* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardiomyopathy, Myocarditis and Pericardial Disease
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
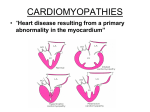
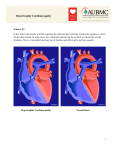
Cardiomyopathy, Myocarditis and Pericardial Disease Dr. Pace September 22, 2005 Chapter 55 Cardiomyopathy 3rd most common form of heart disease in U.S. 2nd most common cause of adolescent sudden death(IHSS or HOCM) Directly affects cardiac structure and impairs myocardial function Cardiomyopathy Four types Dilated Cardiomyopathy(DCM) Hypertrophied Cardiomopathy(HCM) Restrictive Cardiomyopathy Dysrhythmic right ventricular cardiomyopathy Dilated Cardiomyopathy Dilation and compensatory hypertrophy of myocardium Depressed systolic function and pump failure with low cardiac output 80% of DCM cases are idiopathic African Americans and males have 2.5x increased risk Most common age of diagnosis 20-50yrs Dilated Cardiomyopathy Clinical Presentation Signs and symptoms of CHF-dyspnea on exertion, orthopnea and pnd. Chest pain can occur due to low coronary vascular reserve Mural thrombi formation can occur Holosystolic regurgitant murmur or gallop may be present Dependent edema, bibasilar rales Dilated Cardiomyopathy Diagnosis CXR- enlarged heart, biventricular enlargement, and pulmonary vascular congestion(cephalization) ECG- LVH, Left atrial enlargement, Q waves, poor R wave progression, afib Echo-Confirms Dx.-ventricular enlargement, increased systolic and diastolic volumes, decreased EF Dilated Cardiomyopathy Differential Acute MI Restrictive Pericarditis Acute valvular disruption Sepsis Any other condition that results in low cardiac output state Dilated Cardiomyopathy ED care and disposition Newly diagnosed or symptomatic DCMadmit IV lasix and digoxin-improve symptoms Ace inhibitors and B-Blockers-improve survival Amiodarone- for complex venticular ectopy Anticoagulation can be considered Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Asymmetric LVH and/or RVH-primarily involves septum-usually without dilation Abnormal compliance-impaired diastolic relaxation and filling-output usually normal 50% are hereditary Prevelence 1 in 500, Mortality 1% Mortality 4-6% in childhood/adolescence Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Clinical Features Symptom severity progresses with age Dyspnea on exertion-most common initial or presenting symptom Angina-like chest pain, palpitations and syncope may also be present Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Exam Fourth heart sound(S4) Hyperdynamic apical pulse Precordial lift Systolic ejection murmur at apex or lower left sternal border Murmur increased with valsalva maneuver Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Diagnosis EKG-LVH in 30%, Left atrial enlargement In 25-50% Large septal Q waves-25% CXR-usually normal Echo-study of choice-demonstrates disproportionate septal hypertrophy Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy ED Care and Disposition Pts who c/o exercise intolerance or CP with typical HCM murmur-needs echorefer to cardiology B-blocker-treatment of choice for HCM with CP Discourage vigorous exercise(not a problem for most ed patients) Admit HCM with syncopal episode Restrictive Cardiomyopathy One of least common cardiomyopathies Ventricular volume and wall thickness is normal Decreased volume of both ventricles Mostly idiopathic- sometimes familial Systemic disorders-amyloidosis, sarcoidosis, hemochromatosis, scleroderma, and carcinoid. Restrictive Cardiomyopathy Clinical Features Symptoms of CHF-dyspnea, orthopnea, pedal edema- rare chest pain Exam-may have S3 or S4 gallop, rales, jvd, Kussmaul’s sign(jvd with inspiration), hepatomegaly, pedal edema or ascites Restrictive Cardiomyopathy Diagnosis CXR-signs of CHF without cardiomegaly EKG-nonspecific changes most likely Conduction disturbances and low-voltage QRS complexes are common with amyloidosis or sarcoidosis Restrictive Cardiomyopathy Differential Diagnosis Constrictive pericarditis Diastolic left ventricular dysfunction(due to ischemic or hypertensive heart disease) Need to differentiate restrictive cardiomyopathy from constrictive pericarditis(surgical treatment) Restrictive Cardiomyopathy ED Care and Disposition Symptom directed-diuretics and ace inhibitors Corticosteroids for sarcoidosis Chelation therapy for hematochromatosis Admission based on severity of symptoms and availability of prompt follow up Dysrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy(DRVC) Most rare form of cardiomyopathy Progressive replacement of RV myocardium with fibrofatty tissue Typical presentation of sudden death in young or middle aged pt Exam usually normal EKG- RBBB may be present Echo-necessary for diagnosis Myocarditis Inflammation of myocardium Can be result of systemic disorder or infectious agent Viral-Coxsackie B, echovirus, influenza, parainfluenza, Epstein-Bar, and HIV Bacterial-C. Diptheria, N. meningitidis, M. pneumonia, and beta-hemolytic strep Frequently accompanied with