* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 9 Cardiovascular System
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
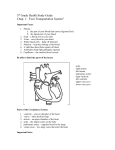
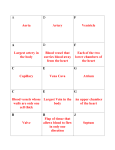
Laboratory 9 Cardiovascular System (LM pages 115–128) Time Estimate for Entire Lab: 2.0 hours Note: Because humans stand upright, the proper terms are the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava, but because pigs are tetrapods, these same vessels should be called the anterior vena cava and the posterior vena cava (pl., vena cavae). Seventh Edition Changes This was lab 8 in the previous edition. In section 9.3 Systemic Circuit, Blood Vessels of the Thoracic Cavity has been rewritten to increase active participation by the student. New or revised figures: 9.2 Human fetal circulation; 9.3 Ventral view of fetal pig heart; 9.5 Arteries in the thoracic cavity of the fetal pig; 9.6 Veins in the thoracic cavity of the fetal pig; 9.9 Scanning electronmicrograph of an artery and a vein MATERIALS AND PREPARATIONS1 9.1 Path of Blood in an Adult Versus a Fetus (LM pages 116-117) _____ model, human fetal circulatory system (Carolina 56-3150) 9.2 – 9.3 Pulmonary Circuit and Systemic Circuit (LM pages 119-126) _____ fetal pigs, preserved, for dissection (Carolina 22-8400 to -8492) _____ dissecting pans, pins, tools, and trays (see Carolina’s “Apparatus: Dissecting” sections) _____ wax pencils _____ labels, for labeling individual pigs _____ plastic bags or containers for pig storage _____ string, heavy, for tying pigs into dissection pans and for tying bags Fetal pigs. Fetal pigs for dissection are available from many supply houses. Large, double-injected specimens are recommended. 9.4 Blood Vessel Comparison (LM pages 126-127) _____ slide, prepared: artery and vein, cross section (Carolina 31-4088, -4094) _____ microscopes, compound light _____ lens paper EXERCISE QUESTIONS 9.1 Path of Blood in an Adult Versus a Fetus (LM page 116) Path of Blood in Adult Humans (LM page 116) Pulmonary Circuit (LM page 117) 1. Trace the path of blood in the pulmonary circuit from the heart to the lungs, and then from the lungs to the heart. right ventricle of heart, pulmonary artery, lungs, pulmonary veins, lungs lungs, pulmonary veins, left atrium of heart 1 Note: “Materials and Preparations” instructions are grouped by exercise. Some materials may be used in more than one exercise. 40 Systemic Circuit (LM page 117) 2. Trace the path of blood in the systemic circuit from the heart to the kidneys, and then from the kidneys to the heart. left ventricle of the heart, aorta, renal artery, kidneys kidneys, renal vein, inferior vena, cava, right atrium of the heart Names of Blood Vessels (LM page 117) Table 9.1 Major Blood Vessels in the Systemic Circuit Body Part Artery Vein Head Carotid Jugular Arms Subclavian Subclavian Kidney Renal Renal Legs Iliac Iliac Intestines Mesenteric Hepatic portal Path of Blood in Fetal Humans (LM page 117) Through the Heart (LM page 119) 1. Trace the path of blood from the right atrium to the aorta, going through the oval opening. 2. Trace the path of blood from the right atrium to the aorta, going through the arterial duct. First pathway: right atrium, oval opening, left atrium, left ventricle, aorta Second pathway: right atrium, right ventricle, pulmonary trunk, arterial duct, aorta To the Placenta and Return (LM page 119) 3. Trace the path of blood from the aorta to the placenta and from the placenta to the inferior vena cava. aorta, iliac artery, umbilical artery, placenta placenta, umbilical vein, venous duct, inferior vena cava Comparison (LM page 119) Table 9.3 Comparison of Human Fetal and Adult Circulation Fetus Adult Vessel with the highest oxygen concentration Umbilical vein Aorta Passage from right to left side of heart Oval opening Pulmonary artery to lungs and pulmonary vein from lungs Entrance of blood into aorta Arterial duct Left ventricle Area of gas exchange Placenta Lungs 9.2 Pulmonary Circuit (LM pages 119-120) Observation: Pulmonary Circuit (LM page 119) Pulmonary Veins (LM page 120) 2. In the adult, which blood vessels carry O2-rich blood? pulmonary veins 9.3 Systemic Circuit (LM pages 120-126) Observation: Blood Vessels of the Thoracic Cavity (LM page 122) Carotid Arteries and Jugular Veins (LM page 122) 3. What part of the body is serviced by the carotid arteries and the jugular veins? the head 5. Name and locate all veins that join to form the anterior vena cava. left internal jugular, left external jugular, left subscapular, left subclavian, right brachiocephalic 41 9.4 Blood Vessel Comparison (LM pages 126-127) Do you predict that arteries or veins are generally more superficial in the body? veins Wall of Artery Compared to Wall of Vein (LM page 126) Observation: Blood Vessel Comparison (LM page 127) 4. Does this layer appear thicker in arteries than in veins? yes 5. Considering the relationship of arteries and veins to the heart, why is this reasonable? Arteries take blood away from the heart. The blood is under high pressure, and it is unlikely that it will flow backwards. Veins take blood to the heart; the lower blood pressure of the veins, combined with gravity, makes one-way valves essential to prevent pooling of blood in the arms and legs. Conclusions (LM page 127) • Which type of blood vessel (arteries or veins) has thicker walls? arteries • Which type of blood vessel has thinner walls? veins • Which type of blood vessel is more apt to lose its elasticity, leading to a discoloration that can be externally observed? veins What is this condition called? varicose veins LABORATORY REVIEW 9 (LM page 128) 1. What fetal structure connects the pulmonary trunk to the aorta? arterial duct 2. What fetal blood vessel contains the most oxygen? umbilical vein 3. What structure allows the blood to pass from the right to the left side of the heart into the fetus? oval opening 4. Does the pulmonary artery in adults carry O2-rich or O2-poor blood? O2-poor blood 5. The coronary arteries and cardiac veins serve what organ? the heart 6. Identify the blood vessel that conducts blood to the head. vein 7. Identify the artery that serves the kidney. renal artery 8. Identify the large artery that runs dorsally along the wall of the abdominal cavity. aorta 9. Identify the arteries that take blood from the aorta to the legs. iliac arteries 10. What part of the human body is served by the subclavian vessels? shoulder 11. Identify the large abdominal vein that runs alongside the aorta and enters the right atrium. inferior vena cava 12. What part of the body is not served by the systemic circuit? lungs 13. Which type of blood vessel (artery or vein) has thicker walls? artery 14. Which type of blood vessel (artery or vein) has valves? veins Thought Questions 15. Do arteries always carry O2-rich blood? Explain. No. In the adult, pulmonary arteries carry O2-poor blood from the heart to the lungs. In the fetus, umbilical arteries carry O2-poor blood to the placenta. 16. Trace the path of blood from the left ventricle to the kidneys and back to the right atrium. Blood leaves the left ventricle and goes to the aorta, to the renal artery, to capillaries, to the renal vein, to the inferior vena cava, to the right atrium.