* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ExamView - SOL Review Life at the Systems and
Survey
Document related concepts
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cambrian explosion wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Taxonomy (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Cancer stem cell wikipedia , lookup
History of biology wikipedia , lookup
Incomplete Nature wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
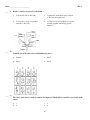
Name: ________________________ Class: ___________________ Date: __________ SOL Review Life at the Systems and Organisms Level Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. The information in the table supports which conclusion? a. Frogs are more closely related to c. Sea anemones are more complex than monkeys than to sea anemones. frogs or monkeys. b. ____ Frogs, monkeys, and sea anemones d. are classified into different kingdoms. Sea anemones and monkeys are adapted to similar environments. 2. A student looking through a light microscope saw this cell in cytokinesis. This cell is most likely from — a. a plant c. an animal b. a virus d. a bacterium 1 ID: A Name: ________________________ ____ ID: A 3. A geneticist studying fruit flies hypothesizes that short wings are a recessive trait coded for by a single gene. Which observation is most likely to have led her to form this hypothesis? ____ ____ a. Flies have wing lengths ranging from very long to very short. b. Flies with long wings are less likely to d. survive. c. Flies with long wings can produce offspring with short wings. Flies with short wings prefer to mate with flies with long wings. 4. What do phototropism and geotropism enable plants to do? a. Grow toward needed resources c. Defend themselves against herbivores b. Prevent invasion by insect colonies d. Develop pesticide resistance by exchanging DNA 5. A population of mice is evenly divided into two groups, and each group is placed on an isolated island with no existing mouse population. Which statement best explains the difference in the mouse populations on Island A and Island B at the end of the 20 years? a. On Island A, the allele for gray fur was dominant, while on Island B, the allele for brown fur was dominant. c. Conditions on Island B favored the brown-furred individuals, while both fur colors were evenly advantaged on Island A. b. More brown mice were in the half of the original population that was sent to Island B than in the group sent to Island A. d. The recapturing of mice on Island A and Island B was done differently. 2 Name: ________________________ ____ ____ ID: A 6. Fungi obtain nutrients by — a. photosynthesis c. absorption b. chemosynthesis d. ingestion 7. A student observed different types of plants and recorded the data shown. Based on the drawings and information in the chart, these plants are most likely — ____ a. gymnosperms c. mosses b. angiosperms d. ferns 8. Many Northern Hemisphere birds respond to seasonal environmental changes by — ____ a. hibernating c. migrating b. mutating d. estivating 9. A student observes that a type of eubacteria contains chlorophyll. Which of these does this type of bacteria have in common with plants? a. It is photosynthetic. c. It contains mitochondria. b. It contains vascular tissues. d. It is heterotrophic. 3 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 10. Students research unicellular, prokaryotic organisms that live in harsh environments such as volcanic hot springs, brine pools, and anaerobic black organic mud. Which of these groups are the students most likely researching? a. Protista c. Eubacteria b. Archaebacteria d. Plantae ____ 11. An early biological theory stated that a change in a population can occur when organisms with favorable variations for a particular environment survive and pass these variations on to the next generation. This theory is better known as the Theory of — a. Natural Selection c. Variation and Adaptation b. Punctuated Selection d. Acquired Characteristics ____ 12. What ratio of the offspring from the cross shown will be homozygous recessive for the trait of tallness? a. 0 in 4 c. 2 in 4 b. 1 in 4 d. 4 in 4 4 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 13. Based on this classification scheme, the European otter and the leopard are in the same — a. kingdom but in different orders c. order but in different families b. genus but in different species d. family but in different genera ____ 14. Which of these best describes an organism’s ability to maintain the constant internal conditions necessary for life? a. Homeostasis c. Reproduction b. Stability d. Adaptation ____ 15. As the seasons change from summer to fall, there are fewer hours of daylight. Which is a typical response of a dogwood tree to this change? a. Producing flowers c. Dropping its leaves b. Increasing its growth rate d. Shedding bark ____ 16. Fungi, such as mushrooms and molds, get their nutrition primarily by — a. producing food by chemosynthesis c. preying on other organisms b. decomposing dead organic matter d. parasitic relationships with plants 5 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 17. The oxygen content in the atmosphere of the