pericarditis Myocarditis Clinical Feature Fever, tachycardia out of proportion to fever, myalgias, headache,rigors Chest pain due to coexisting pericarditis Pericardial friction rub Severe cases may have CHF symptoms Myocarditis Diagnosis and Differential EKG-nonspecific changes, av block, prolonged QRS suration, or ST elevation(with pericarditis) CXR-Normal Cardiac Enzymes- may be elevated Differentail-ischemia or infarct, valvular disease, and sepsis Myocarditis ED Care and Disposition Supportive care Blood cultures Antibiotics for bacterial cause Watch for signs of progressive heart failure Acute Pericarditis Loose visceral pericardium and dense parietal pericardium surround heart Pericardial space may contain up to 50ml normally Etiologies of acute pericarditis-viral, bacterial, fungal, malignancy, drugs, radiation, connective tissue disorder, uremia, myxedema, post-MI, or idiopathic Acute Pericarditis Clinical Features Most common-sudden or gradual onset of sharp or stabbing pain with radiation to back, neck, L shoulder or arm Radiation to L trapezial ridge is distinguishing Pain more severe with lying supine and relieved with sitting Low grade fever, dyspnea and dysphagia Transient, intermittent friction rub Acute Pericarditis Diagnosis EKG-changes in four stages 1-ST elevation in I, V5 and V6, PR depression in II, aVF and V4-V6 2-ST segment normalizes, T wave decreases 3-Inverted T waves in leads with previous ST elevation 4-Return to normal ECG In I, V5, or V6 ST:Twave ratio >0.25 most likely acute pericarditis Acute Pericarditis Diagnosis and Differential Chest Xray-normal and can help r/o other disease Other tests of value-CBC, bun and cr, streptococcal serology, viral serologies, antinuclear/anti-DNA abs, thyroid function, ESR, Cardiac Enzymes Acute Pericarditis ED Care and Disposition Idiopathic or presumed viral etiologyoutpatient with NSAIDs for 1-3 weeks Treat any indentified specific causes Admit for myocarditis or hemodynamic instability Nontraumatic Cardiac Tamponade Pressure in pericardial sac exceeds normal filling pressure in RV-restricts filling and cardiac output Etiology-metastatic malignancy, uremia, hemorrhage(over-anticoagulation), bacterial or tubercular disorders, chronic pericarditis, SLE, post radiation, myxedema Nontraumatic Cardiac Tamponade Clinical Features Dyspnea and decreased exercise tolerance-wt loss, pedal edema, ascites Tachycardia, Narrow pulse pressure Pulsus paradoxus JVD, Muffled heart sounds, Hypotension Nontraumatic Cardiac Tamponade Diagnosis and Differential EKG-low voltage QRS with ST elevation and PR depression possible Electrical Alternans-classic finding—P and R wave beat to beat variability CXR-+/- enlarged cardiac silhoutte ECHO-diagnostic modality of choice Nontraumatic Cardiac Tamponade ED Care and Disposition IV Fluid Bolus-improves RV filling and improves hemodynamics Pericardiocentesis-therapeutic and diagnostic Admission to ICU or monitored setting Constrictive Pericarditis Occurs when fibrous thickening and loss of elasticity interfere with diastolic filling Cardiac trauma, pericardiotomy, intrapericardial hemmorhage, fungal or bacterial pericarditis, uremic pericarditis are most common causes Constrictive Pericarditis Clinical Features Sx’s gradually develop-mimics restrictive CM- CHF, DOE, and decreased exercise tolerance Chest pain, orthopnea and pnd are uncommon Exam-Pedal edema, hepatomegaly, ascites, jvd, and Kussmaul’s sign. Pericardial “knock”-early diastolic sound may be heard at apex Constrictive Pericarditis Diagnosis EKG-not very helpful-may show low voltage QRS and inverted T waves CXR-pericardial calcifications seen in 50% on lateral view(not diagnostic) ECHO, CT, MRI are diagnostic Constrictive Pericarditis Differential Diagnosis Consider acute pericarditis, myocarditis, exacerbation of chronic ventricular dysfunction, or systemic process resulting in decreased cardiac performance(sepsis) Constrictive Pericarditis ED Care and Disposition Supportive care Symptomatic patients require admission and pericardiectomy QUESTIONS Which is the 2nd most common cause of adolescent sudden death? A. Suicide B. MVA C. Overdose D. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy D Which of the following is not useful in cadiac tamponade? a. IV fluids b. Pericardiocentesis c. Bedside ultrasound d. Diuretics e. Ekg d. Which of the following is not found on the EKG of acute pericarditis A. ST elevation and PR depression B. Normal EKG C. Inverted Twave D. Electrical Alternans d Which is not a sign or symptom of acute pericarditis? A. Sharp stabbing chest pain with radiation to back, neck or L shoulder B. Osler’s Nodes C. Friction Rub D. Pain worse with lying supine B, b Which is not one of the 4 types of cardiomyopathy? A. Infectious B. Dilated C. Hypertrophied D. Restrictive E. Dysrhythmic Right Ventricular A Head CT Look at bony structure-fx? Look at periphery for epidural Or Subdural bleeding Look at parenchyma Is there bleeding or infarct? Is there a mass Look at ventriclesAre they normal size? Are they clear