. Know which groups have motile sperm that swim to the egg, and which use pollination. Understand and be able to explain what pollination is and its role in reproduction. 24. Know the names and characteristics of each class of flowering plants. Be able to recognize what class a plant belongs to by reading a physical description of the plant or plant organ, or by looking at the plant or plant organ. 25. Be able to identify everything you looked at in lab, using scientific names if they were given to you. Understand all the questions asked in the lab manual, and know all the terms listed in the lab manual, as well as those given to you by Professor Garrison or the TA.