early Earth is thought to have increased significantly once which of these developed? a. Amino acids c. Photosynthetic bacteria b. Archaebacteria d. Mitochondria ____ 18. Some fish travel from saltwater to freshwater or from freshwater to saltwater but still maintain the concentration of salt in their cells. This is an example of — a. mutation c. homeostasis b. positive feedback d. cellular injury ____ 19. This dichotomous key can be used to distinguish white wildflowers found in Virginia. According to this key, what type of flower is shown? a. Trientalis borealis c. Fragaria virginiana b. Stellaria media d. Gillenia trifoliata 6 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 20. Organisms from which kingdom are most likely to chemically digest their food outside their bodies? a. Fungus c. Protist b. Animal d. Plant ____ 21. Some snake embryos have small buds resembling limbs. These buds disappear at later stages of embryo development. These findings suggest that these snakes — a. had a parent with limbs c. will have offspring with limbs b. have functional limbs as adults d. evolved from an ancestor that had limbs ____ 22. The main reason that eating salty foods makes a person thirsty is that additional fluid is needed to — a. increase the salinity of the blood c. maintain the fluid balance in the cells b. dissolve salt crystals in the stomach d. prevent damage to the lining of the throat ____ 23. In a plant that has red flowers, red flower color, R, is completely dominant to white flower color, r. If the plant is heterozygous for flower color, which alleles will be carried by the gametes it produces? a. R and r c. r only b. R only d. Rr only 7 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 24. Charles Darwin proposed his theory of evolution based on observations of nature. Which observation that contributed to his theory is illustrated by this population of beetles? a. Environmental resources are limited. c. Individuals within a population may vary widely. b. Populations remain stable over time. d. Species produce more offspring than can survive. ____ 25. Which of these species is most closely related to Felis rufus? a. Acer rubrum c. Felis concolor b. Selasphorus rufus d. Canis rufus ____ 26. Timothy has attached earlobes like his maternal grandfather. His mother and father both have free earlobes, which are dominant. Which statement best explains how Timothy inherited attached earlobes? a. He received a recessive allele from each parent. c. He received a recessive allele from his mother and a dominant allele from his father. b. He received a dominant allele from each parent. d. He received a dominant allele from his mother and a recessive allele from his father. 8 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 27. Which of these animals has the same type of symmetry as a vertebrate? a. b. c. d. ____ 28. Gymnosperms (a group of plants including conifers) and angiosperms (flowering plants) share many traits but are classified in separate groups. Which is a difference between gymnosperms and angiosperms? a. Only angiosperms form wood. c. Only angiosperms produce seeds within fruits. b. Only gymnosperms reproduce with spores. d. Only gymnosperms have vascular tissue. ____ 29. In conditions of stress or fear, the human adrenal gland may produce adrenaline. Which of the following is an effect adrenaline can have on the body? a. Increased blood pressure c. Increased production of red blood cells b. Decreased rate of breathing d. Decreased heart rate 9 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 30. Two plants are crossed, and the traits of height and color are assessed in the offspring. The following cross was conducted: TTPP x ttpp. Which of the following choices correctly describes the offspring? a. Three-quarters of the plants are tall and purple. c. All are short and white. b. Three-quarters of the plants are short and white. d. All are tall and purple. ____ 31. In squash plants, yellow fruit (Y) is dominant to white fruit (y). If two plants heterozygous for yellow fruit are crossed, what are the possible genotypes of the offspring? a. Yy only c. Yy, yy only b. YY, yy only d. YY, Yy, yy only ____ 32. Which type of animal is most closely related to a mammal, based on heart structure? a. Fish c. Turtle b. Bird d. Frog 10 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 33. Ascidians are sac-like marine organisms. Their larvae have well-developed brains and dorsal nerve cords. This suggests that ascidians should be classified with the — a. chordates c. cnidarians b. annelids d. sponges ____ 34. Scientists hypothesize that oxygen began to accumulate in Earth’s atmosphere after the appearance of living things with the ability to — a. form tissues c. photosynthesize b. reproduce sexually d. breathe air ____ 35. Which of these organisms contains no specialized cells? a. Paramecium c. Jellyfish b. Sponge d. Sea anemone ____ 36. A mushroom and a humpback whale are alike because both are — a. motile c. prokaryotic b. heterotrophic d. unicellular ____ 37. Bivalves, such as clams, are found in salt water. The clam captures food particles from water that flows over its gills. Which of these is the best classification