* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPT - IVF Center in Delhi
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
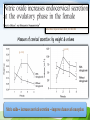
Role of antioxidants in female infertility Dr. Jyoti Agarwal Lifecare IVF Center New Delhi Oxygen toxicity is an inherent challenge to aerobic life • Oxygen is essential for life. • Excess oxygen can have harmful effects. • When oxygen is metabolised in the body , it produces substances called FREE RADICALS which damage our cells. Oxidative process occur in all cells and tissues throughout human body. Oxidation reactions can produce free radicals • Free radicals are produced by exposure to • Pollution • Smoking • Fatty food & • Stress Free radicals are like robbers which are themselves deficient in energy. Free radical with unpaired electron They attack and snatch energy from other cells to satisfy themselves. Free radicals cause damage by oxidation Free radicals are highly reactive and can cause damage to molecules in the cell. ROS PARADOX (delicate balance) ROS are key signal molecules in many physiological process to maintain cell homeostasis Whenever there is an excess they precipitate pathologies ROS act as double edged sword Prooxidants >>> antioxidants = oxidative stress Asthma Infertility Cancer Arthrits Oxidative Stress Diabetes Parkinsons CVD Are we ready to fight the attack of oxidative stress ? Counteracting free radical damage The only defence in this war against free radicals is by antioxidants. What are Antioxidants ? Browning reactions are due to oxidation Antioxidants in action Oxidation occurs when the apple is left exposed to air The apple is protected when dipped in orange juice containing the antioxidant vitamin C Antioxidants Antioxidants “ mop-up ” the free radicals Convert ROS to water ‘scavenging molecules’ Antioxidants prevents • Lipid peroxidation • Oxidative damage to protein • Oxidative damage to DNA • ANTIOXIDANTS have low redox potential and will sacrifice themselves to prevent oxidative damage Antioxidants are of two types • Primary / Enzymatic / natural • superoxide dismutase • catalase • glutathione peroxidase • glutathion reductase • Secondary / Non enzymatic / synthetic / dietary supplements • • • • • • • vitamin C vitamin E selenium zinc taurine , hypotaurine glutathion beta carotene , carotene Antioxidants and infertility • Etiologies of unexplained infertility and recurrent pregnancy loss remains unclear and present a scientific challenge. • Oxidative stress is a piece in this puzzle. Increasing evidence to show that oxidative stress affects both natural and assisted fertility. Oxidative stress is associated with • Age related decline in fertility • Decline in ovarian function • Decrease steroidogenesis • ROS negatively affects oocyte maturation • Decreased oocyte penetration of sperm • ↓ fertilization and blastocyst development • Decreased implantation • Increased loss of implanted embryo OS affects multiple physiological processes ….. oocyte maturation to fertilization & embryo development Reactive oxygen species and the endometrium • There is a cyclical variation in the expression of superoxide dismutase(SOD) in the endometrium. • In the late secretory phase SOD activity decreases and levels of ROS increases. • It is important for endometrial shedding and the onset of menstruation. Reactive oxygen species and the ovary • Various biomarkers of OS has been demonstrated in normal cycling human ovaries. • A delicate balance exists between ROS and antioxidant enzymes in the ovarian tissue. • These antioxidants enzymes neutralise ROS production and protect the oocycte. Role of ROS in Endometriosis • An increased generation of ROS by pelvic macrophages and increased lipid oxidation in patients with endometriosis. (Halme et al) • Antioxidant levels of superoxide dismutase (SOD) were noted to be significantly lower in peritoneal fluid in patients of endometriosis • Increased ROS levels in the tubal and the peritoneal environment negatively alter fertilization and embryonic development . (fertil steril 2003 ) Role of ROS in PCOD Elevated insulin resistance and hyper homocysteinemia has been proposed to be caused by OS in patients with PCOD.