* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 4
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
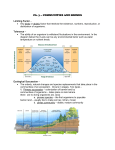
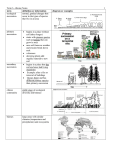
4-1 The Role of Climate Organisms vary in their “ideal” conditions Also vary in tolerance to change Many of these conditions or changes refer to climate/weather Weather vs. Climate Weather: conditions at a particular time and place Climate: average conditions in a particular region Effected by: atmosphere, latitude, winds, currents, precipitation, etc. Greenhouse Effect Natural situation in which heat is retained by layer of gases (CO2, methane) Atmosphere acts as a natural insulator Would be 30 degrees cooler without Latitude Polar zones- always cold Temperate zones- varies hot/cold Tropical zones- always hot Heat transfer by: Water- currents Air- hot air rises/cool air falls (winds) 4-2 What shapes an ecosystem? Habitat: area where an organism lives Made up of: Biotic factors: biological influences Competitors, predators, prey Abiotic factors: nonliving influences Climate, nutrient availability Niche All factors that influence an ecosystem and how the organism uses them The “role” of an organism Competition Exclusion Principle: no 2 organisms can have the same niche Ex: warbler bird Community Interactions Competition: attempt to use same resource at same place/same time Predation: one organisms feeds on another Symbiosis: two species in a relationship together Types of Symbiosis Mutualism: both benefit Ex: flowers and insects Commensalism: 1 benefits, other not effected Ex: barnacle and whale Parasitism: 1 benefits, other is harmed Lives on/inside “host”- does NOT kill Ex: tapeworm, ticks Ecological Succession Gradual change after a disturbance (natural or man-made) Primary: succession when there is no soil Pioneer species: first to populate an area Secondary: succession when soil is still there 4-3 Biomes Biome: group of communities covering a large area Characterized by: soil, climate specific plants and animals The Biomes: 1. Tropical rain forest (ex: Brazil) Hot and wet Ferns, monkeys, toucans 2. Tropical dry forest (ex: India) Warm with wet and dry seasons Deciduous trees, tigers, elephants 3. Tropical savanna (ex: Kenya) Warm with seasonal rain, lightning fires Grasses, shrubs, lions, hyenas 4. Desert (ex: Arizona) Low precipitation (dry), variable temps. Cactus, snakes, lizard 5. Temperate grassland (ex: Texas) Hot/cold seasons, average precipitation, fertile soil Grasses, bison, grasshoppers 6. Temperate woodland (ex: Los Angeles) Hot, dry summer and cool. wet winter Evergreens, coyote, mountain lion 7. Temperate forest (ex: Philadelphia) Moderate winter, warm summer, year round rain Moss, coniferous trees, deer, squirrel 8. Northwestern coniferous forest (ex: Seattle) Mild temps., cool, dry summer- otherwise wet Conifer trees (redwood), bears 9. Boreal forest/ Taiga (ex: northern Europe) Long, cold winter, short, dry summer Fir trees, lynx, moose 10. Tundra (ex: Alaska) Permafrost- layer of permanent frozen soil Short grass, caribou, owl Other land areas: Mountain ranges (ex: WA state) Factors change with elevation Polar ice caps (ex: Antarctica) Border tundra Polar bears, insects 4-4 Aquatic Ecosystems Grouped by abiotic factors Depth (amount of light) Nutrients available O2 available Freshwater (only 3%) Flowing water- organisms adapt to the flow Standing water- flow in and circulation of nutrients, O2 and heat Freshwater wetlands- bogs, marshes and swamps- very diverse! Estuaries Wetlands where rivers meet the sea Detritus = lots of biomass Ideal for feeding, breeding, nesting, spawning Ex: salt marshes and mangrove swamps Salt tolerant Marine Ecosystems Photic zone: well-lit upper layer Aphotic zone: dark (200m and deeper) Marine Zones 1. intertidal Extreme changes with tides Hot and dry to covered in water Waves and currents 2. coastal ocean Low tide mark to continental shelf Photic areas = phytoplankton Ex: kelp forests and coral reefs 3. open ocean Continental shelf outwards Low nutrients = low productivity 4. benthic- along ocean floor Benthos: organisms that live here Food depends on depth: photic producers,, detritus, chemosynthesis