of the clam? a. A filter feeder c. A chunk feeder b. A grazer d. A decomposer ____ 38. If transpiration stopped completely, how would a plant’s homeostasis first be affected? a. More carbon dioxide molecules would be c. taken in by leaves. Carbohydrates would no longer be formed. b. Fewer sugars stored in roots and stems would diffuse into the soil. Water molecules would not be released from leaves. d. 11 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 39. Cells from which of the following organisms would be expected to contain cell walls? a. Sponge c. Water lily b. Cricket d. Paramecium ____ 40. What characteristic do all living things share? a. They contain DNA. c. They reproduce by mitosis. b. They are made up of many parts. d. They need oxygen to survive. ____ 41. Albino individuals lack all pigmentation so that their hair and skin are white. This family tree shows that albinism — a. is carried only by females in this family c. is a sex-linked gene b. is a recessive genetic trait d. requires both parents to be albinos ____ 42. In the human body, muscle cells have an increased need for energy during exercise. To help supply this energy, the body will immediately increase — a. food intake to increase the substances available for respiration c. activity in the nervous system to stimulate intake of carbon dioxide b. the need for waste products to be retained d. the breathing rate to supply more oxygen to cells for the release of energy 12 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 43. In snapdragons, the combined expression of both alleles for flower color produces a new phenotype that is pink. This illustrates incomplete dominance. The Punnett square above shows that both the white and red snapdragons are homozygous. Which of the following would be the correct product from a cross between two heterozygous pink snapdragons? a. 2 red, 1 pink, 1 white c. 1 red, 1 pink, 2 white b. 1 red, 2 pink, 1 white d. 2 red, 2 white ____ 44. Escherichia coli is the scientific name of a bacterium. What category of classification is Escherichia? a. Order c. Phylum b. Genus d. Species ____ 45. Over many generations, unrelated or distantly related species may come to resemble each other due to — a. similar environmental factors c. homologous structural adaptations b. similar genetic mutations d. competition with each other ____ 46. Algae and multicellular plants are autotrophs because they — a. decompose dead organisms c. break down starches to glucose b. absorb nutrients from soil d. capture sunlight to produce sugars ____ 47. Some unicellular organisms are motile (have the ability to move) and some are nonmotile. Which cellular structures are associated with movement? a. Ribosomes c. Chloroplasts b. Flagella d. Vacuoles 13 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 48. According to the table, as vertebrate embryos develop — a. amphibians and humans develop the same structures c. reptiles and amphibians grow external ears b. only mammals develop both limbs and external ears d. limbs and external ears grow on mammals and birds ____ 49. Bones do all of the following EXCEPT — a. make nerve cells c. protect organs b. make blood cells d. store calcium ____ 50. A biologist has just discovered a new life form. The newly described organism is multicellular, does not carry on photosynthesis, and absorbs nutrients from the environment. It is composed of eukaryotic cells with cell walls. In which kingdom would the organism be classified? a. Plant c. Bacteria b. Animal d. Fungi ____ 51. Biochemical substances in the human body are maintained at about a neutral pH except for the — a. blood c. internal material of living cells b. stomach fluids d. lymph ____ 52. When there is a lower concentration of water outside of a plant cell rather than inside a plant cell, the plant will tend to — a. grow toward the sun c. gain water and become rigid b. lose water and wilt d. increase its rate of photosynthesis 14 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 53. These data were collected by observing responses of different organisms to light. Which conclusion is supported by these data? a. Organisms that use photosynthesis are attracted to light. c. Animals are attracted to light. b. Protists are not attracted to light. d. Decomposers are attracted to light. ____ 54. Which of the following is the best evidence that this bird is nocturnal? a. The shape of its beak c. The thickness of its feathers b. The size of its eyes d. The length of its talons 15 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 55. This key can be used to distinguish four species of frogs found in ponds in eastern Virginia. To which species does the frog shown belong? a. Rana sphenocephala c. Rana catesbeiana b. Rana clamitans d. Rana virgatipes ____ 56. Unlike plants, fungi cannot make their own food because they do not have — a. roots c. spores b. hyphae d. chlorophyll 16 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 57. This key can be used to identify the species of some wildflowers found in Virginia. All of the plants have blue or purple flowers with five petals that are fused together. According to this key, to what species does the plant shown