* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2015-05-25 1 Monosaccharides
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
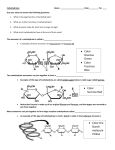
2015-05-25 Unit 4. CARBOHYDRATES Main Questions to Answer: · What are the different types of carbohydrates? · What are the best food sources for carbohydrates? · How are carbohydrates digested and absorbed by the body? · How do carbohydrates function in the body? · What are some of the problems and illnesses associated with carbohydrate metabolism? Types of carbohydrates (mono-, di-, oligo-, poly-saccharides) Monosaccharides • Single units, simple sugars • 6-carbon sugars (hexoses): – Glucose (dextrose); Fructose (levulose); Galactose • 5-carbon sugars (pentoses): – ribose, xylose • (Sugar alcohols, amines, acids) Disaccharides • sucrose, lactose, maltose – Condensation reaction (releases water) of two monosaccharides – Simple sugars Oligosaccharides • fructo-oligosaccharides (FOS) – Health benefits? 1 2015-05-25 Polysaccharides • most abundant forms of carbohydrate; homo- & hetero-polymers (plants: starches, fiber; animals: glycogen) • Starches: Amylose-linear; Amylopectin-branched • Dietary fibers (not all dietary fibres are carbohydrates): – Soluble: pectins, gums,… readily dissolve in water – Insoluble: cellulose, hemicelluloses…do not readily dissolve in water – Typically, not digested by human enzymes – Can influence absorption (or absorpt. rate) of some nutrients – Helps maintain healthy colon function • Glycogen: Stored mainly in muscle & liver Sources of carbohydrates and recommended intakes • sweetened & starchy foods, cereal products, fruits/vegetables…. • Recommendations are for complex carbohydrates (not simple sugars; ‘empty calories’) – 45-65% of total daily calories as carbohydrate (AMDR) – A 2000 kcal diet can include about 300 g carbohydrates (DV) – RDA, a minimum of 130 g/day for most adults – Limit simple sugars to about 10-20% or less of carbohydrate intake • Recommended dietary fibre intake – 38 g/d for men and 25 g/day for women (AI, up to age 50) – A food labeled as a ‘high source’ of fibre has at least 4 g/serving – High fibre diets often require extra fluid Sweeteners…from 0 to 4 kcal/g • No calories (0 kcal/g) – saccharin, acesulfame, sucralose, cyclamate… – ADI (acceptable daily intake) values set by Health Canada • Full calories (4 kcal/g) – table sugar (sucrose), honey, corn syrup… – honey and corn syrup are not recommended for infants – aspartame typically contributes negligible energy to the diet because it is very sweet • A few calories (about 1-3 kcal/g) – xylitol, mannitol, sorbitol… – do not promote tooth decay 2 2015-05-25 Carbohydrate digestion • Pre-digestive: cooking • Mouth – salivary amylase (starch→ maltose) • Stomach – Complex carbohydrates have slower rate of emptying from stomach • Small intestine – pancreatic amylase (→ mono-, disaccharides) – disaccharidases (e.g., lactase) → monosaccharides – absorbed monosaccharides go from enterocytes to liver • Large intestine – unabsorbed carbohydrates fermented ,and some fibre breakdown, by bacteria • Liver: monosaccharides → glucose… Functions of carbohydrates in body • Energy source – Especially important for brain & erythrocytes – Excess carbohydrate can be stored as fat… • Antiketogenic – ketones result from incomplete fatty acid oxidation – Sufficient dietary carbohydrate prevents high fat use for energy • May be problem with some low-carb diets • Sparing of protein breakdown – Dietary carb decreases gluconeogenesis from amino acids (protein stores…extensive breakdown can weaken vital organs) • Many structural and regulatory functions… • Health of the GI tract: dietary fibre… Possible functions of Dietary Fibre • • • • Protection from diverticulosis or associated inflammation Increased rate of transit through colon (insoluble fibres) Prevention of constipation (stool softening…with fluid) Prebiotic effect (also some oligosaccharides)… • Decreased total plasma cholesterol (↓risk of some CVD?) • Decreased glucose absorption rate.. • Increased satiety (…better weight management?) • Decreased risk of some cancers??...... 3 2015-05-25 Other potential problems and diseases associated with carbohydrates • Empty calories & Dental Caries – Simple sugar-rich foods such as soft-drinks have few other nutrients – Caries: influenced by types of carbohydrates and contact time with teeth • Glycemic index and load – Relative rating of the potential that foods have to increase blood glucose • Diabetes (mellitus) & problems with glucose regulation – Type 1: often juvenile onset; lack of insulin production – Type 2: often mature adult onset; resistance to insulin action • Other carbohydrate metabolic diseases … • Lactose intolerance • Deficiency of lactase enzyme • Very low carb diets… 4