* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download KE and PE - Fort Bend ISD
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
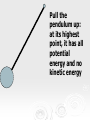
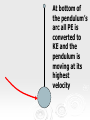
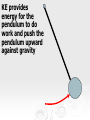
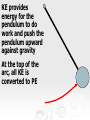
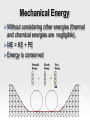
Do Now When a woman stands with two feet on a scale, the scale reads 400 N. When she lifts one foot, what does the scale read and why? 1 Energy Energy the ability to do work. Unit is Joules. There are two types of Energy that we will be talking about: Kinetic Energy – The energy in motion Potential Energy – stored energy Kinetic Energy Kinetic energy (KE ) - the energy an object possesses due to its motion. 1 2 KE mv 2 Example 1 Potential Energy When work is done a resistive force, potential energy (PE) is created equal in magnitude to the work done. PE = mgh Potential energy is sometimes called stored kinetic energy. Potential Energy Potential energy is stored energy. Anytime a particle or object is forced to maintain a position in which it would not naturally exist has potential energy. This natural position is known as equilibrium. Types of Potential Energy (mechanical) Gravitational Potential Energy Elastic Potential Energy Types of Potential Energy (non-mechanical) Electrical Potential Energy Chemical Potential Energy Example 2 Mechanical Energy You can have an energy system with both KE and PE present at the same time. (ignore friction) Ex:Pendulum • A pendulum system shows the interaction of kinetic and potential energy Pendulum at Rest: No kinetic and no potential energy Pull the pendulum up: at its highest point, it has all potential energy and no kinetic energy As it moves through its arc the pendulum’s PE is converted to KE Both PE and KE are present at the same time. At bottom of the pendulum’s arc all PE is converted to KE and the pendulum is moving at its highest velocity KE provides energy for the pendulum to do work and push the pendulum upward against gravity KE provides energy for the pendulum to do work and push the pendulum upward against gravity At the top of the arc, all KE is converted to PE 16 Mechanical Energy Without considering other energies (thermal and chemical energies are negligible), ME = KE + PE Energy is conserved Conservation Law In the absence of friction or work, the total mechanical energy remains the same. This is statement is called the Law of Conservation of Mechanical Energy. KEi PEi KE f PE f Transformation from GPE to KE of a Falling Object 100% GPE 0 % KE 75 % GPE 25% KE 50 % GPE 50% KE 25% GPE 75% KE 0% GPE 100% KE Example 3 What is the velocity of a dropped 4.5 kg bowling ball the instant it hits the ground if it is dropped from a height of 13.6 m? Example 4 A diver dives off a platform 50 m above a tank of water. If he has a mass of 56 kg what will be his kinetic energy, potential energy and speed a) 10 m below the top of the platform b) 30 m below the top, and c) the instant he hits the water? Example 5 An 8.0 kg flower pot falls from a window ledge 12.0 m above a sidewalk. (a) What is the kinetic energy of the pot just as it reaches the sidewalk? (b) Using energy considerations only, determine the speed of the pot just before it strikes the walk.