* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download nucleotides.
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids
Summary
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
August2010
Introduction to nucleic acids and their
biochemical functions
Nucleotide structure and nomeclature
Modified nitrogenous bases
Nucleotide derivatives
Nucleotide synthetic analogs
Polynucleotides
DNA as the genetic material
Manipulations of DNA
HBC108/2010
UON
EGK
2
Introduction to Nucleic acids
{ The major nucleic acids of the cell are:
z Ribonucleic acid (RNA)and Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).
{ DNA is a nucleic acid polymer found in the
nucleus
{ It is the genetic material, the form in which
genetic information is stored
{ Minor DNA is found in the mitochondria and
used in the synthesis of mitochondrial proteins
August2010
HBC108/2010
UON
EGK
3
Introduction to Nucleic acids
{ RNA is a nucleic acid polymer synthesized from
DNA in a process referred to as transcription
{ The ribosome structure in the cytosol is made up
of a type of RNA
{ Another type of RNA forms a nucleic acid
template bearing codes of amino acids which are
used for protein synthesis in the ribosomes
{ A third type of RNA is involved in binding and
transfer of amino acids from the cytosol to the
ribosomes for protein synthesis
August2010
HBC108/2010
UON
EGK
4
Other functions
1.
2.
3.
August2010
Serving as energy stores in phosphate
transfer reactions predominantly carried out
by Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP).
Forming a portion of several important
coenzymes such as NAD+, NADP+, FAD
and coenzyme A.
Controlling numerous enzymatic reactions
through allosteric effects on enzyme activity
e.g. Guanosine Triphosphate (GTP)
HBC108/2010
UON
EGK
5
Functions
{ Serving as mediators of numerous important
cellular processes such as second messengers
in signal transduction events.
z The predominant second messenger is cyclic-Adenosine
Monophosphate (cAMP), a cyclic derivative of AMP formed
from ATP
z Also cyclic-Guanosine Monophosphate cGMP.
{ Serving as activated intermediates in
numerous biosynthetic reactions.
z S-adenosylmethionine (s-AdoMet) involved in methyl
transfer reactions in glycogen synthesis
August2010
HBC108/2010
UON
EGK
6
Introduction to nucleotides
{ Nucleotides are monomers of major
nucleic acids
{ Consists of
z a nitrogen containing base (nitrogenous bases)
{Two types of nitrogenous base occur
z A phosphate group,
z A five carbon sugar (either ribose or deoxyribose)
August2010
HBC108/2010
UON
EGK
7
{ Nucleotides are monomers
consisting of
{ a one or two ring nitrogen
containing base.
{ a phosphate group
{ a five carbon sugar (either
ribose or deoxyribose)
Nitrogenous bases
{
These are functional groups consisting of
one or two rings containing both carbon and
nitrogen.
{ These bases are derivatives of the
heterocyclic highly basic, nitrogenous
compounds:
1. Purines
2. Pyrimidines
{
August2010
It is the chemical basicity of the nucleotides
that has given them the common term
"bases."
HBC108/2010
UON
EGK
9
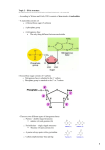
Structure of a purine and a pyrimidine
Pyrimidine
Purine
August2010
HBC108/2010
UON
EGK
10
Nitrogenous bases
{
There are five different nitrogenous bases,
each is denoted by a single letter
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
{
The derivatives of purines are
z
{
Adenine and guanine
And the derivatives of pyrimidines are
z
August2010
Adenine (A)
Cytosine (C)
Guanine (G)
Thymine (T)
Uracil (U)
Thymine, cytosine and uracil
HBC108/2010
UON
EGK
11
Purines
6
1
1
6
7
3
3
7
9
9
Guanine (G)
Adenine (A)
August2010
HBC108/2010
UON
EGK
12
Pyrimidines
2
2
1
6
Cytosine (C)
August2010
1
6
6
1
Thymine (T)
HBC108/2010
UON
Uracil (U)
EGK
13
Nucleosides
{ Purine and pyrimidine bases in cells occur
linked to a carbohydrate
{ and in this form are termed as nucleosides
{ Nucleosides are N-glycosides of two types
of pentose sugars
{ Nucleosides are formed by the loss of water
from a sugar and a purine or pyrimidine
base
Nucleosides
{ The pentose sugars found coupled to
nitrogenous bases to form nucleosides are
1. D-ribose
2. 2'-deoxy-D-ribose
{ The two sugars are linked through a Nglycosidic bond between the anomeric
carbon of the sugar and the N9 of a purine
or N1 of a pyrimidine.
