* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Galaxy clusters - University of Iowa Astrophysics
Gamma-ray burst wikipedia , lookup
X-ray astronomy satellite wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Space Interferometry Mission wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Chronology of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Negative mass wikipedia , lookup
Dark matter wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Astrophysical X-ray source wikipedia , lookup
Physical cosmology wikipedia , lookup
High-velocity cloud wikipedia , lookup
Globular cluster wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Observable universe wikipedia , lookup
Gravitational lens wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
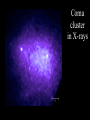
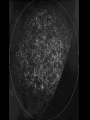
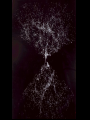
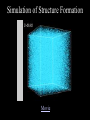
The Large Scale Structure of the Universe • Clusters of galaxies • X-rays from clusters of galaxies • Sheets and voids Our Galaxy is a member of a small cluster called the Local Group Stephane’s Quintet Virgo cluster Abell 2218 Coma cluster Virial Theorem • For gravitationally bound system, 2 K U 0 • Where K is kinetic energy and U is potential • Check for planet orbiting star GMm U r mv K 2 2 GM v r mv2 GMm GM GMm 2K U 2 m 0 2 r r r For Cluster • Kinetic energy 1 1 2 K mi vi M v 2 2 i 2 • Where mi, vi are mass, velocity of each galaxy and M, <v2> are total mass, average velocity • How to find <v2>? • Can measure only line of sight velocity • Note <v2> = <vx2 + vy2 + vz2> = 3 <vz2> = 32 where is the “velocity dispersion” For Cluster • Kinetic energy • Potential energy 3 K M 2 2 GM 2 U 0.4 rh where rh = “half-light radius” • Use virial theorem 2K+U = 0 to find 2 3 GM 2 M 2 0.4 0 2 rh M 7 .5 2 rh G For Coma Cluster • rh = 1.5 Mpc • = 880 km/s • Calculate M = 2×1015 M • Note that this includes dark matter • Mass to light ratio of cluster is 250 M/L Coma cluster in X-rays Coma cluster • X-ray emitting gas is at 100,000,000 K. • The total X-ray luminosity is more than the luminosity of 100 billion Suns. • From this, the amount of X-ray emitting gas can be calculated to be 2×1014 M • The mass of X-ray emitting gas is greater than the mass in all the stars in all the galaxies in the cluster and about 10% of the total mass. Gravitational lens Gravitational lenses • By measuring multiple images of one source, we can figure out the total mass in the lens. This provides an independent confirmation of dark matter. • A lense can act as a huge telescope. The deepest images of the most distant galaxies are obtained with clusters acting as gravitational lenses. The red Galaxy is 13 billion light years away. We are seeing it 750 million years after the Big Bang. Large Scale Structure • Are clusters of galaxies the largest structures in the Universe? Million galaxies Redshift survey Large Scale Structure • Galaxies and clusters of galaxies are organized on irregular sheets separated by voids containing few galaxies. • The density fluctuations seen in the cosmic microwave background are likely the seeds for the formation of the sheets, clusters, and galaxies. • How that process occurs is now being worked out. Simulation of Structure Formation Movie Review Questions • How can we measure the mass of a cluster of galaxies? • At what wavelength do galaxy clusters glow brightest? • On the largest scales, how are galaxies arranged?