* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Seafloor Spreading (LT 1, 3-5)
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
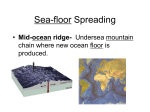
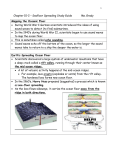
Write the following on the Goal Sheet in your notebook. October 7 Goal: I can explain the evidence for seafloor spreading (LT # 4) Rate your understanding of this topic at this moment, and how much effort you plan to give to class today. Plate Tectonics Learning Targets Indicator: Earth’s crust consists of major and minor tectonic plates that move relative to each other. Learning Targets: I can … 1. Explain how our understanding of plate tectonics has developed through the contributions of Alfred Wegener, Harry Hess, and Robert Dietz 2. 3. 4. 5. Explain 4 pieces of evidence for the theory of continental drift. Describe the process of seafloor spreading Explain at least three pieces of evidence for seafloor spreading Explain how evidence of polar wandering supports plate tectonics 6. Explain which layer of earth is divided into tectonic plates 7. Tell that the tectonic plates float on the asthenosphere 8. Identify and describe the geothermal movements that cause plate motion. Vocabulary: continental drift, seafloor spreading, convection, tectonic plate, Mesosaurus, Glossopteris, Pangaea, mantle, asthenosphere, lithosphere, magnetic field, trench, subduction, rift valley, midocean ridge, polar wandering, geothermal Di etz on Page 7 He ss sound waves at proposed the theory of seafloor spreading magma cools, contracts and begins to sink helping to form the obtains rock samples from the seafloor younger sink below reversed itself many times in the past reverses back and forth over time in strips parallel to the midocean ridges What did they find from all these core samples? The youngest rocks are found at the mid-ocean ridges. As you travel away from the mid-ocean ridge on either side, the rocks get progressively older. This suggests that new rock (crust) is being formed at the mid-ocean ridge, and is pushing the seafloor away from the midocean ridge like a conveyer belt. page 10 midocean ridge deep sea trench A/C B Ocean floor near the center slit is youngest rocks age as move towards side slits the pattern of reversals in Earth's magnetic field that is recorded in rocks as magma cools hot magma rises (because it is less dense) and pushes on crust causing it to move cooler magma sinks back into mantle (convection current) mid-ocean ridge page 11 page 12 the youngest rocks are at the mid-ocean ridge and get progressively older as move away (new rock formed at ridge) the magnetic field gets recorded into rocks when lava cools and the pattern of reversals is the same on both sides of the ridge. the ocean floor gets pushed under continental crust along with ocean water which gets trapped in mantle, continental crust gets folded into mountains page 12 https://www.eeducation.psu.edu/earth520/content/l3_p5.html Polar wandering is..... seen by the layers of lava rocks from a volcano. As you travel deeper into older rocks, the rock's magnetic north points a different direction - so either the magnetic north pole has moved or the continent has. S. America page 13 Rift Valley (African rift valley) New Ocean Basin (Red Sea) Mature Ocean (Atlantic) MidOcean Ridge Sediments October 15 October Question: Notebooks:Savanna & Meltie Timekeeper: Jesse Proposed by Harry Hess in 1960s seafloor spreads allowing magma to rise Theory of creating new ocean floor at midocean ridges; Continental Drift old ocean floor destroyed at trenches (subduction) Theory of Seafloor Spreading Evidence: Pillowshaped rocks found on seafloor Theory of can only form when magma cools underwater Pattern of reversals in magnetic field (recorded in rock) is the same on both sides of midocean ridge youngest rocks found at midocean ridges; rocks get older as move away from the ridge Proposed by W. Jason Morgan and Theory of Xavior Le Pichon in 1967 Earth's lithosphere is divided into Continental Drift plates which move relative to each other; plate movements are caused Theory of by convection currents in Earth's Seafloor Spreading asthenosphere; these movements cause earthquakes and volcanoes Theory of Plate Tectonics