(j clin endocrino metab 2006) . Antioxidant supplementation has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity. The decreased antioxidants status and the increased OS levels may contribute to the increased cardiovascular morbidity in these patients.(fertil steril 2003) Impact of OS on assisted reproduction There are multiple sources of ROS generation in patient undergoing ART… • Oocytes (4 – 5 /dish) • Cumulus cell mass • Sperms • Prolongation of sperm – occyte co incubation time of more than 20 hrs • ROS levels in day 1 culture media Impact of ROS on assisted reproduction Causes a perturbed redox state and affects the development of the embryo by…. • Altering the gene expression • Impaired adenosine triphosphate production • Two cell arrest of embyro • Embyropathies ROS levels can be utilised to counsel patients before IVF. (agarwal et al ferti steri 2005 ) Oxidative stress influences the entire reproductive span of a women’s life and even thereafter , i.e. menopause There are many different ways to test for antioxidants Assessing levels of ROS and OS • Electron spin resonance… it identifies the molecules containing unpaired electrons. • Stable peroxidation product concentrations.. malondialdehyde , lipid peroxidase , and conjugated dienes. No standard reference values No defined Sensitivity & Specificity Strategies to overcome oxidative stress in infertility and ART When OS is diagnosed treatment must focus on identifying and eliminating the source of ROS. Smoking Alcohol Obesity Stress Poor diet Only after the treatment of primary etiology should patients be advised to take antioxidant supplementation Antioxidants in Food: Mere Myth or Magic Medicine? Role of Each Ingredient Antioxidants Iron • Important mineral for general well-being and energy • a subtle deficiency of iron Female subfertility Magnesium • Helpful in unexplained infertility since most have micronutrient deficiency with ROS • In vitro study shows oocyte activation on exposure to magnesium http://conditionsinfo.mitamins.com/sexual-Health-STDs/Female-Infertility-Vitamins.html Zinc essential cofactor for several metabolic reactions Zinc deficiency Impairs Synthesis & Secretion Impairs Abnormal Synthesis & Secretion of LH Ovarian development of FSH Irregular Ovulation Impairment of oocyte maturation Experientia.1994 Jul 15;50(7):626-40 Female Infertility Zinc .. Supplementation helps to: • Regulate ovarian development • Improves oocyte maturation & ovulation Exerts beneficial effect in female infertility Vitamin C • most important antioxidants in extra cellular fluids • Vitamin C is a chain breaking antioxidant. • protects tissues against oxidative damage • It also helps recycle oxidized vitamin E and glutathion. Vitamin E… strongest antioxidant present ‘a free radical scavenger’ Protects the DNA in the cells from damage Beta-Carotene-provitamin • Carotenoids are a group of red, orange and yellow pigments found in plant foods, particularly fruits and vegetables. N-acetyl cysteine : Powerful antioxidant: NAC ↑ reduced glutathione at cellular level Acts directly on reactive oxidant radicals Antioxidant effect N-acetylcysteine. Altern Med Rev. 2000 Oct;5(5):467-71 Rizk et al. Fertil Steril. 2005 Feb;83(2):367-70 Exerts protective effects to cells Not found in diet, available as a nutritional supplement Additional benefits of NAC Improve insulin sensitivity Preserve vascular integrity by vasodilator effects Antiandrogenic effect: ↓ testosterone levels & also ↓ free androgen index (FAI) As an antioxidant and mucolytic agent it detoxify harmful substances in body and promote sperm motility & survival in female genital tract Badawy et al. Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica. 2007; 86: 218-222 Millea PJ. Am Fam Physician. 2009 Aug 1; 80(3):265-9 Fulghesu et al. Fertil Steril 2002; 77:1128 –35 Detti et al. Diabetes. 2003; 52: 499-505 Pieper et al. