* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The coronary arteries supply heart muscle with
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
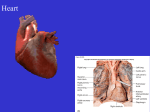
Transport • 6.2.1 Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the heart. • Care should be taken to show the relative wall thickness of the four chambers. Neither the coronary vessels nor the conductive system are required. • 6.2.2 State that the coronary arteries supply heart muscle with oxygen and nutrients. • 6.2.3 Explain the action of the heart in terms of collecting blood, pumping blood, and opening and closing of valves. • A basic understanding is required, limited to the collection of blood by the atria, which is then pumped out by the ventricles into the arteries. The direction of flow is controlled by atrio-ventricular and semi-lunar valves. • 6.2.4 Outline the control of the heartbeat in terms of myogenic muscle contraction, the role of the pacemaker, nerves, the medulla of the brain and epinephrine (adrenaline). • Histology of the heart muscle, names of nerves or transmitter substances are not required. Eliciting prior knowledge: QUIZBUSTERS Hold your hand in front of you and make a fist. Squeeze and relax. How long can you do this for? • The walls of the heart are made of cardiac muscle (MYOCARDIUM) • Only found in heart • Never tires but can’t tolerate lack of O2. Activity: Prior knowledge Drag the labels to the right place to complete the diagram and the key 6.2.1 Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the heart. Care should be taken to show the relative wall thickness of the four chambers. Neither the coronary vessels nor the conductive system are required. Structure of the heart What structure? Blood flow through the heart 6.2.2 State that the coronary arteries supply heart muscle with oxygen and nutrients. The coronary arteries supply heart muscle with oxygen and nutrients 6.2.3 Explain the action of the heart in terms of collecting blood, pumping blood, and opening and closing of valves. Summary: Atria collect blood from veins. Atria contract, atrioventricular valves open. Blood is pumped into ventricles. Ventricle contracts, atrioventricular valves close and semilunar valves open. Blood is pumped into arteries, semilunar valves close. Cycle repeats. A basic understanding is required, limited to the collection of blood by the atria, which is then pumped out by the ventricles into the arteries. The direction of flow is controlled by atrioventricular and semilunar valves. 6.2.4 Outline the control of the heartbeat in terms of myogenic muscle contraction, the role of the pacemaker, nerves, the medulla of the brain and epinephrine (adrenaline). Histology of the heart muscle, names of nerves or transmitter substances are not required. Summary: 1. Heart muscle can contract by itself (myogenic muscle contraction). 2. Pacemaker initiates contractions (The pacemaker is a group of cells in the wall of the right atrium that sends out electrical impulses to initiate contraction) 3. One nerve carries messages from the brain to the pacemaker to speed up the beating of the heart. 4. One nerve carries messages from the brain to the pacemaker to slow down the beating of the heart. 5. Adrenaline signals the pacemaker to increase the beating of the heart.