* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy and Temperature
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Compressed air energy storage wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Micro combined heat and power wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs free energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
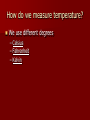
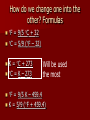
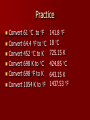
Energy What is energy and how does it fit into chemistry? Energy is the capability to do work. Many chemical reactions either create or release energy when they occur. Forms of energy include: – – – – – – Chemical – energy stored in chemical bonds Mechanical – energy involved in motion Electrical – energy involved in electricity Light – energy that involves light Sound – energy that involves sound Heat – energy transferred between objects that are different temperatures Energy Transfer Energy can be transferred in numerous ways: – Electric current in a wire – electrical energy – Beam of light – light energy – Peddling a bicycle – mechanical energy – A candle – thermal and light energy Gasoline is placed into your car. The engine of your car ignites the gasoline to produce heat. The heat it creates, makes the gases expand that push pistons, which makes your car move. Chemical (gas) heat mechanical So, as you can see, energy is usually transferred from one type of energy to another The Energy Law Law of conservation of energy – During any physical or chemical change, the total quantity of energy remains constant – In other words, energy cannot be created or destroyed. Environment around the Experiment Location of the Experiment Total amount stays the same; it is just transferred from system to surroundings Endothermic Verses Exothermic Reactions First notice the root of the word, Thermic meaning heat or energy Next, look at prefix: – Endo – In – Exo - Out Therefore Endothermic refers to any change in matter in which energy is absorbed Exothermic refers to any change in matter in which energy is released Measuring Heat Energy The English measurement for measuring energy is the calorie – the amount of thermal energy needed to raise the temperature of 1.0 grams of water by 1C. The SI unit for measuring all energy transfers is joules (N.m), abbreviated as J 4.18 joules = 1.0 calories 67.3 Examples: 16.1 calories = ______ joules 13.5 56.3 J = ________ calories Temperature verses Heat Temperature and heat are not synonyms. Heat is the transfer of energy between objects that are at different temperatures from the object with the higher temperature to the object with the lower temperature. Temperature is the measure of how “hot” or “cold” something is. More specifically, temperature is the average kinetic energy of the particles in an object. Temperature verses Heat Temperature is an intensive property – does not depend on the amount of the substance. Heat is an extensive property – the energy that can be transferred depends on the amount of a substance one has. In other words, a pitcher and glass can be filled with water at the same temperature, but the pitcher of water can transfer more energy. How do we measure temperature? We use different degrees – Celsius – Fahrenheit – Kelvin How do we change one into the other? Formulas F = 9/5 C + 32 C = 5/9 (F – 32) K = C + 273 C = K – 273 Will be used the most F = 9/5 K – 459.4 K = 5/9 (F + 459.4) Practice Convert Convert Convert Convert Convert Convert 61 C to F 64.4 F to C 452 C to K 698 K to C 698 F to K 1054 K to F 141.8 F 18 C 725.15 K 424.85 C 643.15 K 1437.53 F