belong? a. Viper’s bugloss (Echium vulgare) c. Gray beardtongue (Penstemon canescens) b. Virginia bluebell (Mertensia virginica) d. Lyre-leaved sage (Salvia lyrata) ____ 58. In order to maintain homeostasis, it is most important for an animal to be able to — a. respond to its environment c. change its habitat b. hide from its predators d. increase its prey population 17 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 59. Which skull belongs to a herbivore? a. b. c. d. ____ 60. What is the body’s first line of defense against disease? a. Enzymes c. Antibodies b. Blood d. Skin ____ 61. Which of these is a common adaptation for mammals in an aquatic environment? a. Keen eyesight c. Sharp teeth b. Streamlined body d. Long fur ____ 62. Based on the method by which they get food, organisms are classified as autotrophs or heterotrophs. Which organism listed below is correctly paired with its metabolism? a. Mushroom-autotroph c. Grass-heterotroph b. Human-heterotroph d. Fish-autotroph 18 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 63. In plants, gymnosperms have cones and angiosperms have flowers. Both of these plant structures are specialized for — a. sexual reproduction c. water absorption b. food production d. photosynthesis ____ 64. Cowbirds often lay eggs in the nests of other songbirds. The young cowbirds grow up hearing the songs of their foster parents but sing cowbird songs when they are adults. This is an example of — a. imprinting c. mimicry b. instinct d. camouflage ____ 65. According to the biological definition of a species, which organisms listed below would belong to the same species? a. Plants that have flowers with the same structures that attract the same pollinators c. Animals that can breed and produce fertile offspring b. Protists that are the same shape and have the same structures for movement d. Mushrooms that are the same color and can grow on trees ____ 66. What conclusion can be drawn from the genetic information above? a. The white parent carried a dominant allele. c. All the white rabbits are heterozygous. b. All the F1 rabbits carried a recessive allele. d. All the black rabbits in the F2 generation are homozygous. ____ 67. A genetic pedigree showing that only males are affected by a certain disorder is evidence of what type of inheritance? a. Dominant c. Recessive b. Sex-linked d. Passive 19 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 68. Early classification systems consisted of two kingdoms; Plantae and Animalia. What scientific development allowed taxonomists to establish the Monera and Protista kingdoms? a. Discovery of DNA c. Invention of the electron microscope b. Creation of electrophoresis d. Development of Koch’s postulates ____ 69. Which characteristic supports the hypothesis that this animal spends a great deal of time burrowing through the soil? a. The shape of its body c. The length of its tail b. The position of its nose d. The size of its claws 20 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 70. The skulls below belong to different animals. Which skull belongs to the animal that is probably unrelated to the other three? a. b. c. d. ____ 71. Unlike other animals, mammals can perspire. The main benefit of perspiring is that it— a. removes extra water from the cells c. removes dirt from the surface of the skin b. cools the skin with evaporation d. relaxes the muscles 21 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 72. In corn plants, green (G) is dominant to albino (g). According to the Punnett square, what is the chance of this heterozygous cross producing albino corn plants? a. One in four c. Three in four b. Two in four d. Four in four ____ 73. Which is not a major muscle in the human body? a. Biceps c. Pectoralis major b. Deltoid d. Sternum ____ 74. Which area of the leaf is most responsible for protecting the leaf from the drying effects of the air? a. The epidermis c. The vein b. The mesophyll d. The cuticle ____ 75. What structure is common to all five kingdoms of living organisms? a. DNA c. Cell wall b. Nucleus d. Mitochondria 22 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 76. The picture shows an organism that lives in the lakes of two caves in Augusta County, Virginia. Its primary food source appears to be fine bits of organic matter that drift into the cave lakes. This cave-dwelling species belongs to the kingdom — a. Monera c. Fungi b. Protista d. Animalia ____ 77. As a result of the above experiment, responses of a planarian to different environmental stimuli were recorded. Planaria seem to have the strongest response to — a. light c. magnetism b. sound d. gravity 23 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 78. Which of these is most closely related to the oak weevil? a. b. c. d. ____ 79. Lamarck was an early scientist who studied the development of characteristics in organisms over time. Which of the following choices best describes his views on how organisms change over time? a. Theory of acquired characteristics c. Theory of artificial selection b. Law of independent assortment d. Theory of relative fossil-dating ____ 80. Which is required by all living things? a. Energy c. Oxygen b. Mobility d. Carbon dioxide 24 