* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Wizard Test Maker
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
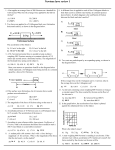
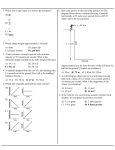
Forces Free response Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the information below. A horizontal force of 8.0 newtons is used to pull a 20.-newton wooden box moving toward the right along a horizontal, wood surface, as shown. 1. Calculate the magnitude of the frictional force acting on the box. [Show all work, including the equation and substitution with units.] 2. Calculate the magnitude of the acceleration of the box. [Show all work, including the equation and substitution with units.] Base your answers to questions 3 and 4 on the information below. An ice skater applies a horizontal force to a 20.kilogram block on frictionless, level ice, causing the block to accelerate uniformly at 1.4 meters per second 2 to the right. After the skater stops pushing the block, it slides onto a region of ice that is covered with a thin layer of sand. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the sand-covered ice is 0.28. 3. Calculate the magnitude of the force applied to the block by the skater [Show all work, including the equation and substitution with units.] Name:___________________ 6. Base your answer to the following question on the information and diagram below. The following diagram is provided for practice purposes only. A 10.0-kilogram block slides at constant speed down a plane inclined at 20.º to the horizontal, as shown. Determine the weight of the block. [Show all calculations, including the equation and substitution with units.] 7. Base your answer to the following question on the information below. A car traveling at a speed of 13 meters per second accelerates uniformly to a speed of 25 meters per second in 5.0 seconds. A truck traveling at a constant speed covers the same total distance as the car in the same 5.0-second time interval. Determine the speed of the truck. 8. Base your answer to the following question on The information below. A force of 60. newtons is applied to a rope to pull a sled across a horizontal surface at a constant velocity. The rope is at an angle of 30. degrees above the horizontal. 4. Determine the magnitude of the normal force acting on the block. 5. A skier on waxed skis is pulled at constant speed across level snow by a horizontal force of 39 newtons. Calculate the normal force exerted on the skier. [Show all work, including the equation and substitution with units.] Determine the magnitude of the frictional force acting on the sled. Base your answers to questions 9 and 10 on the information and diagram below. In the scaled diagram, two forces, F1 and F2, act on a 4.0-kilogram block at point P. Force F1 has a magnitude of 12.0 newtons, and is directed toward the right. 12. An airplane is moving with a constant velocity in level flight. Compare the magnitude of the forward force provided by the engines to the magnitude of the backward frictional drag force. Base your answers to questions 13 and 14 on the information and diagram below. A 10.-kilogram box, sliding to the right across a rough horizontal floor, accelerates at –2.0 meters per second2 due to the force of friction. 9. Calculate the magnitude of the acceleration of the block. 10. Using a ruler and the scaled diagram, determine the magnitude of F2 in newtons. 11. Base your answer to the following question on the information below. A soccer player accelerates a 0.50-kilogram soccer ball by kicking it with a net force of 5.0 newtons. What is the magnitude of the force of the soccer ball on the player’s foot? 13. On the diagram provided, draw a vector representing the net force acting on the box. Begin the vector at point P and use a scale of 1.0 centimeter = 5.0 newtons. 14. Calculate the coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and the floor. Answer as a decimal with one significant digit. 15. State the two general characteristics that are used to define a vector quantity. 16. Jillian wishes to pull a 100. N copper box across a steel surface at a constant velocity. (Refer to your reference table, Approximate Coefficents of Friction.) a) Calculate the horizontal force she must apply. (Show all work) b) Originating from the dot in the center of the box above, construct a scaled vector showing Jillian's force and the frictional force. the forces must be drawn to a scale of 1.0 centimeter = 10. N. Be sure to label with numbers and units your vectors. c) If Jillian wished to make the box accelerate at 1.0 m/s2, what force must she apply? (Show all work) Answer Key [New Exam] 1. 13. 2. The vector should be 4.0 cm ()0.2cm) 14. 3. 15. Allow credit for magnitude or size and credit for direction. 16. a) 36 N; b) drawing; c) 46 N 4. 2.0 ×102 N or196 N 5. 6. w = mg w = (10.0 kg)(9.81 m/s2) 7. 19 m/s. 8. 52 N 9. a = 0.75 m/s2 10. 9.0 N ±0.6 N. 11. Allow credit for 5.0 N or –5.0 N. Note: If the student indicates that the ball is kicked vertically, an answer of 10.0 N is acceptable. If the student indicates that the ball is kicked at an angle, an answer between 5.0 N and 10.0 N is acceptable. 12. Allow credit for stating that the magnitudes of the two forces are equal.