* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Voluminous Data Can be Simplified to Inform Business Decisions
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
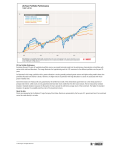
Paper: Approaching the Dip John Kuest 7/13/2016 Voluminous Data Can be Simplified to Inform Business Decisions John Kuest 7/13/2016 PMI Talent Triangle Talents • • • • • • Strategic Planning Problem Solving Business Model Risk Management Gather Data Analysis (Tools) Strategic Planning BI - Business Intelligence Models – Simpler is better Problem Statement • We all want to be more secure with our long term finances – we want to be able to retire with less financial worries. • The investment options faced by individuals are astronomically large. How do we distill the myriad of data into pertinent data and then summarize it into something usable. • The solution is to condense the data into a suitable form fit into a model that produces high performance actionable recommendations. Model Efficient Frontier / Modern Portfolio Theory • The efficient frontier is the set of optimal portfolios that offers the highest expected return for a defined level of risk or the lowest risk for a given level of expected return. Optimal portfolios that comprise the efficient frontier tend to have a high degree of diversification. Portfolios that lie below and to the right of the frontier are sub-optimal, because they do not provide enough return for the level of risk or have a higher level of risk for the defined rate of return. Risk Management Modern Portfolio Theory - A portfolio of highly diversified group of stocks a bonds can produce optimal risk adjusted returns – better returns taking less downside risk. Two Investments Options Barclays Aggregate Bond Fund (AGG) and S&P 500 (SPY) 3 year Return, Monthly Data, ending August 2015 At 25% SPY and 75% AGG same risk as all AGG Risk Standard deviation is a popular basic mathematical concept to measure risk. Standard deviation measures the average amount by which individual data points differ from the mean. It is calculated by first subtracting the mean from each value, and then squaring, summing and averaging the differences to produce the variance. Standard deviation is the square root of the variance, bringing it back to the original unit of measure and making it simpler to use and easier to interpret. Risk Interpretation Stock A Average Return Standard Deviation 10% 10% 10 - 1.65*10 = -6.5% For “Stock A” assuming a normal distribution, 95% of the time the annual return will be greater than a NEGATIVE 6.5%. (5% of the time the annual return is worse than -6.5%) Screener Data Analysis The Paper Grey bars are Recessions Recessions Waves Search for best bear market returns– AAII ETF’s and Mutual Funds • • 30% Maximum in any one Equity Monthly Data from May 2006 to May 2011 Efficient Frontier Diagram Voluminous Data • • 30% Maximum in any one Equity Monthly Data from May 2006 to May 2011 Strategic Planning BI - Business Intelligence PMI Talent Triangle Questions? John Kuest