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 81. Blood is considered a tissue because blood — a. flows inside arteries and veins c. is pumped from the heart and is carried to the cells through arteries b. is necessary to carry oxygen and nutrients to the cells d. is composed of red and white blood cells working together and having specific functions ____ 82. In which part of the flower does fertilization take place? a. Stamen c. Petal b. Pistil d. Sepal ____ 83. The above chart shows vertebrate embryo development. Which of these would be least related to the others? a. b. 1 2 c. d. 25 3 4 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 84. Which of these is a mammal native to Virginia? a. Armadillo c. Kangaroo b. Camel d. Squirrel ____ 85. Which animal develops in a cycle most similar to the one shown above? a. A bird c. A hydra b. A moth d. A grasshopper ____ 86. The cucumber belongs to the Cucurbitacae family and is recognized by its long, trailing vines with fuzzy, three- to five-pointed leaves and long, spiny fruit. Using the characteristics in the chart above, which plant is most closely related to the cucumber? a. Eggplant c. Pepper b. Pumpkin d. Okra 26 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 87. Which of these does not depend on muscle contraction? a. Eye movement c. Reflexes b. Arm movement d. Pain perception ____ 88. In rabbits, short fur (F) is dominant to long fur (f). According to the Punnett square, what is the chance of two heterozygous short-haired rabbits having offspring with short fur? a. One in four c. Three in four b. Two in four d. Four in four ____ 89. This organism is most closely related to animals in the Phylum Arthropoda, the phylum that contains beetles, because it has — a. legs c. jointed appendages b. antennae d. an elongated body 27 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 90. A student was studying the responses of cells to solutions of varying salt concentrations. Which solution below would cause no change in cell size? a. b. c. d. ____ 91. The concentration of glucose must be maintained within a fairly narrow range in most vertebrates. This statement is an example of — a. homeostasis c. glycolysis b. excretion d. fermentation 28 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 92. Which of these processes is carried out in the same way in both plants and animals? a. Cellular respiration c. Circulation of body fluids b. Asexual reproduction d. Excretion of metabolic waste ____ 93. Bacteria are tremendously successful unicellular organisms, yet all large organisms are multicellular. Unicellular organisms cannot grow very large because the — a. energy expenditures would be too great c. diffusion of nutrients into the cell’s interior would be too slow b. locomotion of the organisms would be too slow d. respiratory rate would be too high ____ 94. During a trip to a rain forest, a scientist discovered a new organism living near some rotting logs. The scientist observed that the organism had moist skin, no hair, and an internal skeleton and that it laid its eggs under the logs. This organism was probably a new species of — a. invertebrate c. mammal b. amphibian d. reptile ____ 95. Human red blood cells that lack sufficient hemoglobin would have a low amount of what substance? a. Hydrogen c. Calcium b. Nitrogen d. Oxygen ____ 96. Tuberculosis is caused by a bacterium, Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Many years ago, streptomycin easily controlled the bacterium. Now streptomycin is much less effective against the resistant M. tuberculosis. The increasing resistance of M. tuberculosis to streptomycin is most likely due to the increased — a. use of streptomycin for bacterial infections c. artificial production of streptomycin b. numbers of alternatives to streptomycin d. early detection of bacterial infections 29 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 97. Which characteristic supports the hypothesis that this bird spends a great deal of time in the trees and shrubs? a. The thickness of its bill c. The shape of its feet b. The crest of feathers on its head d. The color of its wings ____ 98. According to this key, to what family does the insect above belong? a. Dytiscidae c. Gyrnidae b. Haliplidae d. Noteridae 30 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 99. According to the graph, the highest metabolic rate is found in — a. amphibians c. birds b. reptiles d. mammals ____ 100. A student wrote this description of a cell after looking at it under a microscope. Which type of cell was the student most likely describing? a. Animal cell c. Bacterium cell b. Fungus cell d. Plant cell 31 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 101. A biology student collected pine needles from four different species of trees. She then made diagrams showing the number and actual length of needles in a bundle and the common and scientific name of each species. Use her diagram above to help you answer the following question. These four different pine trees are not classified in the same — a. order c. genus b. species d. phylum ____ 102. The body of which of these organisms has the least specialized organization? a. Jellyfish c. Starfish b. Sea urchin