* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Kingdom
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Lilioid monocots wikipedia , lookup
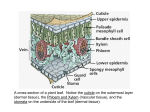
Plant Kingdom Characteristics of Plants: . Plants are: 1 Cell Type: Eukaryotic a. . Number of cells that make up plants? Multicellular b c. How do plants get their energy? autotrophic / photosynthesis d. Cell Walls are made of : Cellulose • • • • • • • Have True Roots: with mycorrhizae Reproduction on land: pollen carries sperm Vascular tissue – transport water Prevent water loss: • Cuticle – waxing layer on leaves • Stomata – pores in leaves that allow for gas exchange 3. Have Root like structures, Stem like structures, leaflike structures Seedless Vascular Plants • . Ferns Produce spores • Has vascular tissue (simple) • Have true roots, stems, • leaves moss and fern comparison activity.notebook Plant Diversity Activity.notebook Monocots vs. Dicots answers behind pictures Dicot Monocot How are they different? Which one is Monocot and which is Dicot? Rule: Monocots have a fibrous or branching root system, and dicots have a main taproot. Monocots vs. Dicots answers behind pictures Dicot Monocot How are they different? Which one is Monocot and which is Dicot? Rule: Monocots have a fibrous or branching root system, and dicots have a main taproot. Monocots vs. Dicots answers behind pictures Dicot Monocot How are they different? Which one is Monocot and which is Dicot? Rule: Monocots have flower parts in multiples of 3, where dicots have flower parts in multiples of 4 or 5. Monocots vs. Dicots answers behind pictures Monocot Dicot How are they different? Which one is Monocot and which is Dicot? Rule: Monocots have flower parts in multiples of 3, where dicots have flower parts in multiples of 4 or 5. Monocots vs. Dicots answers behind pictures Dicot Monocot How are they different? Which one is Monocot and which is Dicot? Rule: Monocots have flower parts in multiples of 3, where dicots have flower parts in multiples of 4 or 5. Monocots vs. Dicots answers behind pictures Dicot Monocot How are they different? Which one is Monocot and which is Dicot? Rule: Monocots have parallel leaf venation, and Dicots have a branching leaf venation n O lutio o v E ts Plan ts: Plan y Earl f The first plants evolved from an organism much like the multicellular green algae of today Evolutionary realtionship among various plants flowers:seeds enclosed in fruit seeds Water- conducting tissue Place the proper plant in its position on the cladogram Plants on Earth today Conebearing plants 760 species Ferns and their relatives 11,000 species Mosses and their relatives 15,600 species Flowers 1. Flower is a reproductive structure!!! 2. Attracts pollinators like birds, insects, bats, etc. Angiosperms and their Divisions Click to reveal answers What are some parts of the flower? Petiole Sepals Petals Carpel Pistol Stigma Stamen Filament Anther Flower Diagram Petal Style Anther Ovule Stigma Ovary Receptacle Filament Stamen Pistil Sepal Style Ovule Ovary Flower Part Functions Style Receptacle Pistil Ovule The long neck that connects of the pistil Protect the flower before it opens The base of the flower The male portion of the flower Sepal The female portion of the flower Ovary To attract pollinators. Stigma Produces pollen Petal Anther Stamen Filament Produces the eggs Sticky part of the pistil that the pollen falls on to The long neck of the stamen Protects the embryo and becomes the fruit