* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download coronary arteries
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Drug-eluting stent wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
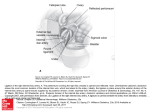
The Cardiovascular System: The Heart & Blood Vessels 黃敏銓 德國敏斯特大學 細胞生物學/遺傳學 博士 主修:細胞生物學/遺傳學 第一副修:微生物學 第二副修:生物化學 基醫大樓6樓 0646室 [email protected] 2 Position and surface projection of the heart 3 p. 389 Pericardium and heart wall Heart wall 4 p. 390 Structure of the heart: surface features Anterior external view 5 p. 392 Structure of the heart: surface features Posterior external view 6 p. 393 Structure of the heart: internal anatomy Anterior view of frontal section 7 p. 394 Valves of the heart and great vessels 8 9 Fibrous skeleton of the heart Functions: a) Attachment of heart valves b) Insertion of cardiac muscle bundles c) Prevention of valve overstretching d) Electrical insulation between the atria and the ventricles 10 p. 396 Systemic and pulmonary circulations 5 4 6 3 10 10 7 9 1 2 8 4 6 5 11 p. 398 Coronary (cardiac) circulation: coronary arteries Anastomoses Collateral circulation 12 p. 400 Coronary (cardiac) circulation: coronary veins 13 p. 400 The conduction system of the heart 14 p. 403 Autonomic innervation of the heart. Dorsal motor nucleus of vagus The vagus nerve (parasympathetic) decreases heart rate. Cardioinhibitory center Cardioacceleratory center Medulla oblongata Sympathetic trunk ganglion Thoracic spinal cord Sympathetic trunk Sympathetic cardiac nerves increase heart rate and force of contraction. AV node SA node Parasympathetic fibers Sympathetic fibers 15 Interneurons Location of valves (purple) and auscultation sites (red) for heart sounds Heart sounds: blood turbulence S1: AV valves S2: semilunar valves S2 S1 16 p. 406 The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels 17 Artery Arteriole Capillary Venule Vein (動脈) (小動脈) (微血管) (小靜脈) (靜脈) Systemic veins and venules (blood reservoirs) 60% Vasa vasorum(血管滋養管) 18 Artery Vein (intima) 19 Elastic arteries The largest-diameter arteries Ascending aorta Common iliac 20 Muscular arteries The medium-sized arteries Left brachial 21 Arteriole: control resistance Vascular shunt Precapillary sphincters ― control blood pressure and blood flow to a tissue Metarteriole Thoroughfare channel True capillaries Terminal arteriole Postcapillary venule Sphincters open—blood flows through true capillaries. Terminal arteriole Postcapillary venule Sphincters closed—blood flows through metarteriole – thoroughfare channel and bypasses true capillaries. 22 Continuous capillary: brain, skeletal and smooth muscle, connective tissue, lungs Fenestrated capillary: kidneys, villi of the small intestine, choroid plexuses sinusoid: red bone marrow, liver, spleen, anterior pituitary gland, parathyroid gland 23 Venule • The smallest venule has only a few scattered smooth muscle fibers and fibroblast. • The walls of the smallest venules are very porous. • Many leukocytes emigrate through the postcapillary venules during inflammation. 24 Venous valve: two or more thin folds of tunica interna that form cusps pointing toward the heart (b) Varicose veins(靜脈曲張): leaky venous valves 25 Circulatory routes • Systemic circulation – Coronary circulation – Cerebral circulation – Hepatic portal circulation • Pulmonary circulation • Fetal circulation 26 Circulatory routes 27 The aorta and its branches Arch of aorta Ascending aorta Thoracic aorta Abdominal aorta 28 Ascending aorta and its branches Right coronary artery Left coronary artery 29 Arch of aorta and its branches 30 Brachiocephalic trunk and its branches in neck and head 31 Cerebral arterial circle (Circle of Willis) Anastomoses 32 Circle of Willis 33 Radial pulse Brachial artery 橈動脈 Radial artery Ulnar artery 尺動脈 34 Thoracic aorta 35 Abdominal aorta and its branches Celiac trunk: left gastric artery, splenic artery, common hepatic artery Celiac trunk 36 Abdominal aorta and its branches Superior mesenteric artery 37 Abdominal aorta and its branches Inferior mesenteric artery 38 Arteries of the pelvis and lower limb Common iliac artery: internal iliac & external iliac Aorta Common iliac artery Internal iliac artery External iliac artery Anterior view Internal iliac arteries: Pelvic vescera and wall 39 Figure 20.15 Arteries of the right pelvis and lower limb. Common iliac artery Internal iliac artery Superior gluteal artery External iliac artery Femoral artery Deep artery of thigh Lateral circumflex femoral artery Descending branch Medial circumflex femoral artery Obturator artery Adductor hiatus Popliteal artery Popliteal artery Genicular artery Anterior tibial artery Anterior tibial artery Posterior tibial artery Posterior tibial artery Fibular artery Fibular artery Lateral plantar artery Dorsalis pedis artery Arcuate artery Medial plantar artery Plantar arch Dorsal metatarsal arteries Anterior view Dorsalis pedis artery (from top of foot) Posterior view of leg 40 Veins of the systemic circulation 1. Coronary sinus 2. Superior vena cava 3. Inferior vena cava deliver deoxygenated blood to the right atrium 41 Principal veins of the head and neck 42 Principal veins of the right upper limb (superficial veins) Cephalic vein Basilic vein Median antebrachial vein Median cubital: injection, transfusion, blood withdraw 43 Deep veins usually accompany arteries that have similar names 44 Most thoracic structures are drained by the azygos system of veins Azygos 45 Principal veins of the pelvis and lower limbs Great saphenous veins: the longest veins in the body 46 Hepatic portal circulation ― deliver venous blood from the organs of gastrointestinal tract and spleen to the liver Hepatic portal vein Splenic vein Superior mesenteric vein 47 Figure 20.22a The hepatic portal system. Arterial blood Venous blood Stomach and intestine Liver Nutrients and toxins absorbed Inferior vena cava Liver cells (hepatocytes) Nutrients and toxins leave Hepatic portal vein Hepatic vein Second capillary bed (liver sinusoids) First capillary bed Hepatic portal system Schematic of the hepatic portal system 48 Fetal circulation Circulation after birth Fetal circulation 49