d. Sponge 32 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 103. In 1910, Thomas Morgan discovered traits linked to sex chromosomes in the fruit fly. The Punnett square above shows the cross between red-eyed females and white-eyed males. Fruit flies usually have red eyes. If a female and male offspring from the cross shown above are allowed to mate, what would the offspring probably look like? a. 2 red-eyed females; 2 white-eyed males c. 1 red-eyed female and 1 white-eyed female; 2 red-eyed males b. 2 red-eyed females; 1 red-eyed male, 1 white-eyed male d. 2 white-eyed females; 1 white-eyed male and 1 red-eyed male ____ 104. A chart of human chromosome pairs is called a karyotype. What information is revealed in the karyotype above? a. The sex c. Trisomy b. The age d. Gene dominance ____ 105. A microorganism which releases water into its environment to regulate its salinity during osmosis is undergoing a process that is similar to a human being who releases moisture on a hot day. This process that helps keep both the microorganism and the human body fluids in balance is known as — a. homeostasis c. heredity b. cell division d. mutation 33 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 106. A flower with this shape would use what type of pollinator? a. Wind c. Rain b. Mammal d. Hummingbird ____ 107. In pea plants, tall plants are dominant to short plants. If two heterozygous tall plants are crossed, what percent of the offspring will probably be short? a. 75% c. 25% b. 50% d. 0% 34 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 108. All the organisms shown above belong to the Phylum Chordata. The structural similarity in the organisms suggests that — a. the humerus is attached to the skeleton by immovable joints c. the humerus is the same size in all chordates b. only animals that walk on 4 legs need the humerus d. chordates have common ancestors ____ 109. What is the major function of the valves found in human veins? a. Preventing movement of blood clots c. Adding oxygen to blood plasma b. Reducing the back flow of blood d. Slowing the red blood cells ____ 110. Cleaner fish feed off the algae, fungi, and other microorganisms that are found on larger fish. Other species of fish, which look like the cleaners, are able to approach the larger fish and remove large bites of flesh. If the look-alike populations outnumber the cleaner fish, the — a. microorganisms on large fish would decrease c. behavior of large fish would change b. cleaner populations would increase d. cleaners and mimics would interbreed 35 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 111. Which of these is capable of moving quickly in response to its environment? a. b. c. d. ____ 112. The respiration system of frogs differs from mammals because frogs — a. have lungs at hatching and develop gills for life in the water c. have gills throughout their life cycle b. hatch with gills and develop lungs as they mature d. breathe only through their skin 36 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 113. This experiment was performed in the mid-1600s by Francesco Redi. He used it to show that organisms — a. can spontaneously generate c. come from preexisting organisms b. need air to live d. require food to survive ____ 114. The picture shows a section of a woody stem. In what area does the growth of this stem occur? a. Woody layers c. Cambium b. Pith d. Outer bark 37 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 115. The pictures below show the cross section of the intestines of different animals. Which intestine can absorb the least amount of food per centimeter of length of the intestine? a. b. c. d. ____ 116. Amoeba is to pseudopod as paramecium is to — a. vacuole c. oral groove b. cilium d. lysosome 38 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 117. The picture shows a fern that is sometimes used in an aquarium or outdoor pool to provide shade and a spawning medium for fish. To which kingdom does Azolla caroliniana belong? a. Monera c. Fungi b. Protista d. Plantae ____ 118. Which part of this life cycle is most like the reproductive process in animals? a. b. A B c. d. C D ____ 119. Which part of human blood is required for carrying oxygen from the lungs to body cells? a. Plasma c. Red blood corpuscles b. Platelets d. White blood cells 39 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 120. The female in the second generation must be — a. normal because her daughter is normal c. colorblind because her mother was a carrier b. normal because the majority of her children are normal d. a carrier because one of her sons is colorblind ____ 121. In holly trees, red fruit (A) are dominant to white fruit (a), and spiny leaves (L) are dominant to smooth leaves (l). According to this Punnett square, how many of the new holly trees from this cross could have white fruit and smooth leaves? a. None c. 9 out of 16 b. 1 out of 16 d. All ____ 122. In turkeys, the dominant gene B results in black pigment throughout the feathers. Most of the feathers of homozygous recessive individuals have light edges. Heterozygous individuals have a few feathers with light edges. If two turkeys with mostly light-edged feathers are crossed, how many chicks