* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nrsg 407 Disorders of the Endocrine Glands
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Graves' disease wikipedia , lookup
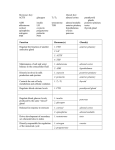
Disorders of the Endocrine Glands Nrsg 407 Function • Various glands in body • Secretes hormones • Transported throughout body Negative feedback • One hormone controls secretion of another • Last hormone in the pathway controls secretion of first hormone Pituitary gland • Master gland • Controls several organs and hormones • Works together with hypothalamus Pituitary Gland • Anterior or Adenohypophysis contains glandular tissue • Posterior or Neurohypophysis contains nervous tissue Anterior Pituitary Hormones Posterior Pituitary Posterior pituitary - SIADH • Lack of ADH [aka Syndrome of inappropriate ADH] or diabetes insipidus • Vasopressin (pitressin) • Act on renal tubules to promote reabsorption of water • Vasopressor effect (raise BP) Thyroid • 2 types of cells • Parafollicular cells – calcitonin • Follicular cells – composed of iodine atoms • Thyroxine (T4) • Triiodothyronine (T3) Thyroid cont’d • Regulates body metabolism • Thermal regulation • Regulation of physical/mental development Thyroxine hormone (T4) Triiodothyronine (T3) • Same as T4 • Converted once thyroxine enters cells • 1 iodine atom eliminated by enzymes • Binds to intracellular receptors in nucleus Thyrocalcitonin (Calcitonin) • Lowers plasma Ca and PO4 • Increases Ca deposits in bone • Not as important due to parathyroid Negative feedback mechanism • Low serum thyroxine incr TSH incr thyroxine maintain normal BMR Hypothyroidism • Poorly functioning thyroid (primary disease) OR • Low secretion of TSH by pituitary gland (secondary cause) • Most common: chronic autoimmune thyroiditis – Hashimoto’s disease Myxedema • • • • • • Fatigue General weakness Muscle cramps Dry skin Bradycardia Cold intolerance Hyperthyroid • • • • • • Most Common: Graves’ disease (primary) Oversecretion of thyroid Increased body metabolism Tachycardia Anxiety Heat intolerance Adrenal Cortex Glucocorticoids (Sugar) Cortisol Sex hormones (Sex) Androgens Adrenal Cortex Mineralcorticoids (Salt) Aldosterone Mechanism of Control Negative feedback mechanism Glucocorticoids and androgens: Anterior pituitary release of ACTH stimulates adrenal glucocorticoid and androgen Mechanism of Control Mineralcorticoids: RAAS Hormone: Aldosterone produced Promote sodium reabsorption and potassium excretion Hypofunction • Primary • Destruction by systemic infectious disease • Cancer • Autoimmune process • Secondary • Decrease ACTH or hypothalamus disease Hypofunction • • • • • • • Hypoglycemia Fatigue Hypotension Increased skin pigmentation Anorexia Vomiting diarrhea Hypofunction • Chronic primary adrenocortical insufficiency (Addison’s disease) • Deficiency of all 3 hormones • Rare – usually caused by autoimmune destruction Acute Adrenocortical Insufficiency • Caused when glucocorticoids abruptly withdrawn • Provide negative feedback to pituitary to stop secreting ACTH • No ACTH adrenal stops secreting endogenous glucocorticoids • Adrenal cortex shrinks (adrenal atrophy) Symptoms of Adrenal crisis • • • • • Nausea Vomiting Lethargy Confusion Coma / Shock Cushing’s Syndrome • Primary • Cortisol-secreting tumors • Secondary • Pituitary or hypothalamus tumor • ACTH secreting tumor • Iatrogenic • Overdosage of glucocorticoid Signs/Symptoms • • • • • • Hyperglycemia Protein tissue wasting Bruising Osteoporosis Peptic ulcers Delayed wound healing Signs/Symptoms • Abnormal fat distribution • • • • Truncal obesity Striae “Buffalo hump” Moon face • Acne • Mood/ personality changes Signs/Symptoms • Hypokalemia • Na and water retention • Decrease inflammatory response