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1998; 32:101–5 L-Arginine • An semi-essential amino acid • Well known as a precursor to nitric oxide (NO) • Lower levels of L Arginine causes delayed conception, decline in oocyte fertilization and implantation rates Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2005; 84: 1029-1034 Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2005; 84: 883-886 Measure of cervical secretion: by weight & volume (p < 0.01) (p < 0.05) Nitric oxide→ increases cervical secretion → improve chances of conception Takasaki A et al. 2010; 93(6): 1851-8 L-arginine supplementation was reviewed in patients with thin endometrium and high radial artery resistance index 9 patients were given L-arginine and 10 control patients were not given any medication L-arginine improved RA-RI in eight (89%) out of nine pts & endometrial thickness (ET) in six (67%) patients which was seen in only 1 patient in control group Improves RA-RI and ET → ↑ uterine blood flow & endometrial receptivity Sources of L-arginine: Animal sources: – Dairy products (e.g. milk, yogurt, cottage cheese etc.) – Beef, poultry food, seafood (e.g. lobster, shrimp, snails etc.) Vegetable sources: – Wheat, oatmeal, peanuts – Nuts (coconut, walnuts, almonds etc.), soybeans Grape Seed Extract Grape Seed Extract In vitro study: (superoxide anion and hydroxyl radical) Antioxidants Inhibition of free radicals GSPE 78-81 % Vitamin C 12-19 % Vitamin E succinate 36-44 % (Concentration: 100mg/l) In animal study: Protective effects of GS-Proanthocyanidins & other antioxidants in mice Antioxidants ↓ production of ROS GSPE (20-100mg/kg) 70 % Vitamin C (100mg/kg) 18 % Vitamin E succinate (100mg/kg) 47 % Beta-carotene (50mg/kg) 16 % Powerful antioxidant: proanthocyanidins Bagchi D. et al. Res Commun Mol Pathol Pharmacol, 1997; 95(2): 179-89 Bagchi D. et al. Gen Pharmacol, 1998; 30(5): 771-6 • Green tea, Vit B6, B12, • Reduces free radical damage • Improves overall reproductive health Green tea catechins are 100 times more potent than vitamin C Hot cocoa tops red wine and tea in antioxidants 2-3 times stronger than green tea, and 4-5 times stronger than black tea Vitamin B12 & Vitamin B6 Deficiency of Vitamin B12 & Vitamin B6 Increase in Oxidative Stress Failure in Ovulation Female Infertility Defective Implantation Human Reproduction Update 2007; 13(3): 225–238 Asia Pac J Clin Nutr.2005;14(3):250-5 J Reprod Med.2001 Mar;46(3):209-12 Int J Fertil.1991Jan-Feb;36(1):36-8 Schweiz Med Wochenschr.1984 Feb 4;114(5):178-9 Vitamin B12 &Vitamin B6 Supplementation helps to : Reduce oxidative stress Improve ovulation Thus improve reproductive health J of Reproductive Medicine April 2004 Folate (Folic Acid) Deficiency of folate Homocysteine & Reduced folliculogenesis Production of inflammatory cytokine All leads to Human Reproduction Update 2007; 13(3): 225–238 X Folate Oxidative stress Altered Nitric oxide metabolism Female Infertility Apoptosis Improve Selenium .. Selenium works synergistically with vitamin A • Sources • Nuts • Seafood • Pasta Antioxidants in combination Antioxidants are believed to work better in combination than supplementing alone. • Together they protect oxidation of each other • Together they preclude the need for large doses of single nutrient Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol. 2006;33(4):205-8 There is lack of consenus on the type and dosage of antioxidants to be used. Validation by large randomised double blind case control trials is needed as evidence Take Home Message….. • Oxidative stress has a significant impact on female infertility. • The role of oxidative stress in female reproduction cannot be underestimated. • The best way to add antioxidants to the diet is to eat generous servings of fruits and vegetables daily. J of Reproductive Medicine April 2004 Antioxidants optimize the environment and offers complementary role to correct and support female factor fertility and conception “The real voyage of discovery consists of not in seeking new landscapes but in having new eyes.” - Marcel Proust