would probably have only the black-pigmented feathers? a. All c. About one half b. About one fourth d. None 40 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 123. An expert should have been called in to identify the bones. The fisherman probably found bones of a large — a. mollusk, like a giant squid c. fish, like a sea bass b. mammal, like a sea lion d. crustacean, like a king crab ____ 124. Snakes have a reputation for being slimy, while actually their skin is cool and dry. A class of vertebrates that does have moist, mucous-covered skin is — a. Aves c. Mammalia b. Amphibia d. Nematoda 41 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 125. This organism belongs to the same phylum as — a. b. c. d. 42 ID: A SOL Review Life at the Systems and Organisms Level Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. ANS: TOP: 2. ANS: TOP: 3. ANS: TOP: 4. ANS: TOP: 5. ANS: TOP: 6. ANS: TOP: 7. ANS: TOP: 8. ANS: TOP: 9. ANS: TOP: 10. ANS: TOP: 11. ANS: TOP: 12. ANS: TOP: 13. ANS: TOP: 14. ANS: TOP: 15. ANS: TOP: 16. ANS: TOP: 17. ANS: TOP: 18. ANS: TOP: 19. ANS: TOP: 20. ANS: TOP: A PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level A PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level C PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level A PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level C PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level C PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level C PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level A PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level A PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level A PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level C PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level A PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level C PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level C PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level C PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level A PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level A PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level 1 2008 STA: RC003 2008 STA: RC003 2008 STA: RC003 2008 STA: RC003 2008 STA: RC003 2008 STA: RC003 2008 STA: RC003 2008 STA: RC003 2008 STA: RC003 2008 STA: RC003 2008 STA: RC003 2008 STA: RC003 2008 STA: RC003 2008 STA: RC003 2007 STA: RC003 2007 STA: RC003 2007 STA: RC003 2007 STA: RC003 2007 STA: RC003 2007 STA: RC003 ID: A 21. ANS: TOP: 22. ANS: TOP: 23. ANS: TOP: 24. ANS: TOP: 25. ANS: TOP: 26. ANS: TOP: 27. ANS: TOP: 28. ANS: TOP: 29. ANS: TOP: 30. ANS: TOP: 31. ANS: TOP: 32. ANS: TOP: 33. ANS: TOP: 34. ANS: TOP: 35. ANS: TOP: 36. ANS: TOP: 37. ANS: TOP: 38. ANS: TOP: 39. ANS: TOP: 40. ANS: TOP: 41. ANS: TOP: 42. ANS: TOP: 43. ANS: TOP: D PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level C PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level A PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level C PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level C PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level A PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level C PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level A PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level D PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level D PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level A PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level C PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level A PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level A PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level D PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level C PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level A PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level D PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Molecular and Cellular Level 2 2007 STA: RC003 2007 STA: RC003 2007 STA: RC003 2007 STA: RC003 2007 STA: RC003 2007 STA: RC003 2007 STA: RC003 2007 STA: RC003 2006 STA: RC003 2006 STA: RC003 2006 STA: RC003 2006 STA: RC003 2006 STA: RC003 2006 STA: RC003 2006 STA: RC003 2006 STA: RC003 2006 STA: RC003 2006 STA: RC003 2006 STA: RC003 2006 STA: RC003 2006 STA: RC003 2006 STA: RC003 2005 STA: RC003 ID: A 44. ANS: TOP: 45. ANS: TOP: 46. ANS: TOP: 47. ANS: TOP: 48. ANS: TOP: 49. ANS: TOP: 50. ANS: TOP: 51. ANS: TOP: 52. ANS: TOP: 53. ANS: TOP: 54. ANS: TOP: 55. ANS: TOP: 56. ANS: TOP: 57. ANS: TOP: 58. ANS: TOP: 59. ANS: TOP: 60. ANS: TOP: 61. ANS: TOP: 62. ANS: TOP: 63. ANS: TOP: 64. ANS: TOP: 65. ANS: TOP: 66. ANS: TOP: B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Molecular and Cellular Level A PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Molecular and Cellular Level D PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Molecular and Cellular Level B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Molecular and Cellular Level B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Molecular and Cellular Level A PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Molecular and Cellular Level D PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Molecular and Cellular Level