* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geography Basics
History of cartography wikipedia , lookup
Environmental determinism wikipedia , lookup
Iberian cartography, 1400–1600 wikipedia , lookup
History of navigation wikipedia , lookup
Royal Geographical Society wikipedia , lookup
Enhanced 9-1-1 wikipedia , lookup
History of longitude wikipedia , lookup
Location-based service wikipedia , lookup
Department of Geography, University of Kentucky wikipedia , lookup
Children's geographies wikipedia , lookup
Military geography wikipedia , lookup
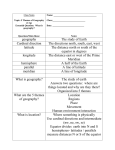
Geography Basics Objective: - Explain the job of a geographer and its importance. - Describe the five themes of geography. What is geography? • Geography: the study of the physical and human features on earth – Physical geography: how the earth’s natural features vary from place to place • Examples: water resources, plants and animals, landforms like mountains and plateaus – Human geography: how people and their activities differ from place to place • Examples: how they make a living, what types of governments they have, what they do for fun Picture Examples Physical Geography Human Geography What are the five themes of geography? • A way of thinking about and organizing geography so it’s easier to understand • The five themes are… – – – – – Location Place Human-Environment Interaction Movement Regions • How do I remember that? – MR. HELP Theme #1: Location • Location: where something is • There are two types of location: – Absolute location – Relative location • Let’s talk about the difference Absolute Location • Absolute location: the exact location of something, often found using latitude and longitude • Latitude ↔ – Lines running east and west (sideways or horizontal) – Measured in degrees north or south of the equator • Longitude ↨ – Lines running north and south (up and down or vertical) – Measured in degrees east and west of the Prime Meridian Finding the Absolute Location of a Place 1. 2. 3. Locate the equator. How many degrees north or south of the equator is it? Latitude = _______ degrees N or S Locate the Prime Meridian. How many degrees east or west of the Prime Meridian is it? Longitude = _______ degrees E or W You did it! It is located at: ______ º N or S and ______ º E or W Example #2 (the blue X) 1. 2. 3. Locate the equator. How many degrees north or south of the equator is it? Latitude = _______ degrees N or S Locate the Prime Meridian. How many degrees east or west of the Prime Meridian is it? Longitude = _______ degrees E or W You did it! It is located at: ______ º N or S and ______ º E or W X Finding a Place When We Know It’s Absolute Location 1. 2. 3. Locate the equator. Use the latitude (____ º N or S). Go up for N, go down for S. Locate the Prime Meridian. Use the longitude (____ º E or W). Go left for W, right for E). Move your fingers until they touch. This is the location! Put an X there. Let’s try it! What is located at 42.6 degrees N, 82.56 degrees W? ____________ Relative Location • Relative location: where something is located in relation to other places • Can be described using: – – – – Landmarks: I live near the 7-11. Time: The store is about 1 hour from here. Direction: Algonac is northeast of Detroit. Distance: We live 50 miles from here. Theme #2: Place • Place: special characteristics that make each place on earth unique • 2 types of characteristics: – Physical characteristics: weather, land features, plants, animals – Human characteristics: people, cultures, ideas • How is Algonac unique? – Algonac’s physical characteristics? – Algonac’s human characteristics? Theme #3: Human-Environment Interaction • Human-environment interaction: how people influence their surroundings, and how their surroundings influence them – People adapt to their environment (their environment influences them) – People change their environment (they influence the environment) People ↔ Environment Theme #4: Movement • Movement: people, goods, and ideas all travel – Example: people go on a vacation – Example: Nintendo Wii (goods) moves from Japan to the United States – Example: fashion ideas spread from Los Angeles and New York City to other parts of the country Theme #5: Region • Region: an area that has similar characteristics • Some regions are defined by more than one characteristic • Example: the Middle East What is a geographer? • Geographer: a person who uses the five themes of geography to understand the world • Examples of jobs: – Study the environment – Make decisions about how products should be transported – Working for the United Nations – Teaching people so they are more understanding about the world and its people What is cartography? • Cartography: the branch of geography that studies maps and map making • How do you make a map? – Computers store images from old maps, satellite images, photographs, and data from surveys and reports – Cartographer draws the map on computer screen – Viola! The map is printed! Let’s Review • Geography = physical and human • • • • • • M = movement R = region H = humanE = environment interaction L = location P = place • Cartographers make maps