* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1 The motion of many objects involves a combination of kinetic and
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
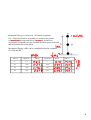
Conservation of Energy Date ______ The motion of many objects involves a combination of kinetic and potential energy. A pendulum swings back and forth At the highest point of its swing there is only gravitational potential energy (GPE) associated with its position. At other point in its swing, the pendulum is in motion so it has kinetic energy as well. With objects with a simple motion like a pendulum a useful quantity, mechanical energy can be used. Mechanical energy is the sum of the kinetic and potential energy. 1 Mechanical Energy is Conserved. (If friction is ignored.) If a 1.5 kg ball located on a lab table 1.0 m above the ground is knocked off the edge and falls to the ground, because the acceleration is constant you can calculate the linear speed of the ball and the distance that is has fallen. Mechanical Energy (ME) can be calculated using the equations for GPE and KE Time (s) Height (m) GPE (J) Speed (m/s) KE (J) ME (J) 0 0 1.0 0.1 0.95 0.98 0.2 0.80 1.96 0.3 0.56 2.94 2 In the absence of friction, the total mechanical energy remains the same. The amount of mechanical energy remains constant, mechanical energy itself can change form. As the ball falls off the table the gravitational potential energy is converted into kinetic energy. If the ball was thrown up in the air, the kinetic energy would be converted into gravitiational kinetic energy. Initial mechanical energy = Final mechanical energy MEi = MEf 3 A child and a sled with a combined mass of 50.0 kg slide down a frictionless hill that is 7.34 m high. If the sled starts from rest, what is its speed at the bottom of the hill? 4 Mechanical energy is not conserved in the presence of friction. For example, when sanding wood a force must be applied to keep the block moving. The friction between moving sanding block and the surface causes the kinetic energy of the block to be converted into a nonmechanical form of energy, thermal energy. This is observable because the sanding block and the surface become warmer. In the presence of friction, mechanical energy is not conserved because energy is converted into nonmechanical energy. 5 Total energy is ALWAYS conserved. Energy cannot be created or destroyed; it may be transformed from one form into another but the total amount of energy never changes. Energy Mechanical Kinetic Nonmechanical Potential Gravitational Elastic 6 Match the types of kinetic energy with correct definition Rotational Thermal Translational Sound Energy due to linear motion __________________ Energy due to an object rotating around its center of gravity _________________ Energy caused by the vibration of particles in matter _________________ Energy due to the motion of particles in matter ___________________ 7 Match the types of potential energy with correct definition Gravitational Nuclear Chemical Electrical Elastic Energy stored in chemical bonds _______________ Energy due to the position of electrical charges _______________ Energy that depends on position relative gravitational source ________________ Energy that is stored in an object that is stretched, compressed or coiled _______________ Energy stored in atomic nuclei __________________ We can't forget ___________________ energy which is energy that travels through space as waves. 8 Energy is usually seen when it is being transformed from on form to another. This is called an energy trail. Examples: 9 10