B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Molecular and Cellular Level B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Molecular and Cellular Level A PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Molecular and Cellular Level B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Molecular and Cellular Level A PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Molecular and Cellular Level D PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Molecular and Cellular Level B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level A PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level D PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level D PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level A PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level C PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level 3 2005 STA: RC003 2005 STA: RC003 2005 STA: RC003 2005 STA: RC003 2005 STA: RC003 2005 STA: RC003 2005 STA: RC003 2005 STA: RC003 2005 STA: RC003 2005 STA: RC003 2005 STA: RC003 2005 STA: RC003 2005 STA: RC003 2004 STA: RC003 2004 STA: RC003 2004 STA: RC003 2004 STA: RC003 2004 STA: RC003 2004 STA: RC003 2004 STA: RC003 2004 STA: RC003 2004 STA: RC003 2004 STA: RC003 ID: A 67. ANS: TOP: 68. ANS: TOP: 69. ANS: TOP: 70. ANS: TOP: 71. ANS: TOP: 72. ANS: TOP: 73. ANS: TOP: 74. ANS: TOP: 75. ANS: TOP: 76. ANS: TOP: 77. ANS: TOP: 78. ANS: TOP: 79. ANS: TOP: 80. ANS: TOP: 81. ANS: TOP: 82. ANS: TOP: 83. ANS: TOP: 84. ANS: TOP: 85. ANS: TOP: 86. ANS: TOP: 87. ANS: TOP: 88. ANS: TOP: 89. ANS: TOP: B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level C PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level D PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level D PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level A PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level D PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level D PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level A PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level D PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level A PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level A PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level A PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level D PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level A PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level D PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level D PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level C PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level C PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level 4 2004 STA: RC003 2004 STA: RC003 2004 STA: RC003 2004 STA: RC003 2003 2003 2003 2003 2003 2003 2003 2003 2003 2003 2003 2003 2003 2003 2002 2002 2002 2002 2002 ID: A 90. ANS: TOP: 91. ANS: TOP: 92. ANS: TOP: 93. ANS: TOP: 94. ANS: TOP: 95. ANS: TOP: 96. ANS: TOP: 97. ANS: TOP: 98. ANS: TOP: 99. ANS: TOP: 100. ANS: TOP: 101. ANS: TOP: 102. ANS: TOP: 103. ANS: TOP: 104. ANS: TOP: 105. ANS: TOP: 106. ANS: TOP: 107. ANS: TOP: 108. ANS: TOP: 109. ANS: TOP: 110. ANS: TOP: 111. ANS: TOP: 112. ANS: TOP: B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level A PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level A PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level C PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level D PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level A PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level C PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level D PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level C PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level D PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level D PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level A PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level A PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level D PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level C PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level D PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level C PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level D PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level 5 2002 2002 2002 2002 2002 2002 2002 2002 2002 2001 2001 2001 2001 2001 2001 2001 2001 2001 2001 2001 2001 2001 2001 ID: A 113. ANS: TOP: 114. ANS: TOP: 115. ANS: TOP: 116. ANS: TOP: 117. ANS: TOP: 118. ANS: TOP: 119. ANS: TOP: 120. ANS: TOP: 121. ANS: TOP: 122. ANS: TOP: 123. ANS: TOP: 124. ANS: TOP: 125. ANS: TOP: C PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level C PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level D PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level C PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level C PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level D PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level D PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level B PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level A PTS: 1 REF: Life at the Systems and Organisms Level 6 2000 2000 2000 2000 2000 2000 2000 2000 2000 2000 2000 2000 2000