Pentoses found in nucleotides
The chemical structure of pentose which contains five carbon atoms, labeled
as C1' to C5'. The pentose is called ribose in RNA and deoxyribose in DNA,
because the DNA's pentose lacks an oxygen atom at C2'.
Structure of nucleosides
1
1
3
9
9
3
1'
1'
syn-Adenosine
August2010
HBC108/2010
anti-Adenosine
UON
EGK
17
Structures of purine nucleosides
Base Formula
Base (X=H)
Adenine, A
Guanine, G
Nucleoside
X=ribose or
deoxyribose
Adenosine, A
Guanosine, A
Adenosine
Guanosine
Structures of pyrimidine nucleosides
Base Formula
Base (X=H)
Nucleoside
X=ribose or
deoxyribose
Cytosine, C
Cytidine, A
Uracil, U
Uridine, U
Thymine, T
Deoxythymidine, T
Cytidine
Uridine
Deoxyribonucleosides
Deoxyadenosine
H
Deoxyguanosine
H
Deoxycytidine
H
Thymidine
(Deoxythymidine)
H
Practice
{ Draw and name the nucleosides derived
from the different bases
Nucleotides
{ Nucleosides are found in the cell
primarily in their phosphorylated form.
{ These are termed nucleotides.
{ Nucleotides are phosphate esters of
nucleosides
{ The most common site of
phosphorylation of nucleotides is the
OH group attached to the 5'-carbon of
the ribose
August2010
HBC108/2010
UON
EGK
25
Nucleotides
{ Monophospates can be further phosphorylated
to produce di- and tri- phosphates
{ Thus nucleotides can exist in the mono-, di-,
or tri-phosphorylated forms
{ At physiological pH, the phospates are
ionized
{ The ionization of the phospates means that
RNA and DNA bear multiple negative
charges (polyelectrolytes)
{ Thus cations of various kinds, especially
Mg++, tend to cluster near the phosphates.
August2010
HBC108/2010
UON
EGK
26
Structures of purine nucleotides
Base Formula
Base (X=H)
Adenine, A
Guanine, G
Nucleoside
X=ribose or
deoxyribose
Nucleotide
X=ribose phosphate
Adenosine, A
Adenosine
monophosphate
AMP
Guanosine, A
Guanosine
monophosphate
GMP
Adenylate phosphorylations
Structures of pyrimidine nucleotidess
Base Formula
Base
(X=H)
Cytosine, C
Nucleoside
X=ribose or
deoxyribose
Cytidine, A
Nucleotide
X=ribose phosphate
Cytidine
monophosphate
CMP
Uracil, U
Uridine, U
Uridine
monophosphate
UMP
Thymine, T
Thymidine,
T
Deoxy-thymidine
monophosphate
TMP
Nucleotide nomenclature
{ Nucleotides are given distinct
abbreviations to allow easy
identification of their structure and state
of phosphorylation.
{ The monophosphorylated form of
adenosine (adenosine-5'monophosphate) is written as, AMP.
{ The di- and tri-phosphorylated forms are
written as, ADP and ATP, respectively.
August2010
HBC108/2010
UON
EGK
30
Nucleotide- acid anhydride bonds
{ The use of these abbreviations assumes that
the nucleotide is in the 5'-phosphorylated
form.
{ The di- and tri-phosphates of nucleotides are
linked by acid anhydride bonds.
{ Acid anhydride bonds have a high ΔG for
hydrolysis imparting upon them a high
potential to transfer the phosphates to other
molecules.
August2010
HBC108/2010
UON
EGK
31
Deoxyribonucleotides
{ The nucleotides found in DNA are
unique from those of RNA
{ The ribose exists in the 2'-deoxy form
and the abbreviations of the nucleotides
contain a d designation.
{ The monophosphorylated form of
adenosine found in DNA
(deoxyadenosine-5'-monophosphate) is
written as dAMP.
August2010
HBC108/2010
UON
EGK
32
Deoxynucleotides
{ The nucleoside uridine is never found in
DNA and thymine is almost exclusively
found in DNA.
{ Thymine is found in tRNAs but not
rRNAs nor mRNAs.
{ There are several less common bases
found in DNA and RNA.
August2010
HBC108/2010
UON
EGK
33
Learning check 1
{ Draw the structures and name the di-
and tri- nucleotides derived from the
five bases
{ Show the abbreviated name for each
August2010
HBC108/2010
UON
EGK
34
August2010
HBC108/2010
UON
EGK
35