* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 6 Studyguide: The Periodic Table
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
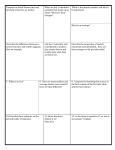
Chapter 6 Studyguide: The Periodic Table Define the following terms: 1. electronegativity 6. periodic law 2. ionization energy 7. cation 3. atomic radius 8. period 4. metal 9. group 5. transition metal 10. electrons 11.Name all the elements in the same period as phosphorus. 12.What does each period in the periodic table corresponds to? 13.The modern periodic table is arranged in order of increasing atomic ____. 14.Who arranged the elements according to atomic mass and used the arrangement to predict the properties of missing elements? 15.What general category classifies the majority of the elements? 16.Of the elements Pt, V, Li, and Kr, which is a nonmetal? 17.The atomic number of an element is the total number of which particles in the nucleus? 18.What is true about the electron configurations of the noble gases? 19.Which subatomic particle plays the greatest part in determining the properties of an element? 20.How does atomic radius change from top to bottom in a group in the periodic table? 21.How does atomic radius change from left to right across a period in the periodic table? 22.What causes the shielding effect to remain constant across a period? 23.What is the general trend with atomic size? 24.What element in the second period has the largest atomic radius? 25.What factors contribute to the increase in atomic size within a group in the periodic table as the atomic number increases? 26.What is the charge of a cation? 27.Why is the second ionization energy greater than the first ionization energy? 28.In which of the following sets are the charges given correctly for all the ions? c. Rb , Ba , P a. Na , Mg , Al d. N , O , F b. K , Sr , O 29.In which of the following groups of ions are the charges all shown correctly? a. Li , O , S c. K , F , Mg d. Na , I , Rb b. Ca , Al , Br 30.What is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom in the gaseous state called? 31.For Group 2A metals, which electron is the most difficult to remove? 32.Which of the following elements has the smallest first ionization energy? a. sodium c. potassium b. calcium d. magnesium 33.How does the relative size of an ion compare to its neutral atom? 34.What factors contribute to the increase in ionization energy from left to right across a period? 35.Of the following elements, which one has the smallest first ionization energy? a. boron c. aluminum b. carbon d. silicon 36.In going from left to right in any given row in the periodic table, the size of atoms generally _____. 37.Compared to the neutral atom from which it is derived, a negative ion is _____in size. 38.The valence configuration shared by carbon, silicon, and germanium is _____. 39.Transition elements, such as chromium, are likely to have what kinds of oxidation numbers? 40.A metallic ion is _____in size to its corresponding atom. 41.Bromine is a typical nonmetal. A bromide ion is _____ in size to a bromine atom. 42.Ionic radii _____ down a group in the periodic table. 43.Alkaline earth metals lose _____ electrons to achieve the electron configuration of the noble gas in the preceding period. 44.The most unreactive group of elements is the _____. 45.Transition metals have multiple oxidation states because of the involvement of the _____ electrons in chemical bonding. 46.All Group 1 elements have _____valence electron. 47.The blank spaces in Mendeleev's periodic table represented _____. 48.Modern periodic law states that properties of elements repeat in a regular pattern when the elements are arranged in order of increasing _____.