* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 8 Test Review – Structure of Living Things Integumentary
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
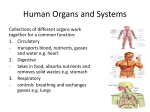
Unit 8 Test Review – Structure of Living Things Integumentary System What are the major organs? Skin, Hair, Nails What are the 4 main functions? Protection Touch Vitamin D formation Regulates body temperature The skin is the __ Largest ___ organ of the integumentary system/body! Three tissue layers of the skin: 1. Epidermis 2. Dermis 3. Fatty Layer Muscular System What are the major organs? Muscles What is the function? Provides movement for the body What is the difference in voluntary and involuntary muscles? Voluntary you choose to move these muscles Involuntary the muscle move on their own without being told to move List the three types of muscle tissue and briefly describe each one. 1. Skeletal: moves bones, voluntary, contract quickly and tire easily, striated 2. Smooth: found in the digestive tract, involuntary 3. Cardiac: found only in the heart, involuntary, striated Skeletal System What are the major organs? Bones What is the function? Shapes and supports body, protection, movement, makes red blood cells Describe the structure of a bone. Periostium – outside layer that covers and protects bone nd Compact Bone 2 layer which is tough, hard bone that can heal itself when broken. rd Spongy Bone – 3 layer which contains red marrow Marrow – soft, inner center of bones makes red blood cells What is a joint? Any place where two or more bones join together. List the 5 types of joints and give an example of each. 1. Fixed Joint (ex: Skull) 2. Pivot Joint (ex: neck) 3. BallandSocket Joint (ex: hip, shoulder) 4. Hinge Joint (ex: knee, elbow) 5. Sliding Joint (ex: wrist, ankle) Digestive System What are the major organs? Mouth, esophagus, stomach, small & large intestines, liver, gall bladder, rectum, anus What is the function? Break down food into nutrients for the body Digestive System continued… Explain the following and give an example of each. ● Chemical Digestion Chemical change – food is turned into mushy substance using stomach acid, saliva, bile, etc ● Mechanical Digestion .Physical change – food is chewed, mixed, or churned What is the difference between an accessory organ and a digestive tract organ? Accessory organ – food DOES NOT pass through these organs, the organ still helps the digestive process Digestive tract – food DOES pass through these organs List the steps of digestion in order, starting with the mouth. mouth → esophagus → stomach→ small intestine → large intestine → rectum → anus Explain the difference between the large and small intestines. Which one absorbs the most nutrients? SI – food enters this long tube first which is lined with villi that increase the surface area for MAXIMUM nutrient absorption. LI – undigested chyme enters the LI after leaving the SI. The LI absorbs water and any nutrients undigested by the SI Circulatory System What are the major organs? Heart, Blood, Blood Vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries) What is the function? Circulates nutrients and oxygen to the cells and waste and carbon dioxide away from the cells. The heart has 4 chambers, 2 __ Atria __ on the top and 2 _ Ventricles _ on the bottom. Three types of blood vessels: 1. arteries 2. veins 3. capillaries Circulatory System continued… Explain the 4 parts of blood. 1. Plasma – watery part of blood 2. Red blood cells – carries oxygen to the cells 3. White blood cells – fight bacteria and viruses 4. Platelets – cell fragments that work to form a scab Lymphatic/Immune System What are the major organs? Lymph nodes, spleen What is the function? Makes white blood cells and protects our body from viruses and disease What is the significance of White Blood Cells? They are our bodies fighters against viruses and disease. Respiratory System What are the major organs? Nose, mouth, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, alveoli What is the function? Breathes in oxygen for use and breathes out carbon dioxide waste List the steps of respiration (path of air) in order beginning with the mouth/nose. mouth/nose → pharynx → larynx → trachea → bronchi → alveoli Excretory System What are the major organs? Kidneys, bladder, ureter, urethra What is the function? Collects and removes cellular waste from the body in the form of urine Nervous System What are the major organs? Brain, spinal cord, nerves What is the function? Sends messages throughout the body What is a neuron? Cells that carries nerve impulse information. Explain the following: ● Central Nervous System Includes the brain and spinal cord. Brain is the control center of the body and the spinal cord links the brain with body nerves. ● Peripheral Nervous System The nerves branch from the CNS to the rest of the body. What are the five senses? Vision, touch, hearing, smell, and taste Reproductive System What is the purpose of the reproductive system? The purpose of sexual reproduction is to increase the diversity of traits within a species. What are the major organs of the MALE reproductive system? Hormone? Organs: penis and testes Male hormone: testosterone What are the major organs of the FEMALE reproductive system? Hormone? Organs: ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina Female hormone: estrogen Endocrine System What are the major organs? Glands What is the function? Glands produce hormones for the body List and explain the 5 glands of the endocrine system. 1. Pituitary controls all glands which controls growth, water balance and blood pressure 2. Adrenal produces adrenaline which controls “fight or flight” response 3. Pancreas – produces insulin which regulates blood sugar 4. Thyroid – regulates metabolism 5. Ovaries & Testes – releases sex hormones which regulate puberty. Adaptations List the 3 specific adaptations we talked about and give reasons for each adaptation. 1. Fish have gills that help with their respiration (breathing). 2. Birds have light, hollow bones that help with flight. 3. Plants have Xylems that helps circulate water and nutrients throughout the plants . Give an example of an adaptation made by an organism. (You may not use any that are listed above.) Answers will vary.