* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Body`s Transport System
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
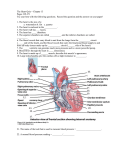
Name Date Circulation ■ Class Adapted Reading and Study The Body’s Transport System (pages 78–84) The Cardiovascular System (pages 78–79) Key Concept: The cardiovascular system carries needed substances to cells and carries waste products away from cells. In addition, blood contains cells that fight disease. • The cardiovascular system is made up of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The heart pumps blood through the blood vessels. • Blood carries oxygen and other needed materials to all of the body’s cells. Blood also picks up wastes, such as carbon dioxide, from the cells. • Some cells in blood kill germs. The cells fight disease and help you get well. Answer the following questions. Use your textbook and the ideas above. 1. The system that is made up of the heart, blood vessels, system. 2. Circle the letter of each job of the cardiovascular system. a. carries materials to cells b. fights disease c. picks up wastes from cells © Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved. 39 Circulation and blood is the Name Date Circulation ■ Class Adapted Reading and Study The Heart (pages 80–82) Key Concept: Each time the heart beats, it pushes blood through the blood vessels of the cardiovascular system. The right side of the heart is completely separated from the left side by a wall of tissue called the septum. Each side has two compartments, or chambers—an upper chamber and a lower chamber. • The heart is a hollow organ about the size of a fist. It is mostly made of muscle. The heart is in the center of the chest. • The heart is separated into a left side and a right side. Each side of the heart is divided into an upper and lower “room,” or chamber. The upper chamber on each side is called the atrium (AY tree um) (plural atria). The lower chamber on each side is called the ventricle. • With each beat of the heart, muscles in the heart pump blood by contracting. First, both atria contract. This squeezes blood out of the atria and into the ventricles. Then, both ventricles contract. This squeezes blood out of the ventricles and into blood vessels. • A valve is a flap of tissue over a hole that lets blood flow through the hole in just one direction. There are two valves in each side of the heart. • How fast your heart beats is controlled by a group of cells in the heart called the pacemaker. Answer the following questions. Use your textbook and the ideas above. 3. The organ that pumps blood throughout the body is the . 4. A group of cells in the heart that controls how fast the heart beats is called the . © Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved. 40 Name Date Circulation ■ Class Adapted Reading and Study 5. Fill in the blanks in the table comparing the upper chambers and the lower chambers of the heart. Chambers of the Heart Name of Chamber What It Does a. pumps blood into a ventricle b. pumps blood into a blood vessel 6. The diagram below shows the heart and its four chambers. When the heart beats, which two chambers contract first? Circle the letter of the correct answer. a. A and B b. C and D c. A and C The Heart B A D C © Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved. 41 Name Date Circulation ■ Class Adapted Reading and Study Two Loops (pages 82–84) Key Concept: The overall pattern of blood flow through the body is something like a figure eight. The heart is at the center where the two loops cross. In the first loop, blood travels from the heart to the lungs and then back to the heart. In the second loop, blood is pumped from the heart throughout the body and then returns again to the heart. • After leaving the heart, blood travels through arteries. Arteries are blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart. • From arteries, blood flows into capillaries. Capillaries are tiny blood vessels with very thin walls. In capillaries, materials are passed back and forth between the blood and body cells. • From capillaries, blood flows into veins. Veins are blood vessels that carry blood back to the heart. • The right ventricle of the heart pumps blood to the lungs. In the lungs, the blood drops off wastes and picks up oxygen. From the lungs, the blood returns to the heart. This path of the blood is called the first loop, or loop one. • The left ventricle of the heart pumps blood to the rest of the body. The blood leaving the heart is full of oxygen. The blood drops off oxygen and picks up wastes at the body cells. Then the blood returns to the heart. This path of the blood is called the second loop, or loop two. Answer the following questions. Use your textbook and the ideas above. 7. Is the following sentence true or false? Blood flows through the body in one large loop. © Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved. 42 Name Date Circulation ■ Class Adapted Reading and Study 8. Fill in the blanks in the table comparing different kinds of blood vessels. Kinds of Blood Vessels Kind of Blood Vessel What It Does Artery carries blood away from the heart a. passes materials between blood and body cells b. carries blood back to the heart 9. The diagram shows how blood flows through the body. In which loop—loop one or loop two—does blood travel from the heart to the body and back to the heart again? Loop One Arteries to lungs Veins from lungs Right atrium Left atrium Veins from body Artery to body Right ventricle Left ventricle Loop Two © Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved. 43