* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Epithelial Tissues
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Stem-cell therapy wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Induced pluripotent stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Nerve guidance conduit wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
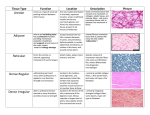
“Epi”= upon “Pseudo”= false “Squam” = scale “Strat”= layer Simple- one layer Stratified- multiple layers Cuboidal- cube shaped Columnar- rectangle shape- column Squamous- flat shape * a group of cells with specialized functions Types: 1) 2) 3) 4) Epithelial Connective Muscle Nerve Covers all free body surfaces Characteristics: Lacks blood vessels, attached to a basement membrane, replaced continuously Functions: protects, secretes, absorbs, excretes Simple Squamous- single layer of flat cells Found: lungs, lines blood vessels, body cavities Simple cuboidal- single layer of cube shaped cells Found: kidneys and other glands Simple columnar- single layer of elongated cells, nucleus is located near bottom of cell Contains microvilli- helps with absorption Contains goblet cells- secretes mucus Found: uterus, digestive tract Pseudostratified columnar- single layer of cells that look layered due to nuclei placement cilia- to move mucus or sex cells Found: reproductive system, respiratory system Stratified Squamous- many flat layers of cells, protects Found: skin, mouth, throat, vagina, anal canal Stratified cuboidal- layers of cube shaped cells, protects Found: mammary glands, sweat glands, salivary glands, pancreas Stratified columnar- top layer is elongated, bottom layers are cube shaped, protects Found: male urethra, pharynx Transitional- specialized to change shape under tension Found: Bladder General Characteristics: Support Protection Fills spaces Stores fat Produce blood cells Protect against infection Helps repair damaged tissue Cells are separated by matrix (intercellular material) Types of cells: Fibroblasts- produce collagenous and elastic fibers Macrophages- are phagocytes (eat other cells and materials) Mast cells- help with blood clotting and immune response Types of fibers in CT: Collagenous fibers- thick fibers made of collagen, grouped in parallel bundles, holds tissues together, found in tendons Elastic fibers- thin fibers, stretch easily, build networks, made of elastin Reticular fibers- very thin fibers, delicate support Forms delicate, thin membranes Has many fibroblasts Has a lot of collagenous and elastic fibers Function: Binds skin to tissue beneath and provides nourishment to epithelial tissue, fills space between muscle Type of loose connective tissue, Fat Function- protection, traps heat, and energy stores in the body Found: beneath skin, around vital organs, around joints. Note how nucleus is pushed to the side. Made of tightly packed collagenous fibers Function: Rigid structure, connects tissues Found: tendons, ligaments, white of eyes, deep layer of skin Cartilage- rigid yet partially flexible Function: provides support, protects, forms structure for developing bones 3 types of Cartilage Hyaline: Fine collagenous fibers, chondrocytes, intercellular matrix- looks like white plastic Found : ends of bone in joints, soft part of nose, rings of respiratory passage Elastic cartilage Made of dense network of elastic cartilage- flexible Found: makes framework for ears, and parts of larynx Fibrocartilage Very tough tissue, contains many collagenous fibers Shock absorbers Found between disks in vertebral column Osteocytes, Intercellular matrix contains mineral salts and collagen, which makes bone rigid and collagen reinforces the mineral components Function: structure, protection, provides framework Found throughout whole body in Skelton Cells suspended in fluid matrix (plasma), red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets Blood forms in red marrow of long bones Function: Transports, helps maintain stable internal environment Found: throughout body in blood vessels and heart chambers Characteristics: contract, move structures attached to them 3 Types: Skeletal, Smooth, cardiac Structure: Long cells (muscle fibers), striations Function: attached to bones and helps with movement, can move by voluntary action Muscle fibers contract when stimulated by nerves, then relax immediately. Structure: cells lack striations, short, spindle shaped Function: muscle that works involuntary, constricts/ contracts to move things Found: digestive system, bladder, blood vessels Structure: cells are striated and joined end to end, has an intercalated disk between muscle fibers Function: involuntary contractions in pumping blood Found only in heart Structure: neuron (basic cell) has axons and dendrites, neuroglial cells (supports and binds nervous tissue) Function: Sensitivity and conduction of nerve impulses Found: Brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves