* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemical Reaction
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
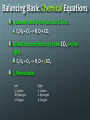
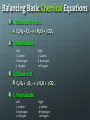
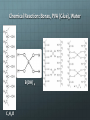
Chemical Chemical Engineering •It is the application of chemistry to converting raw materials and chemicals into usable and more valuable forms •2 Types •Process Engineering – Design plants, processes and machines that perform chemical reactions •Product Engineering – Formulate chemical substances Products of Chemical Engineering Chemistry Review: Basic Terms •Atom •Proton •Electron •Neutron •Atomic Number •Mass Number •Elements •Compound •Molecule - Basic, smallest unit of all matter - Positive particle in the atom’s nucleus - Negative particle outside the nucleus - Neutral particle in the atom’s nucleus - The number of protons in an atom - The number of protons and neutrons - Simple substances that consist of only one type of atom - Combination of elements - Smallest part of a compound Balancing Basic Chemical Equations 1. Write down the equation. C3H8 + O2 --> H2O + CO2 2. Write down the number of atoms on each side of the equation. Left -3 Carbon -8 Hydrogen -2 Oxygen Right -1 Carbon -2 Hydrogen -3 Oxygen Balancing Basic Chemical Equations 3. Leave H and O for last, do C first. C3H8 + O2 --> H2O + CO2 4. Add the coefficient 3 to the CO2 on the right. C3H8 + O2 --> H2O + 3CO2 5. Reevaluate. Left -3 Carbon -8 Hydrogen -2 Oxygen Right -3 Carbon -2 Hydrogen -6 Oxygen Balancing Basic Chemical Equations 6. Balance H next. C3H8 + O2 --> 4H2O + 3CO2 7. Reevaluate. Left -3 Carbon -8 Hydrogen -2 Oxygen Right -3 Carbon -8 Hydrogen -10 Oxygen 8. Balance O. C3H8 + 5O2 --> 4H2O + 3CO2 9. Reevaluate. Left -3 Carbon -8 Hydrogen -10 Oxygen Right -3 Carbon -8 Hydrogen -10 Oxygen Why is it important to balance equations? Law of Conservation of Mass: Matter is neither created nor destroyed During a chemical reaction, elements don’t appear or disappear but instead are just rearranged Number of atoms of each element must be equal on both sides of the equation Polymers •A POLYMER is a large molecule formed by smaller repeating molecules called MONOMERS •The process of binding monomers to form a polymer is called POLYMERIZATION •Polymers are naturally occurring and can also be made synthetically Sample Polymers PLASTIC PROTEIN RUBBER PAPER Concepts Applied to Activity Chemical Reactions Balancing Equations Polymers Activity: Polymer Balls •Main Ingredient: Polyvinyl alcohol based glue •Polyvinyl alcohol is a water-soluble polymer •Glue is made up of monomers bonded together to form the polymer Borax sodium tetraborate decahydrate Na2B4O7.10H2O Borax is the cross-linker in the experiment, it will connect the chains of polymers Chemical Reaction: Borax, PVA (Glue), Water Na2B4O7 + _H2O _NaOH + _H3BO3 Na2B4O7 + 7H2O 2NaOH + 4H3BO3 H3BO3 Boric Acid H3BO3 + 2H2O B(OH)- 4 + H3O+ B(OH)- 4 is the cross-linker Polyvinyl alcohol is C2H4O Chemical Reaction: Borax, PVA (Glue), Water B(OH)- 4 C2 H 4 O Activity: Polymer Balls Instructions: Stir and dissolve the 1 TEASPOON Borax powder in 1 CUP water. Set aside the mixture. Pour out 2 spoons of glue onto the paper plate and add one drop of the food coloring of your choice. Slowly pour 3 spoons of the Borax mixture into the glue and mix together. Don’t expect the Borax to mix completely with the glue. Roll the mixture around the Borax on the plate. Shape them into spheres.