* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heart, blood, and circulation Assignment
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
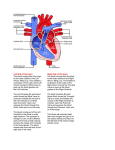
Name: Heart, blood, and circulation Assignment 1) List the four chambers of the heart Left and right atrium, left and right ventricle 2) List the four valves and what they separate Tricuspid atrioventricular valve- between right atrium and right ventricle Bicuspid atrioventricular valve- between left atrium and left ventricle Pulmonic semi-lunar valve- between right ventricle and pulmonary artery Aortic semi-lunar valve- between left ventricle and aortic artery 3) Give the function of valves Prevent backflow 4) What are the 3 tissue types in the heart? Pericardium, myocardium, endocardium 5) List the two nodes in the body and explain their function. Be sure to mention purkinje fibers Sinoatrial (SA) node initiates the muscles around the atria to conctract once blood has pooled in the right atrium SA node then sends a message to the atrioventricular node which will use the purkinje fibres to stimulate the ventricles to contract Name: 6) Label the parts of the heart Superior Vena cava Pulmonic semi-lunar valve Tricuspid atrioventricular valve Aortic semi-lunar valve Bicuspid (Mitral) atrioventricular valve Inferior Vena Cava 7) Explain the blood flow circuit. Start with the blood coming from the body to the heart and end with the blood leaving the heart to the body. Use all appropriate terminology Blood will enter the right atrium via the superior and inferior vena cava. The blood will pass through the tricuspid atrioventricular valve into the right ventricle. The blood will pass through the pulmonic semilunar valve out the pulmonary arteries to the lungs. Oxygenated blood will return to the left atrium via the pulmonary veins where it will be pushed through the bicuspid atrioventricular valve into the left ventricle. It will then pass through the aortic semilunar valve and out the aorta to the rest of the body. 8) Explain how the autonomic nervous system is involved with heart contractions The medulla will send messages to the heart to increase the cardiac output Name: 9) What is a “normal” blood pressure? Give the names of the top and bottom number. What do those terms represent? 120- systolic- pressure exerted on the vessel walls when the ventricles contract 80- diastolic- pressure exerted on the vessel walls when the ventricles are at rest 10) Compare arteriosclerosis to atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis- general hardening of the arteries Atherosclerosis- hardening of the arteries due to plaque build-up 11) What is plaque? Buildup of fatty deposits, cholesterol, and calcium 12) What is hypotension and hypertension and what are some associated health risks? Hypotension- low blood pressure- low energy, dizziness Hypertension- high blood pressure- heart attack, embolism, stroke 13) Give the structure, location, and function of the 3 major blood vessels Arteries- thick and elastic, near bone for protection, take blood away from heart Veins- thin and has valves, near muscle for movement, take blood to the heart Capillaries- very thin, everywhere, gas and nutrient exchange 14) Describe the location and function of all the major arteries and veins discussed in class See notes in from class 15) What are the main components of blood? What function do they all serve? Cells- RBCs- transportation of gases (oxygen carbon dioxide), WBCs- immune response, platelets- blood clotting Plasma- mostly water but also antibodies, clotting proteins, vitamins, minerals, glucose, Amiono acids 16) Explain the mechanism of blood clotting Vessel damaged Platelet releases calcium and thromboplastin The calcium and thromboplastin converts Prothrombin into thrombin The thrombin coverts fibrinogen into fibrin (insoluble) The fibrin creates an insoluble net that captures platelets and RBCs which form a clot 17) Explain antigens and antibodies and the relationship between them An identifiable marker on a cell (RBS) that will alert the immune system. Antibodies are Y-shaped proteins created by the immune system. Antibodies will bind to antigens which is called agglutination 18) What is Agglutination? See above 19) What are the four major blood types? What is responsible for the difference between them? How are the blood types decided by genetics? Name: A B AB O Their genes will determine what proteins are being created. The proteins in the cell membrane of the RBCs will determine the blood type AA, AO = A BB, BO= B AB= AB OO= O 20) Discuss the differences in the fetal heart structure and circulation Umbilical vein will bring oxygenated blood from placenta to fetus 2 X umbilical arteries will bring deoxygenated blood from both iliac arteries to the placenta Ductus venosus- allows some blood to bypass the liver to maintain suitable BP Foramen ovale- allows blood to go from right atrium to left atrium (lung bypass) Ductus arteriosis- allows blood to go from pulmonary artery to aorta (lung bypass)