* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution of the Human Brain
Archaic human admixture with modern humans wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Origins of society wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Origin of language wikipedia , lookup
Before the Dawn (book) wikipedia , lookup
Early human migrations wikipedia , lookup
Discovery of human antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Homo erectus wikipedia , lookup
Recent African origin of modern humans wikipedia , lookup
Homo floresiensis wikipedia , lookup
Craniometry wikipedia , lookup
Homo heidelbergensis wikipedia , lookup
Homo naledi wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral modernity wikipedia , lookup
History of anthropometry wikipedia , lookup
Anatomically modern human wikipedia , lookup
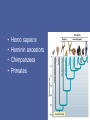
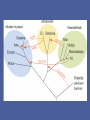
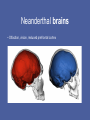
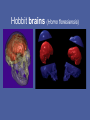
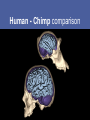
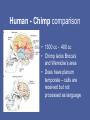
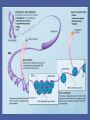
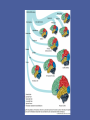
Evolution of the Human Brain • • • • Homo sapiens Hominin ancestors Chimpanzees Primates Evolution of Homo sapiens Origin of anatomically modern humans • ~200,000 ya • Human population genetics • Archeology, Fossil record Origin of anatomically modern humans • • • • • • Average brain size 1300 cc Extended life history Increased post-natal brain growth Expanded prefrontal cortex relative to early ancestors Lack of brow ridges, presence of chin Behavioral flexibility Origins of behavioral modernity • ~70,000 ya • Art, jewelry, stone tool refinement What behaviors are uniquely human? • • • • • • Language Abstract thinking Art Music Sociality Disorders (Schizophrenia, Autism, Alzheimer’s) What neurological changes made us human? • No brain size change 200,000-70,000 ya • Decrease in genetic diversity • Need comparative data for evidence (genetic and fossil) Homo sapiens were not alone Neanderthals, Hobbits and Denisovans Homo neanderthalensis • • • • First hominin fossil discovered, 1856 200,000-35,000 ya Europe, Middle East Brain size 1420 cc Homo neanderthalensis • • • • Tools, fire Language? Art? Ritual burial Homo floresiensis • • • • 18,000 ya Flores, Indonesia Brain 400 cc Tools ! Denisovans • 40,000 ya • Siberia • Small fossil fragment only Neanderthal brains • Olfaction, vision, reduced prefrontal cortex Hobbit brains (Homo floresiensis) Comparative genomics: Homo sapiens /early hominins • • • • FOXP2 – language Brain size Autism Nerve development Denisovian genes • 8 associated with brain function or nervous system development (NOVA1, SLITRK1, KATNA1, LUZP1, ARHGAP32, ADSL, HTR2B, CNTNAP2). • 4 of these are involved in axonal and dendritic growth (SLITRK1, KATNA1) and synaptic transmission (ARHGAP32, HTR2B) • 2 implicated in autism (ADSL, CNTNAP2). (CNTNAP2 is also associated with susceptibility to language disorders). Hominin brains Taung child (Australopithecus africanus) • Raymond Dart – 1924 • Taung, South Africa • 2.5 mya Human - Chimp comparison Human - Chimp comparison • 1300 cc - 400 cc • Chimp lacks Broca’s and Wernicke’s area • Does have planum temporale – calls are received but not processed as language Human - Chimp comparison “ A small number of genetic changes in the expression of genes may account for the substantial organismal differences between humans and chimpanzees.” Gene expression (epigenetics) Gene expression (epigenetics) Human - Chimp comparison Divergent Whole-Genome Methylation Maps of Human and Chimpanzee Brains Reveal Epigenetic Basis of Human Regulatory Evolution - Zeng et al. Encephalization quotient Evolution of animal models