* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Final - Courses
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
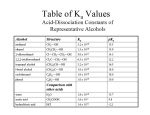
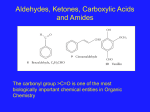
Organic Chemistry II Final Exam (200pts) Spring 2009 Name: Instructions: Answer all of the following questions. Please provide as much illustration and/or explanation as possible so that I can understand how you arrived at your answer. Please provide written detail and illustrations to answer the questions as completely as possible. The exam is open book, open note, but you may not refer to any other sources to prepare your answers. You have 3 hours to complete the exam. Exams are due at my office on Monday 5/11/09 by 12:00 noon. Long answer section – 15 questions, 12 pts each 1. A traditional view of carboxylic acids says that the formation of the resonance-stabilized carboxylate anion is responsible for their high acidity, and explains the difference in acidity of carboxylic acids and alcohols: Resonance-stabilization O O O O + H+ H3C OH H3C O H 3C O H 3C O No resonance stabilization RCH2-OH R-CH2-O- + H+ But a newer body of research says we should look instead at the molecules before deprotonation for the real explanation of the difference in acidity between carboxylic acids and alcohols. What might this explanation be, and which one do you think is correct? 1 2. Metabolism of arginine produces urea and the rare amino acid ornithine. Ornithine has an isoelectric point close to 10. Propose a structure for ornithine. Draw structures for this amino acid at pH 12 and pH 1. 3. The reaction of (CH3)3CH with Cl2 forms two products: (CH3)2CHCH2Cl (63%) and (CH3)3CCl (37%). Why is the major product formed by cleavage of the stronger 1° C-H bond? 2 4. Predict the number of signals expected (disregarding splitting) in the 1H spectrum of: a. o-chlorophenol (2-chlorophenol) b. dibutyl ether c. 1,1-dimethylcyclobutane 5. Draw stereoscopic views of each of the following molecules and label each stereogenic center as R or S: CH2NH2 CH2Br Cl H CHO CHO Cl H CH2NH2 Cl H CH2OH 3 6. Explain why fluoracetic acid has a lower pKa than acetic acid. O O F H3C OH Acetic acid C H2 OH Fluoroacetic acid 7. Draw the products, and the mechanism for producing them, for the following reaction: OH OCH2CH3 H+ O + CH3CH2OH O 4 8. Write the complete structures for the following peptides. Indicate the classification of each: neutral, acidic or basic a. Methionylthreonine b. Threonylmethionine c. arginylaspartate 9. Acetals can be synthesized from aldehydes and ketones, but this process requires a strong acid. Show why base-catalyzed acetal formation doesn’t work. 5 10. Consider the mechanism for the synthesis of ylides used in the Wittig reaction. Triphenylphosphine is used in this process but it is quite expensive. Trimethylphosphine is much cheaper, but unsuitable for making most phosphorous ylides – why? Use an illustration to help explain your answer. 11. Rank the following compounds in the order of increasing λmax and explain as completely as possible the reasons for your ranking: 6 12. Polymers and other large molecules are not very soluble in water, but their solubility increases if they contain charged groups. Casein is a protein in milk that contains many carboxylic acid groups on its side chains. Histones are proteins that are essential to the proper function of DNA. They are weakly basic due to the presence of side chains with –NH2 and =NH groups. Explain how the solubility of casein and histones in water varies with pH. 13. Acetic acid vs. acetamide, round 2. In addition to the presence of a carbonyl carbon, and two EN atoms attached to it (2 O’s in the case of acetic acid, and an O and an N in the case of acetamide) what structural feature of these molecules might help explain why acetic acid is more acidic than acetamide? O H3C O OH H 3C NH2 7 14. By what mechanism does aspirin prevent inflammation? 15. The following polypeptide is drawn in an unconventional manner. Label the N terminus and the C terminus, label the peptide bonds, and identify and label each amino acid present. CH3 H3CH2C C H O O H C COOH H N C H C HN CH2CH2 C C NH2 CH2NH2 O 8 Crossword puzzle – 1.5pts each, 30 pts possible (note this includes 10 extracredit points) 9