* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Uveitis and Topamax – Dr. Amir Hadayer
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
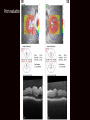
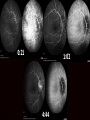
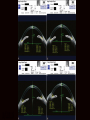
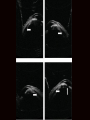
Uveitis & Phacodonesis Topamax Ophthalmology & Visual Sciences University of Louisville School of Medicine February, 2016 Presentation CC: Photopsia and blurry vision, OU, with recurrent headaches and tinnitus, 18 months. HPI: 20 yo while male hit his head on sand playing volley ball 18 months ago (? concussion). Symptomatic and diagnosed with post-traumatic stress syndrome and pseudotumor cerebri. Started on oral Diamox; changed to Topamax (50mg PO, b.i.d) on 8/2015; discontinued 12/2015. History POHx: None PMHx: None Meds: None Allergies: NKDA Ophthalmic Exam 20/60 BCVA 20/40 +1.5+0.5X180 M +3.00+1.00X90 full VF full full EOM full 4.5 Pupils 4.5 +APD 16 IOP 17 Alternating horizon nystagmus Ophthalmic Exam WNL No injection No KP L/L Conjunctiva Cornea WNL No injection No KP 2+ cells, 4+ flare A/C 1.5 cells, 2+ flare Iridophacodonesis Iris Iridophacodonesis Clear 1+ vitreous cells, ON edema + macular edema Lens Fundus Clear 2+ vitreous cells, ON edema + macular edema Prior evaluation 0:21 1/2016 1:02 4:44 Prior work up HVF: Enlarged blind spots ou OCT RNFL: Diffusedly increase RNFL thickness LP: Opening pressure 280. CSF content normal TSH,PTH: wnl Vit A: wnl FA/ICGA at UofL Assessment / Plan Impression: 1. Occult multifocal choroidites OU with secondary macular edema and optic disc edema 2. Iridiophacodenesis OU (secondary to Topamax) 3. Alternating horizontal nystagmus Plan: – Further diagnostic work up of occult multifocal choroiditis – 40 mg prednisone po qAM Topamax Ocular SE Topiramate (brand name Topamax) is an anticonvulsant (antiepilepsy) drug. In late 2012, topiramate was approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in combination with phentermine for weight loss. It is also Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved for, and most frequently prescribed for, the prevention of migraines Complications: Uveal effusion syndrome – – – – – – Angle Closure Glaucoma Acute myopia Uveitis Ciliary body edema Uveal effusion Ant. rotation of the lens and iris Pathophysiology Idiosyncratic effect: The most prevalent hypothesis is the hapten hypothesis. The reactive drug metabolites bind to the proteins on the zonular fibers of the lens and these altered proteins are perceived as foreign and induce an immune response. Unrelated to dosage Sulfonamides: Indapamide, Topiramate, Acetazolamide Side effects start within the first 2 weeks Treatment Stop the offending medication – Topiramate has a number of physiologic effects, including inhibition of voltage-gated sodium and calcium channels, augmentation of GABA-induced chloride flux, inhibition of glutamate-related excitatory neurotransmission and carbonic anhydrase Cycloplegia Corticosteroids IOP control if acute angle closure has occurred 1/2016 References 1. Senthil S, Garudadri C, Rao HBL, Maheshwari R. Bilateral simultaneous acute angle closure caused by 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. sulphonamide derivatives: A case series. Indian Journal of Ophthalmology. 2010;58(3):248-252. Mitra A, Ramakrishnan R, Kader MA. Anterior segment optical coherence tomography documentation of a case of topiramate induced acute angle closure. Indian Journal of Ophthalmology. 2014;62(5):619-622. Acharya N, Nithyanandam S, Kamat S. [Letter to the Editor] Topiramate-associated bilateral anterior uveitis and angle closure glaucoma. Indian Journal of Ophthalmology. 2010;58(6):557-559 Desai CM, Ramchandani SJ, Bhopale SG, Ramchandani SS. Acute myopia and angle closure caused by topiramate, a drug used for prophylaxis of migraine. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2006 Sep;54(3):195-7. Aminlari A, East M, Wei W, Quillen D. Topiramate Induced Acute Angle Closure Glaucoma. The Open Ophthalmology Journal. 2008;2:46-47. Jabbarpoor Bonyadi MH, Soheilian R, Soheilian M. Topiramate-induced bilateral anterior uveitis associated with hypopyon formation. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2011 Feb;19(1):86-8. Katsimpris JM, Katsimpris A, Theoulakis PE, Lepidas J, Petropoulos IK. Bilateral severe anterior uveitis and acute angle-closure glaucoma following topiramate use for migraine crisis. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2014 Apr;231(4):439-41.