* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review Lecture 5
Planet Nine wikipedia , lookup
Earth's rotation wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Space: 1889 wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Giant-impact hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
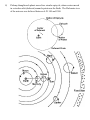
Review Lecture 5 1) Calendar 46 B.C. Julius Caesar - 365days + leap year every 4 years 1582 A.D. Gregory XIII - subtracted 10 days from the calendar, cut leap year in centuries not divisible by 400, this is close to a synodic year = 265.2422 days 2) Some distances 3) History Earth’s radius Sun’s radius Earth - Moon Earth - Sun Moon’s radius rearth = 6.4 x 106 m rsun = 6.95 x 108 m ~ 100 rearth 3.8 x 108 m 1 A.U. = 1.5 x 1011 m rmoon = 1.7 x 106 m Thales ~ 600 B.C., predicted eclipses from Saros cycle. Pythagorus ~ 500 B.C., said Earth was spherical from observation of lunar phases. Aristotle ~ 350 B.C. proposed Earth at center of universe. This is the geocentric world view of Solar System. Aristarchus ~ 250 B.C. estimated all the distances above. He claimed the Sun was the center of the universe. This is the heliocentric world view. Eratosthenes ~ 200 B.C., estimated rearth from shadows cast on the Moon during a lunar eclipse. Hipparchus ~ 130 B.C., discovered the precession of the north celestial pole. Ptolemy ~ 150 A.D., explained motion of the Sun, planets, and Moon with Epicycle Theory. This is the Earth at center of universe theory = geocentric world view. Copernicus ( 1473-1543) published De Revolutionibus (1543) to explain heliocentric world view. Tycho Brahe (1546-1630) built first modern European observatory. Johannes Kepler (1571-1630) Brahe’s assistant calculated planetary positions using heliocentric assumption. Isaac Newton (1642-1727) explained all by introducing the Universal Law of Gravitation. 4) Ptolemy thought each planet moved in a circular epicycle, whose center moved in a circular orbit (deferent) around a point near the Earth. The Ptolemaic view of the universe was believed between A.D. 100 and 1500. 4) Kepler’s Laws and Planetary Motion (1) Law or Orbits - orbits are elliptical with sun at one focus (2) Law of Areas - A line joining a planet to the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal times (3) Law of Periods - (orbital radius)3 ~ (orbital period)2 (1) Law of Orbits - All planets move in elliptical orbits with the sun at one focus. e = eccentricity a = semi-major axis b = semi-minor axis for an ellipse: r1 + r2 = 2a = constant x2 y2 + =1 a2 b2 b = a 1 − e2 A few values for comparison: e = .093 or b = .996 a only a .15% difference from sphericity Mars e = .007 Venus e = .017 Earth Jupiter e = .048 (2) Law of Areas - A line joining the planet to the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal times. For the areas to be the same in the same time implies that the velocities V >> v. This says that a comet with a very elliptical orbit will spend most of its time at the farthest point from the sun. (3) Law of Periods - The square of the period of any planet is proportional to the cube of the semimajor axis of its orbit. Name of Planet Mean Distance from the Sun Period T2 Eccentricity R3 m A.U. Sec Earth Years Mercury 5.79 x 1010 0.387 7.6 x 106 0.241 0.2056 1.01 Venus 1.08 x 1011 0.723 1.94 x 107 0.615 0.0068 1.02 Earth 1.50 x 1011 1.000 3.16 x 107 1.000 0.0167 1.00 Mars 2.28 x 1011 1.574 5.94 x 107 1.881 0.0934 1.01 Jupiter 7.78 x 1011 5.204 3.74 x 108 11.86 0.0485 1.02 Saturn 1.43 x 1012 9.58 9.35 x 108 29.6 0.055 1.01 Uranus 2.86 x 1012 19.14 2.64 x 109 83.7 0.047 1.01 Neptune 4.52 x 1012 30.2 5.22 x 109 165.4 0.008 1.01 Pluto 5.90 x 1012 39.4 7.82 x 109 248 0.249 1.01